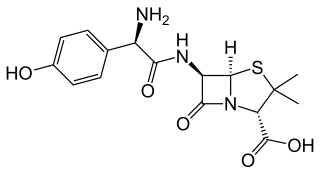
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth, or less commonly by injection.

Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.

Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart, usually the valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and low red blood cell count. Complications may include backward blood flow in the heart, heart failure – the heart struggling to pump a sufficient amount of blood to meet the body's needs, abnormal electrical conduction in the heart, stroke, and kidney failure.
Nocardiosis is an infectious disease affecting either the lungs or the whole body. It is due to infection by a bacterium of the genus Nocardia, most commonly Nocardia asteroides or Nocardia brasiliensis.

Actinomyces is a genus of the Actinomycetia class of bacteria. They all are gram-positive. Actinomyces species are facultatively anaerobic and they grow best under anaerobic conditions. Actinomyces species may form endospores, and while individual bacteria are rod-shaped, Actinomyces colonies form fungus-like branched networks of hyphae. The aspect of these colonies initially led to the incorrect assumption that the organism was a fungus and to the name Actinomyces, "ray fungus".

Actinomycosis is a rare infectious bacterial disease caused by Actinomyces species. The name refers to ray-like appearance of the organisms in the granules. About 70% of infections are due to either Actinomyces israelii or A. gerencseriae. Infection can also be caused by Streptomyces somaliensis and Propionibacterium propionicus. The condition is likely to be a polymicrobial anaerobic infection.

Subacute bacterial endocarditis, abbreviated SBE, is a type of endocarditis. Subacute bacterial endocarditis can be considered a form of type III hypersensitivity.
Streptococcus sanguinis, formerly known as Streptococcus sanguis, is a Gram-positive facultative anaerobic coccus species of bacteria and a member of the Viridans Streptococcus group. S. sanguinis is a normal inhabitant of the healthy human mouth where it is particularly found in dental plaque, where it modifies the environment to make it less hospitable for other strains of Streptococcus that cause cavities, such as Streptococcus mutans.

Eikenella corrodens is a Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacillus that can cause severe invasive disease in humans. It was first identified by M. Eiken in 1958, who called it Bacteroides corrodens. E. corrodens is a rare pericarditis associated pathogen. It is a fastidious, slow growing, human commensal bacillus, capable of acting as an opportunistic pathogen and causing abscesses in several anatomical sites, including the liver, lung, spleen, and submandibular region. E. corrodens could independently cause serious infection in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised hosts.
Capnocytophaga canimorsus is a fastidious, slow-growing, Gram-negative rod of the genus Capnocytophaga. It is a commensal bacterium in the normal gingival flora of canine and feline species, but can cause illness in humans. Transmission may occur through bites, licks, or even close proximity with animals. C. canimorsus generally has low virulence in healthy individuals, but has been observed to cause severe, even grave, illness in persons with pre-existing conditions. The pathogenesis of C. canimorsus is still largely unknown, but increased clinical diagnoses have fostered an interest in the bacillus. Treatment with antibiotics is effective in most cases, but the most important yet basic diagnostic tool available to clinicians remains the knowledge of recent exposure to canines or felines.
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe, nonmotile bacterium that is often found in association with localized aggressive periodontitis, a severe infection of the periodontium. It is also suspected to be involved in chronic periodontitis. Less frequently, A. actinomycetemcomitans is associated with nonoral infections such as endocarditis. Its role in aggressive periodontitis was first discovered by Danish-born periodontist Jørgen Slots, a professor of dentistry and microbiology at the University of Southern California School of Dentistry.

Haverhill fever is a systemic illness caused by the bacterium Streptobacillus moniliformis, an organism common in rats and mice. If untreated, the illness can have a mortality rate of up to 13%. Among the two types of rat-bite fever, Haverhill fever caused by Streptobacillus moniliformis is most common in North America. The other type of infection caused by Spirillum minus is more common in Asia and is also known as Sodoku.

Actinomycosis is an infection caused by a bacterium of the genus Actinomyces, usually Actinomyces bovis; the disease it causes has several common names. When it is a moveable tumour or lump on the jaw area, it is referred to as lump jaw; when it spreads into the hard bone of the jaw, it is referred to as big jaw; and when it affects the tongue, it is referred to as wooden tongue.

Kingella kingae is a species of Gram-negative facultative anaerobic β-hemolytic coccobacilli. First isolated in 1960 by Elizabeth O. King, it was not recognized as a significant cause of infection in young children until the 1990s, when culture techniques had improved enough for it to be recognized. It is best known as a cause of septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, spondylodiscitis, bacteraemia, and endocarditis, and less frequently lower respiratory tract infections and meningitis.

Actinomyces israelii is a species of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria within the genus Actinomyces. Known to live commensally on and within humans, A. israelii is an opportunistic pathogen and a cause of actinomycosis. Many physiologically diverse strains of the species are known to exist, though not all are strict anaerobes. It was named after the German surgeon James Adolf Israel (1848–1926), who studied the organism for the first time in 1878.
Rothia dentocariosa is a species of Gram-positive, round- to rod-shaped bacteria that is part of the normal community of microbes residing in the mouth and respiratory tract.
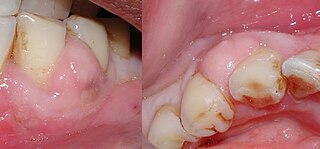
A periodontal abscess, is a localized collection of pus within the tissues of the periodontium. It is a type of dental abscess. A periodontal abscess occurs alongside a tooth, and is different from the more common periapical abscess, which represents the spread of infection from a dead tooth. To reflect this, sometimes the term "lateral (periodontal) abscess" is used. In contrast to a periapical abscess, periodontal abscesses are usually associated with a vital (living) tooth. Abscesses of the periodontium are acute bacterial infections classified primarily by location.
Anaerobic infections are caused by anaerobic bacteria. Obligately anaerobic bacteria do not grow on solid media in room air ; facultatively anaerobic bacteria can grow in the presence or absence of air. Microaerophilic bacteria do not grow at all aerobically or grow poorly, but grow better under 10% carbon dioxide or anaerobically. Anaerobic bacteria can be divided into strict anaerobes that can not grow in the presence of more than 0.5% oxygen and moderate anaerobic bacteria that are able of growing between 2 and 8% oxygen. Anaerobic bacteria usually do not possess catalase, but some can generate superoxide dismutase which protects them from oxygen.

Actinomyces bovis is a branching, Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacterium of the genus Actinomyces. It is the causative agent of lumpy jaw in cattle, and occasionally causes actinomycosis infections in humans. A. bovis normally populates the gastrointestinal tract of healthy ruminants, but is opportunistic in nature and will move into tissues through ulcerations or abrasions of the mucosa to cause infection. The disease occurs when there is physical damage to the tissue of the mouth, allowing the bacteria to colonize the deep tissue and bone, typically affecting the mandible and maxilla. Actinomycosis is pathognomonic for abscesses containing "sulfur" granules, and its colonies appear basophilic with club-shaped reaction products on a histological preparation. Lumpy jaw is commonly treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics with varying success, and can be a major economic loss for producers in countries where it is endemic. Because this organism is zoonotic, it is a human health concern and can cause granulomas, abscesses, skin lesions, and bronchopneumonia.
There are many circumstances during dental treatment where antibiotics are prescribed by dentists to prevent further infection. The most common antibiotic prescribed by dental practitioners is penicillin in the form of amoxicillin, however many patients are hypersensitive to this particular antibiotic. Therefore, in the cases of allergies, erythromycin is used instead.











