
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the Agri Decumates in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, which by the eighth century were collectively referred to as Alamannia.

Narses was, with Belisarius, one of the great generals in the service of the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I during the Roman reconquest that took place during Justinian's reign. Narses was a Romanized Armenian. He spent most of his life as an important eunuch in the palace of the emperors in Constantinople.

Theudebert I was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 533 to his death in 548. He was the son of Theuderic I and the father of Theudebald.
Agathias Scholasticus was a Greek poet and the principal historian of part of the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian I between 552 and 558.

The Greek Anthology is a collection of poems, mostly epigrams, that span the Classical and Byzantine periods of Greek literature. Most of the material of the Greek Anthology comes from two manuscripts, the Palatine Anthology of the 10th century and the Anthology of Planudes of the 14th century.
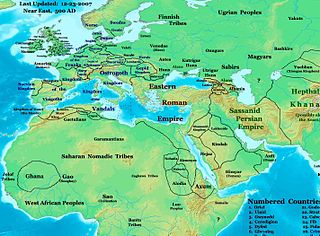
The Sabirs (Savirs, Suars, Sawar, Sawirk among others; were a nomadic Turkic equestrian people who lived in the north of the Caucasus beginning in the late-5th -7th century, on the eastern shores of the Black Sea, in the Kuban area, and possibly came from Western Siberia. They were skilled in warfare, used siege machinery, had a large army and were boat-builders. They were also referred to as Huns, a title applied to various Eurasian nomadic tribes in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe during late antiquity. Sabirs led incursions into Transcaucasia in the late-400s/early-500s, but quickly began serving as soldiers and mercenaries during the Byzantine-Sasanian Wars on both sides. Their alliance with the Byzantines laid the basis for the later Khazar-Byzantine alliance.
Menander Protector was a Byzantine historian, born in Constantinople in the middle of the 6th century AD. The little that is known of his life is contained in the account of himself quoted in the Suda. Menander mentions his father Euphratas, who came from Byzantium, and his brother Herodotus. He at first took up the study of law, but abandoned it for a life of pleasure. When his fortunes were low, the patronage accorded to literature by the Emperor Maurice, at whose court he was a military officer, encouraged him to try writing history.

Mount Ida, known variously as Idha, Ídhi, Idi, and Ita, is the highest mountain on the island of Crete, with an elevation of 2,456 metres (8,058 ft). It has the highest topographic prominence of any mountain in Greece. A natural park which includes Mount Ida is a member of UNESCO's Global Geoparks Network.
Musaeus Grammaticus probably belongs to the beginning of the 6th century AD, as his style and metre are evidently modeled on those of Nonnus. He lived before Agathias (530–582) and has been identified with the friend of Procopius whose poem on the story of Hero and Leander is considered the most beautiful of the age. The little love-poem Alpheus and Arethusa is also ascribed to Musaeus.

Myrina was one of the Aeolian cities on the western coast of Mysia, about 40 stadia to the southwest of Gryneion. The former bishopric is now a Latin Catholic titular see.

The Sangarius Bridge or Bridge of Justinian is a late Roman bridge over the river Sakarya in Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. It was built by the East Roman Emperor Justinian I (527-565 AD) to improve communications between the capital Constantinople and the eastern provinces of his empire. With a remarkable length of 430 m, the bridge was mentioned by several contemporary writers, and has been associated with a supposed project, first proposed by Pliny the Younger to Emperor Trajan, to construct a navigable canal that would bypass the Bosporus.

Agathia is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae described by Achille Guenée in 1858.

AnacampserosL. is a genus comprising about a hundred species of small perennial succulent plants native to Southern Africa, Ethiopia and Latin America. The botanical name Anacampseros is an ancient one for herbs supposed to restore lost love.
The 557 Constantinople earthquake took place on the night of December 14. This earthquake, described in the works of Agathias, John Malalas, and Theophanes the Confessor, caused great damage to Constantinople, then capital of the Byzantine Empire in a region frequently afflicted with earthquakes. More minor quakes had preceded the large event, including two in April and October respectively. The main quake in December was of unparalleled ferocity, and "almost completely razed" the city. It caused damage to the Hagia Sophia which contributed to the collapse of its dome the next year, as well as damaging the walls of Constantinople to the extent that Hun invaders were able to penetrate it with ease the following season.
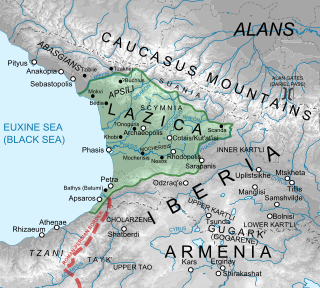
The siege of Phasis took place in 555–556 during the Lazic War between the Byzantine and Sasanian Empires. Expecting an easy victory, the Persians besieged the town of Phasis in Lazica, held by the Byzantines, but were defeated in the ensuing irregular battle. The main source for the siege is the 6th-century historian Agathias.

Ioannis Fountoulis is a Greek professional water polo player. He is currently the captain of Greece men's national water polo team, with whom he won a bronze medal at the 2015 World Championships, a bronze medal at the 2016 World League, 2020 World League and competed at the 2012 and 2016 Olympics. He played for the Greek powerhouse Olympiacos since 2009, and in 2018 he won the 2017–18 LEN Champions League with the Greek giants, scoring 4 goals in the final game against Pro Recco in Genoa. Is a very big scorer and leader is considered one of the top players in the world and it is typical how in 2016 and 2018 he was voted as the second top player in the world. Currently playing for the Greek club Olympiacos.

Agathia lycaenaria is a species of moth of the family Geometridae first described by Vincenz Kollar in 1848. It is found from India to Australia.

Agathia obsoleta is a species of moth in the family Geometridae first described by William Warren in 1897. It is found in Java, Sumatra, Borneo and the Philippines. A. obsoleta is a rare species of lowland forests, including heath forest.

Onoguris, renamed as Stephanopolis in the Byzantine period, was a town in Lazica recorded by Byzantine historian Agathias in his narration of the Lazic War between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire. Its exact location is still under study.

Mount Agathias, at 2,424 m, is one of the highest mountains on Crete.


















