The first inhabitants of Tuvalu were Polynesians, so the origins of the people of Tuvalu can be traced to the spread of humans out of Southeast Asia, from Taiwan, via Melanesia and across the Pacific islands of Polynesia.
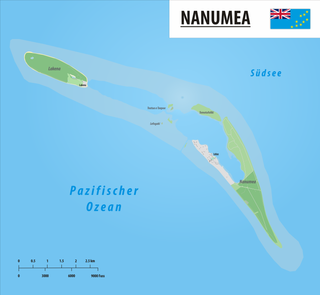
Nanumea is the northwesternmost atoll in the Polynesian nation of Tuvalu, a group of nine coral atolls and islands spread over about 400 miles (640 km) of the Pacific Ocean just south of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Nanumea is 4 km2 (1.5 sq mi) with a population of 512 people.

Nukulaelae is an atoll that is part of the nation of Tuvalu, and it has a population of 300. The largest settlement is Pepesala on Fangaua islet with a population of 300 people. It has the form of an oval and consists of at least 15 islets. The inhabited islet is Fangaua, which is 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) long and 50 to 200 metres wide. The easternmost point of Tuvalu is Niuoko islet. The Nukulaelae Conservation Area covers the eastern end of the lagoon. A baseline survey of marine life in the conservation zone was conducted in 2010.

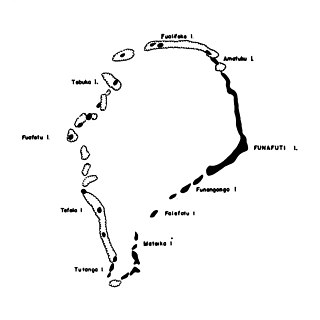
Nukufetau is an atoll that is part of the nation of Tuvalu. The atoll was claimed by the US under the Guano Islands Act some time in the 19th century and was ceded in a treaty of friendship concluded in 1979 and coming into force in 1983. It has a population of 597 who live on Savave islet.
Tepuka is an island eighteen kilometers west of Fongafale, in the northwest of Funafuti, the main atoll of the Oceanian nation of Tuvalu. Te puka, or Pouka, is the name of a tree - Hernandia peltata.
Lake na is an islet of Nanumea atoll, Tuvalu. Nanumean traditions describe Lakena as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha, the Tongan warrior who became the ancestor of the people of Nanumea.

Lafogaki is an islet of Nanumea atoll, Tuvalu. It is a small uninhabited islet, which Nanumean traditions describe as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha, the Tongan warrior who became the ancestor of the people of Nanumea.

Teaafua a Taepoa or Teaafua-a-Taepoa, is an islet of Nanumea atoll, Tuvalu. It is a small uninhabited islet, which Nanumean traditions describe as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha, the Tongan warrior who became the ancestor of the people of Nanumea.

Te Motu Foliki is an islet of Nanumea atoll, Tuvalu. It is a small uninhabited islet, which Nanumean traditions describe as being formed when sand spilled from the baskets of two women, Pai and Vau, when they were forced off Nanumea by Tefolaha, the Tongan warrior who became the ancestor of the people of Nanumea.

Fenua Tapu is an islet of Nui atoll in the Pacific Ocean state of Tuvalu.
Tokinivae is an islet of Nui atoll, in the Pacific Ocean state of Tuvalu. Nui tradition is that Kolaka, a warrior from Nukufetau came on several raiding expeditions to Tokinivae, until he was killed and buried at Tararorae.

Lafanga or Lafaga is an islet of Nukufetau, Tuvalu. The traditional history of Nukufetau recalls that in order to protect the atoll from raiders from Tonga, Fialua, an Aliki (chief), was given Lafanga, which is the largest of the eastern islets of Nukufetau. Fialua would attack raiders with his club and bury the bodies at a place called Temata.

Motumua is an islet of Nukufetau, Tuvalu to the east of Fale islet. On 11 February 1947 the community of Nukufetau opened a boarding school on Motumua so that the children of the island could get an education. The school continued until 1951 when the Education Department requested that it be transferred to Savave and become the government primary school for Nukufetau.

Motulalo is the largest islet of Nukufetau, Tuvalu. The traditional history of Nukufetau recalls that in order to protect the atoll from raiders from Tonga, Tauasa, an aliki (chief), was given Motulalo. Tauasa would pull up coconut trees and throw them at the raiders.

Sakalua is an islet of Nukufetau, Tuvalu. In the 19th century whalers established a shore camp on Sakalua where coal was used to melt down the whale blubber. The islet has been known as 'Coal Island'.

Savave is a village and islet of Nukufetau, Tuvalu, which is on the lagoon side of Fale islet. It is also the name of the small village on the island. In the late 19th century, after the coming of the missionaries, the people of Nukufetau lived on Fale islet before shifting to Savave which is on the lagoon side of the Fale settlement.
Telikiai is an islet of Nui atoll in the Pacific Ocean state of Tuvalu. Meang means "west". The islet features in the legends of the Tekaunibiti family, whose members went to catch birds on the islet and found three teanti-ma-aomata and captured two.

Nanumea Airfield is a former World War II airfield on the island of Nanumea in the Ellice Islands.

Tuvaluan mythology tells stories of the creation of the islands of Tuvalu and of the founding ancestors of each island. While on some of the islands there are stories of spirits creating the islands, a creation story that is found on many of the islands is that te Pusi mo te Ali created the islands of Tuvalu; te Ali is believed to be the origin of the flat atolls of Tuvalu and te Pusi is the model for the coconut palms that are important in the lives of Tuvaluans. The strength of this belief has the consequence that Moray eel are tapu and are not eaten.