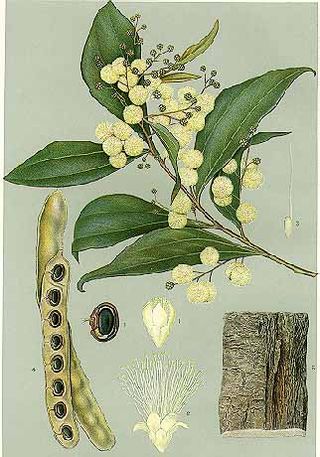
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia cognata, commonly known as bower wattle, river wattle or narrow-leaved bower wattle, is a tree or shrub species that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia notabilis, known colloquially as mallee golden wattle, Flinders wattle or stiff golden wattle, is a species of Acacia native to Australia.

Acacia homalophylla is a small tree found in the eastern half of Australia, where it is known as the yarran. It has also been introduced into India and Pakistan.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia orthocarpa, also commonly known as Pilbara weeping wattle, needle-leaf wattle or straight-podded wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to tropical parts of northern Australia. The indigenous Nyangumarta peoples know it as yartupu.
Acacia paula is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a small area of north western Australia.

Acacia sibirica, commonly known as bastard mulga or false witchetty bush, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid areas of Australia.

Acacia stigmatophylla, also known as djulurd, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to northern parts of Western Australia.

Acacia dictyophleba, also known as the sandhill wattle, waxy wattlefeather veined wattle, and spear tree, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae. The Nyangumarta peoples know the plant as Langkur or Lungkun; the Thalanyji know it as Jabandi; and the Pintupi know it as mulyati.

Acacia georgensis, commonly known as Bega wattle or Dr George Mountain wattle, is a species of Acacia native to southeastern Australia. It was one of eleven species selected for the Save a Species Walk campaign in April 2016 when scientists walked 300 km to raise money for collection of seeds to be prepared and stored at the Australian PlantBank at the Australian Botanic Garden Mount Annan.

Acacia melleodora, commonly known as scented wax wattle, waxy wattle, honey wattle or honey scented wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia trineura, known colloquially as three-nerve wattle or three nerved wattle or green wattle, is a species of Acacia native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia macdonnelliensis, commonly known as the MacDonnell mulga or the Hill mulga, is a species of Acacia native to central Australia. The Indigenous Australians the Alyawarr peoples know the plant as irrar, the Kaytetye know it as arleth-arlethe or arwele arleth-arlethe and the Western Arrernte peoples know it as irrkwarteke.
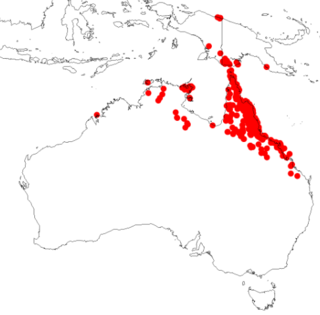
Acacia simsii is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia in the family Fabaceae. It is native to New Guinea and northern Australia. In Australia it is found in both the Northern Territory and Queensland.
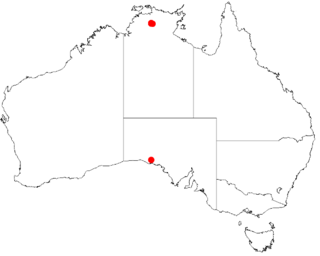
Acacia amanda is a shrub in the genus Acacia that is native to Northern Territory.

Acacia doratoxylon, commonly known as currawang, lancewood, spearwood or coast myall, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern and south eastern Australia.

Acacia latzii, also known as Latz's wattle and Tjilpi wattle, is a shrubby tree of the genus Acacia. It is native to the Finke bioregion.

Acacia latescens, also known as Ball wattle, is a tree in the genus Acacia. It is native to the Northern Territory where it is common in the Top End.

Acacia sericoflora is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.




















