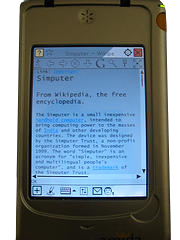
The Simputer is a self-contained, open hardware Linux-based handheld computer that was first released in 2002, developed in, and primarily distributed within India. The product was envisioned as a low-cost alternative to personal computers. The Simputer project had the initial goal of selling 50,000 units, but only sold about 4,000 units by 2005, and has been called a failure by news sources.

Amitābha is the principal Buddha of Pure Land Buddhism. He is also known as Amitāyus, which is understood to be his enjoyment body (Saṃbhogakāya). In Vajrayana Buddhism, Amitābha is known for his longevity, discernment, pure perception, and the purification of aggregates with deep awareness of the emptiness of all phenomena. The name Amitābha means "Infinite Light", and the name Amitāyus means "Infinite Life".

Byōdō-in is a Buddhist temple in the city of Uji in Kyoto Prefecture, Japan, built in the late Heian period. It is jointly a temple of the Jōdo-shū and Tendai-shū sects.

Hōnen was the religious reformer and progenitor of the first independent branch of Japanese Pure Land Buddhism called Jōdo-shū. He is also considered the Seventh Jōdo Shinshū Patriarch.

Diyarbakır, formerly Diyarbekir, is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.

Jōdo-shū, also known as Jōdo Buddhism, is a branch of Pure Land Buddhism derived from the teachings of the Japanese ex-Tendai monk Hōnen. It was established in 1175 and is the most widely practiced branch of Buddhism in Japan, along with Jōdo Shinshū. In the general classification of Buddhism in Japan, the Jōdo-shū, the Jōdo Shinshu, the Ji-shu and the Yuzu Nembutsu shu are collectively classified into the lineage of Jōdo Buddhism.

Aëtius of Amida was a Byzantine Greek physician and medical writer, particularly distinguished by the extent of his erudition. His birth and death years are not known, but his writings appear to date from the end of the 5th century or the beginning of the 6th.
Aetius, Aëtius, or Aetios (Ἀέτιος) may refer to:

The siege of Amida was a military investment of the Roman fortified frontier city of Amida by the Sasanian Empire. It took place in AD 359 when the Sasanian army under king Shapur II invaded the eastern provinces of the Roman Empire. Shapur wanted to exploit the absence of the Roman Emperor Constantius II who was overseeing affairs in the western part of the Empire. The city fell, but the strategic gain was little.

Higashi Hongan-ji (東本願寺), or, "the Eastern Monastery of the Original Vow", is one of two dominant sub-sects of Shin Buddhism in Japan and abroad, the other being Nishi Honganji. It is also the name of the head temple of the Ōtani-ha branch of Jōdo Shinshū in Kyoto, which was most recently constructed in 1895 after a fire burned down the previous temple. As with many sites in Kyoto, these two complexes have more casual names and are known affectionately in Kyoto as Onissan and Ohigashisan.

For other temples by similar names, see Zenrin-ji.

Raigō in Japanese Buddhism is the appearance of the Amida Buddha on a "purple" cloud (紫雲) at the time of one's death.

The Anastasian War was fought from 502 to 506 between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire. It was the first major conflict between the two powers since 440, and would be the prelude to a long series of destructive conflicts between the two empires over the next century.

Euglyphis is a genus of moths in the family Lasiocampidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1820.

Amida was an ancient city in Mesopotamia located where modern Diyarbakır, Turkey now stands.
Divine grace is a theological term present in many religions. It has been defined as the divine influence which operates in humans to regenerate and sanctify, to inspire virtuous impulses, and to impart strength to endure trial and resist temptation; and as an individual virtue or excellence of divine origin.

Amida Abiola Brimah is a Ghanaian professional basketball player for the Mets de Guaynabo of the Baloncesto Superior Nacional (BSN). He played college basketball for the UConn Huskies.
Legio V Parthica was a legion of the Roman Empire garrisoned in Amida, Mesopotamia, established by the Roman emperor Diocletian (284–305), who reorganized the eastern frontier. The legion is described by the historian Ammianus Marcellinus. The cognomen "Parthica" was an archaism, as the Parthian Empire was already replaced by the Sasanian Empire at the time of the establishment of the legion.
Siege of Amida may refer to:















