
Limanda is a genus of righteye flounders native to the northern Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
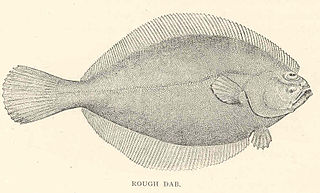
Hippoglossoides is a genus of righteye flounders native to the North Pacific and North Atlantic oceans.

Pleuronichthys is a genus of fish in the family Pleuronectidae found in the Pacific Ocean.

Achirus is a genus of American soles native to tropical and subtropical parts of the Americas. They are mainly found in coastal areas, including salt and brackish water, but some species are found in fresh water.

Catathyridium is a genus of mainly freshwater American soles native to South America.

Gymnachirus is a genus of American soles native to the Atlantic coast of the Americas.

Trinectes is a genus of American soles native to the Americas. Most species are coastal, occurring in both salt and brackish water, but several may enter fresh water and one, T. hubbsbollinger, is restricted to rivers. They are fairly small, with the largest species only reaching 25 cm (9.8 in) in length.

Etropus is a genus of large-tooth flounders native to the coastal waters of the Americas.

Brachirus is a genus of small and medium-sized soles. Most are native to marine and brackish waters in the Indo-Pacific, but several species can also be seen freshwater in southern Asia, Eastern Africa, New Guinea and Australia.
Leptachirus is a genus of small soles native to brackish and fresh water in New Guinea and northern Australia.

Pegusa is a genus of soles native to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, and Black Sea.

Solea is a genus of soles from the Indo-Pacific and East Atlantic Oceans, and the Mediterranean Sea.
The American sole is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Robson Tamar da Costa Ramos, Telton Pedro Anselmo Ramos and Paulo Roberto Duarte Lopes in 2009. It inhabits the Mucuri River in Brazil, from which its species epithet is derived. It reaches a maximum standard length of 9 cm (3.5 in).

The longtail sole is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Johann Jakob Kaup in 1858. It inhabits the Amazon, Corantijn, Grajaú, Orinoco, and Oyapock rivers. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 10 m. It reaches a maximum total length of 15 cm (5.9 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 11 cm (4.3 in).

Apionichthys finis is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Carl H. Eigenmann in 1912, originally under the genus Soleonasus. It inhabits the Essequibo, Potaro and Amazon rivers. It reaches a maximum standard length of 8.8 cm (3.5 in).
Apionichthys menezesi is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Robson Tamar da Costa Ramos in 2003. It inhabits the Amazon, Negro, Napo and Orinoco rivers. It reaches a maximum standard length of 6 cm (2.4 in).
Apionichthys nattereri is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Franz Steindachner in 1876, originally under the genus Solea. It inhabits the Amazon River. It reaches a maximum standard length of 23.4 cm (9.2 in).
Apionichthys rosai is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Robson Tamar da Costa Ramos in 2003. It is found in the Amazon River. It reaches a maximum standard length of 3.5 cm (1.4 in).
Apionichthys sauli is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Robson Tamar da Costa Ramos in 2003. It inhabits the Orinoco and Meta rivers in South America. It reaches a maximum standard length of 7 cm (2.8 in).
Apionichthys seripierriae is a species of sole in the family Achiridae. It was described by Robson Tamar da Costa Ramos in 2003. It is found in the Amazon River. It reaches a maximum standard length of 8.8 cm (3.5 in).













