
Catalan, known in the Valencian Community and Carche as Valencian, is a Western Romance language. It is the official language of Andorra, and an official language of three autonomous communities in eastern Spain: Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and the Valencian Community, where it is called Valencian. It has semi-official status in the Italian comune of Alghero, and it is spoken in the Pyrénées-Orientales department of France and in two further areas in eastern Spain: the eastern strip of Aragon and the Carche area in the Region of Murcia. The Catalan-speaking territories are often called the Països Catalans or "Catalan Countries".
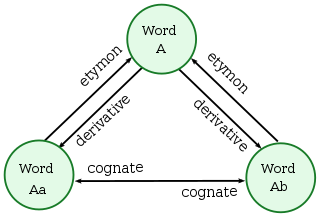
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language.

Norwegian is a North Germanic language from the Indo-European language family spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age.

Occitan, also known as lenga d'òc by its native speakers, sometimes also referred to as Provençal, is a Romance language spoken in Southern France, Monaco, Italy's Occitan Valleys, as well as Spain's Val d'Aran in Catalonia; collectively, these regions are sometimes referred to as Occitania. It is also spoken in Calabria in a linguistic enclave of Cosenza area. Some include Catalan in Occitan, as the distance between this language and some Occitan dialects is similar to the distance between different Occitan dialects. Catalan was considered a dialect of Occitan until the end of the 19th century and still today remains its closest relative.

Gascon is the vernacular Romance variety spoken mainly in the region of Gascony, France. It is often considered a variety of Occitan, although some authors consider it a different language.

Ó, ó (o-acute) is a letter in the Czech, Emilian-Romagnol, Faroese, Hungarian, Icelandic, Kashubian, Polish, Slovak, Karakalpak, and Sorbian languages. This letter also appears in the Afrikaans, Catalan, Dutch, Irish, Nynorsk, Bokmål, Occitan, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian and Galician languages as a variant of letter "o". In some cases, the letter "ó" is used in some languages as in a high rising tone. It is sometimes also used in English for loanwords.
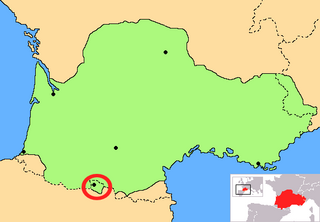
Aranese is a standardized form of the Pyrenean Gascon variety of the Occitan language spoken in the Val d'Aran, in northwestern Catalonia close to the Spanish border with France, where it is one of the three official languages beside Catalan and Spanish. In 2010, it was declared the third official language in Catalonia by the Parliament of Catalonia.

lernu! is a multilingual, web-based free project for promoting and teaching Esperanto. The name Lernu comes from the imperative form of the Esperanto verb lerni, meaning "to learn". The site is run by E@I, an international youth organization, which started as a working group of the World Esperanto Youth Organization.

There are two Norwegian language editions of Wikipedia: one for articles written in Bokmål or Riksmål, and one for articles written in Nynorsk or Høgnorsk. There are currently 634,233 articles on the Norwegian Wikipedia edition in Bokmål/Riksmål, and 170,247 articles on the Nynorsk edition.

Softcatalà is a non-profit association that promotes the use of the Catalan language on computing, Internet and new technologies. This association consists of computer specialists, philologists, translators, students and all kind of volunteers that work in the field of translating software into Catalan, in order to preserve this language in the English-controlled software environment. They also offer several linguistic tools to help users improve their language knowledge.

Google Translate is a multilingual neural machine translation service developed by Google to translate text, documents and websites from one language into another. It offers a website interface, a mobile app for Android and iOS, as well as an API that helps developers build browser extensions and software applications. As of August 2024, Google Translate supports 243 languages at various levels. It served over 200 million people daily in May 2013,, and over 500 million total users as of April 2016, with more than 100 billion words translated daily.

Gollum browser is a web application for accessing the encyclopedia, Wikipedia. Since 2017, Gollum is no longer accessible online.

The majority of languages of Spain belong to the Romance language family, of which Spanish is the only one with official status in the whole country. Others, including Catalan/Valencian and Galician, enjoy official status in their respective autonomous regions, similar to Basque in the northeast of the country. A number of other languages and dialects belonging to the Romance continuum exist in Spain, such as Aragonese, Asturian, Fala and Aranese Occitan.
Constraint grammar (CG) is a methodological paradigm for natural language processing (NLP). Linguist-written, context-dependent rules are compiled into a grammar that assigns grammatical tags ("readings") to words or other tokens in running text. Typical tags address lemmatisation, inflexion, derivation, syntactic function, dependency, valency, case roles, semantic type etc. Each rule either adds, removes, selects or replaces a tag or a set of grammatical tags in a given sentence context. Context conditions can be linked to any tag or tag set of any word anywhere in the sentence, either locally or globally. Context conditions in the same rule may be linked, i.e. conditioned upon each other, negated, or blocked by interfering words or tags. Typical CGs consist of thousands of rules, that are applied set-wise in progressive steps, covering ever more advanced levels of analysis. Within each level, safe rules are used before heuristic rules, and no rule is allowed to remove the last reading of a given kind, thus providing a high degree of robustness.
This article compares several selected client-based genealogy programs. Web-based genealogy software is not included.

Transfer-based machine translation is a type of machine translation (MT). It is currently one of the most widely used methods of machine translation. In contrast to the simpler direct model of MT, transfer MT breaks translation into three steps: analysis of the source language text to determine its grammatical structure, transfer of the resulting structure to a structure suitable for generating text in the target language, and finally generation of this text. Transfer-based MT systems are thus capable of using knowledge of the source and target languages.

There are four languages with official status in Catalonia : Catalan; Spanish, which is official throughout Spain; Aranese, a dialect of Occitan spoken in the Aran Valley; and Catalan Sign Language. Many other languages are spoken in Catalonia as a result of recent immigration from all over the world.

Western Romance languages are one of the two subdivisions of a proposed subdivision of the Romance languages based on the La Spezia–Rimini Line. They include the Gallo-Romance, Occitano-Romance and Iberian Romance branches. Gallo-Italic may also be included. The subdivision is based mainly on the use of the "s" for pluralization, the weakening of some consonants and the pronunciation of "Soft C" as /t͡s/ rather than /t͡ʃ/ as in Italian and Romanian.

Yandex Translate is a web service provided by Yandex, intended for the translation of web pages into another language.
Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) was a neural machine translation (NMT) system developed by Google and introduced in November 2016 that used an artificial neural network to increase fluency and accuracy in Google Translate. The neural network consisted of two main blocks, an encoder and a decoder, both of LSTM architecture with 8 1024-wide layers each and a simple 1-layer 1024-wide feedforward attention mechanism connecting them. The total number of parameters has been variously described as over 160 million, approximately 210 million, 278 million or 380 million. It used WordPiece tokenizer, and beam search decoding strategy. It ran on Tensor Processing Units.


















