Related Research Articles
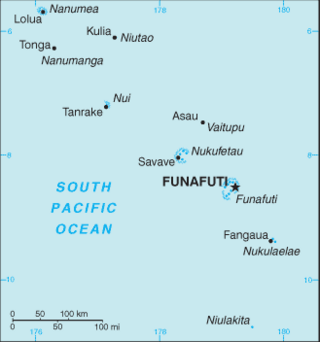
The Western Pacific nation of Tuvalu, formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is situated 4,000 kilometers (2,500 mi) northeast of Australia and is approximately halfway between Hawaii and Australia. It lies east-northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands, southeast of Nauru, south of Kiribati, west of Tokelau, northwest of Samoa and Wallis and Futuna and north of Fiji. It is a very small island country of 26 km2 (10 sq mi). Due to the spread out islands it has the 38th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 749,790 km2 (289,500 sq mi). In terms of size, it is the second-smallest country in Oceania.

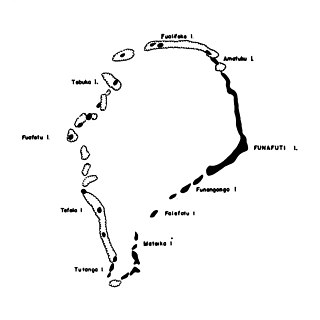
Fongafale is the largest of Funafuti's islets in Tuvalu. It is a long narrow sliver of land, 12 kilometres long and between 10 and 400 metres wide, with the South Pacific Ocean and reef on the east and the protected lagoon on the west. The north part is the Tengako peninsula, and Funafuti International Airport runs from northeast to southwest on the widest part of the island, with the village and administrative centre of Vaiaku on the lagoon side.
Tepuka is an island eighteen kilometers west of Fongafale, in the northwest of Funafuti, the main atoll of the Oceanian nation of Tuvalu. Te puka, or Pouka, is the name of a tree - Hernandia peltata.

Funafuti International Airport is an airport in Funafuti, in the capital city of the island nation of Tuvalu. It is the sole international airport in Tuvalu. Fiji Airways operates between Suva and Funafuti.
Avalau is an islet within the atoll of Funafuti, Tuvalu. Charles Hedley described Avalau in 1896 "this islet is said to possess a spring of fresh water".
Fatato is an uninhabited islet (motu) of Funafuti, Tuvalu. In 2002 the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research (APN) chose this island for a systematic study of its coast in relation to the impact of global climate change on atolls. The islet can be accessed by foot with a 20-30 minute walk from Fongafale across the reef at low tide.
Funafala is an islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu that is inhabited by five families, with a church also located on the islet. Funafala means 'the pandanus of Funa', the name of a chief, after whom also the group has been named Funafuti.
Fuagea is an islet located in the archipelago of Tuvalu in the south-western part of the atoll of Funafuti.

Fualefeke is a small islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu.

Mateika or Mateiko is an uninhabited islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu.
Motuloa is an islet in the atoll of Funafuti, Tuvalu. Motu loa means long island. It lies on the southeastern rim of the atoll and is 800 metres (0.50 mi) long northeast–southwest, but only 50 metres (160 ft) wide. It is only about 25 metres (82 ft) southwest of Telele and can be reached by foot from it during low tide. The islet is densely vegetated.

Nukusavalevale is an islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu. It lies on the southeastern rim of the atoll, south of Motuloa.

Tefala is an islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu.

Telele is an uninhabited islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu. The estimate terrain elevation of the island is 12 metres above sea level.

Tutanga is an uninhabited islet which is the most southern islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu. This islet has also been called Tuaeriki.
Vasafua is an islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu. Vasafua is part of the Funafuti Conservation Area, established in 1996 with the aim of preserving the natural fauna and flora of the area.

Tengako is a peninsula at the north end of Fongafale islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu. At the end of the peninsula is Amatuku islet on which the Tuvalu Maritime Training Institute is located.

Funafuti is the capital of the island nation of Tuvalu. It has a population of 6,320 people. More people live in Funafuti than the rest of Tuvalu combined, with it containing approximately 60% of the nation's population. It consists of a narrow sweep of land between 20 and 400 metres wide, encircling a large lagoon 18 km long and 14 km wide. The average depth of the Funafuti lagoon is about 20 fathoms. With a surface area of 275 square kilometres (106.2 sq mi), it is by far the largest lagoon in Tuvalu. The land area of the 33 islets around the atoll of Funafuti totals 2.4 square kilometres (0.9 sq mi); taken together, they constitute less than one percent of the total area of the atoll. Cargo ships can enter Funafuti's lagoon and dock at the port facilities on Fongafale.

The Tuvalu Maritime Training Institute (TMTI) is on Amatuku motu, on Funafuti atoll in Tuvalu. TMTI provides training to approximately 120 marine cadets each year, to provide them with the basic skills necessary for employment as seafarers on merchant shipping. TMTI operates under the Tuvalu Maritime Training Institute Act 2000.
References
- ↑ Admiralty Nautical Chart 2983 Tuvalu - Funafuti atoll. United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO).
- ↑ "Maritime Training Project: Program Completion Reports" (PDF). Asian Development Bank. September 2011. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- ↑ Lal, Andrick. South Pacific Sea Level & Climate Monitoring Project - Funafuti atoll (PDF). SPC Applied Geoscience and Technology Division (SOPAC Division of SPC). p. 73. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-02-03.
8°26′19″S179°10′17″E / 8.43861°S 179.17139°E