Acacia anastomosa, also known as Carson River wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia effusifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to an area in the Mid West and the Wheatbelt regions of Western Australia.

Acacia hamersleyensis, also known as Karijini wattle or Hamersley Range wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is endemic to a small area in central Western Australia.

Acacia latior is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia ptychophylla is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to arid areas of north western Australia.

Acacia rhodophloia, commonly known as minni ritchi or western red mulga, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a large area of arid central western Australia. The Indigenous group the Kurrama peoples know the plant as mantaru.

Acacia richardsii is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.
Acacia sulcaticaulis, also commonly known as the Mount Mulgine fluted wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia hystrix is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia pachypoda is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia profusa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia robiniae, commonly known as Robin's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia simulans is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia cassicula is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia pharangites, commonly known as Wongan gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to the Wongan Hills of south western Australia and is listed as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
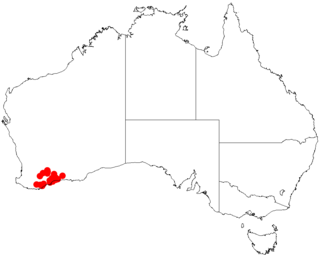
Acacia tetanophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia abbreviata is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to arid parts of northern Australia. It is a spreading, glabrous, resinous shrub with linear to narrowly oblong phyllodes, spike of golden flowers, and linear to lance-shaped pods.

Acacia cataractae is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.


















