
Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1) also known as carnitine acyltransferase I, CPTI, CAT1, CoA:carnitine acyl transferase (CCAT), or palmitoylCoA transferase I, is a mitochondrial enzyme responsible for the formation of acyl carnitines by catalyzing the transfer of the acyl group of a long-chain fatty acyl-CoA from coenzyme A to l-carnitine. The product is often Palmitoylcarnitine, but other fatty acids may also be substrates. It is part of a family of enzymes called carnitine acyltransferases. This "preparation" allows for subsequent movement of the acyl carnitine from the cytosol into the intermembrane space of mitochondria.
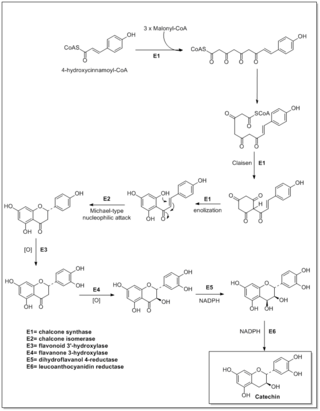
Flavonoids are synthesized by the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in which the amino acid phenylalanine is used to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This can be combined with malonyl-CoA to yield the true backbone of flavonoids, a group of compounds called chalcones, which contain two phenyl rings. Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone. The metabolic pathway continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavanones → dihydroflavonols → anthocyanins. Along this pathway, many products can be formed, including the flavonols, flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins (tannins) and a host of other various polyphenolics.
In enzymology, a 3,4-dichloroaniline N-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 6'-deoxychalcone synthase (EC 2.3.1.170) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acridone synthase (EC 2.3.1.159) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [acyl-carrier-protein] S-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthocyanin 5-O-glucoside 6'''-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthocyanin 6"-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a benzophenone synthase (EC 2.3.1.151) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a biphenyl synthase (EC 2.3.1.177) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a D-tryptophan N-malonyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.112) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-beta-glucoside O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isoflavone-7-O-beta-glucoside 6"-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pinosylvin synthase (EC 2.3.1.146) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trihydroxystilbene synthase (EC 2.3.1.95) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Biochanin A is an O-methylated isoflavone. It is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as flavonoids. Biochanin A can be found in red clover in soy, in alfalfa sprouts, in peanuts, in chickpea and in other legumes.

Benzoyl-CoA is a molecule implied in the activity of the different enzymes 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA reductase, benzoyl-CoA 3-monooxygenase, benzoate-CoA ligase, 2alpha-hydroxytaxane 2-O-benzoyltransferase, anthranilate N-benzoyltransferase, biphenyl synthase, glycine N-benzoyltransferase, ornithine N-benzoyltransferase and phenylglyoxylate dehydrogenase (acylating).
Very-long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA synthase (EC 2.3.1.199, very-long-chain 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, very-long-chain beta-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, condensing enzyme, CUT1 (gene), CERS6 (gene), FAE1 (gene), KCS (gene), ELO (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name malonyl-CoA:very-long-chain acyl-CoA malonyltransferase (decarboxylating and thioester-hydrolysing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3,5,7-Trioxododecanoyl-CoA synthase (EC 2.3.1.206, TKS) is an enzyme with systematic name malonyl-CoA:hexanoyl-CoA malonyltransferase (3,5,7-trioxododecanoyl-CoA-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-hydroxycoumarin synthase (EC 2.3.1.208, BIS2, BIS3) is an enzyme with systematic name malonyl-CoA:2-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA malonyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction




