
Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi)1 in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided between two settlements, the larger of which is Cambridge Bay (Nunavut) and the other Ulukhaktok.
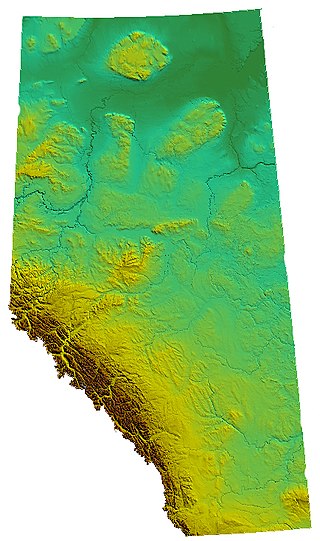
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 km2 (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the United States state of Montana along 49° north for 298 km (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 km (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 km (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west. Along with Saskatchewan it is one of only two landlocked provinces or territories.

Lake Athabasca is in the north-west corner of Saskatchewan and the north-east corner of Alberta between 58° and 60° N in Canada. The lake is 26% in Alberta and 74% in Saskatchewan.
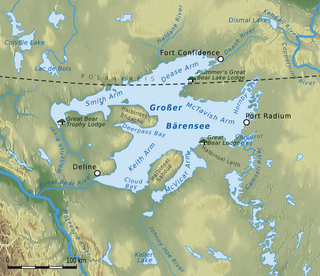
Great Bear Lake is a lake in the boreal forest of Canada. It is the largest lake entirely in Canada, the fourth-largest in North America, and the eighth-largest in the world. The lake is in the Northwest Territories, on the Arctic Circle between 65 and 67 degrees of northern latitude and between 118 and 123 degrees western longitude, 156 m (512 ft) above sea level.

Old Wives Lake is a shallow endorheic salt lake in south central Saskatchewan, Canada, about 30 kilometres (19 mi) south-west of Moose Jaw. The lake is fed by the Wood River but seasonal water relatively flattened the terrain, and as such results in significant mudflats. A Migratory Bird Sanctuary was established at the lake on March 9, 1925. This lake, in conjunction with Reed Lake and Chaplin Lake, forms a site of hemispheric importance in the Western Hemisphere Shorebird Reserve Network. It was designated in April 1997, and is "one of the most important inland sites for migratory birds in North America". At the north-eastern part of the lake is the Isle of Bays Wildlife Refuge. The wildlife refuge encompasses the entirety of Isle of Bays.

Sioux Lookout is a town in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. Located approximately 350 km (220 mi) northwest of Thunder Bay, it has a population of 5,838 people, an elevation of 383 m (1,257 ft), and its boundaries cover an area of 536 km2 (207 sq mi), of which 157 km2 (61 sq mi) is lake and wetlands. Known locally as the "Hub of the North", it is serviced by the Sioux Lookout Airport, Highway 72, and the Sioux Lookout railway station. According to a 2011 study commissioned by the municipality, health care and social services ranked as the largest sources of employment, followed by the retail trade, public administration, transportation and warehousing, manufacturing, accommodation and food services, and education.

Alsask is a special service area in the Rural Municipality of Milton No. 292, in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. Alsask is located 60 km (37 mi) west of the town of Kindersley. Highway 44 runs to the east of Alsask, and Highway 7 lies a few kilometres to the north. The community had a population of 113 in the 2021 Canadian census.

The Churchill River is a major river in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, Canada. From the head of the Churchill Lake it is 1,609 kilometres (1,000 mi) long. It was named after John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and governor of the Hudson's Bay Company from 1685 to 1691. The Cree name for the river is Missinipi, meaning "big waters". The Denesuline name for the river is des nëdhë́, meaning "Great River".

Meadow Lake is a city in the boreal forest of northwestern Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is about 246 kilometres (153 mi) northeast of Lloydminster and 156 kilometres (97 mi) north of North Battleford. Founded as a trading post in 1799, it became a village in 1931 and a town in 1936. On November 9, 2009, it officially became Saskatchewan's 14th city.

The Red Deer River is a river in Alberta and a small portion of Saskatchewan, Canada. It is a major tributary of the South Saskatchewan River and is part of the larger Saskatchewan / Nelson system that empties into Hudson Bay.

Gull Lake is a town in Saskatchewan, Canada, situated on the junction of the Trans-Canada Highway and Highway 37, west of Swift Current.

Regina Beach is a town in south central Saskatchewan, located on Highway 54, close to where Highway 11 intersects with the Qu'Appelle Valley.

The geography of Saskatchewan is unique among the provinces and territories of Canada in some respects. It is one of only two landlocked regions and it is the only region whose borders are not based on natural features like lakes, rivers, or drainage divides. The borders of Saskatchewan, which make it very nearly a trapezoid, were determined in 1905 when it became a Canadian province. Saskatchewan has a total area of 651,036 square kilometres (251,366 sq mi) of which 591,670 km2 (228,450 sq mi) is land and 59,366 km2 (22,921 sq mi) is water.

Greater Madawaska is an incorporated township in Renfrew County in eastern Ontario, Canada, created on January 1, 2001, through the amalgamation of the Township of Bagot and Blythfield, the Township of Brougham, and the Township of Griffith and Matawatchan. As of 2021, it has a population of 2,864.

Broadview is a town in Saskatchewan along Highway 1, the Trans-Canada Highway, about 155 kilometres (96 mi) east of Regina. The local economy is based mainly on agriculture. It is also the administrative headquarters of the Rural Municipality of Elcapo No. 154

Radisson is a town in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada. It was named after Pierre-Esprit Radisson (1636–1710), an explorer who was instrumental in creating Hudson's Bay Company.

Mount William Booth was named in 1965 after William Booth, the founder of the Salvation Army. It is part of the Ram Range in Alberta, Canada, and situated near the southern end of Abraham Lake. It is located in the North Saskatchewan River valley of the Canadian Rockies, and can be seen from the David Thompson Highway east of Saskatchewan Crossing.

Geikie River is a river in the northern part of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is Costigan Lake, which is near the uranium producing areas around the Key Lake mine in the Athabasca Basin. It flows in a north-easterly direction and flows into Wollaston Lake.



















