
Isopoda is an order of crustacean, which includes woodlice and their relatives. Members of this group are called Isopods and include both terrestrial and aquatic species. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax.

Sphaeromatidae is a family of isopods, often encountered on rocky shores and in shelf waters in temperate zones. The family includes almost 100 genera and 619 known marine species. Within these genera, there are groups that share distinctive morphologies; further research may reclassify these genus-groups as separate families.
Curassanthura is a genus of isopod crustaceans in the family Leptanthuridae. It contains the following species:
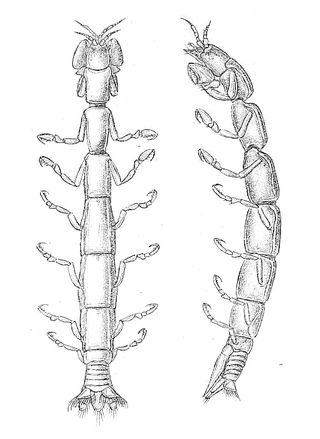
Anthuroidea is a superfamily of isopod crustaceans, formerly treated as a suborder, Anthuridea. The group is characterised by "an elongate cylindrical body form, without dorsal coxal plates, and with a uropodal exopod attached to the peduncle proximally and dorsally". There are more than 500 described species in 57 genera, arranged across six families:
Iais is a genus of isopod crustaceans. Iais species are found in association with larger isopods of the family Sphaeromatidae, usually on the ventral surface of the larger animal, between the pereiopods and on the pleopods. They are native to Australasia and South America, although Iais californica and its host Sphaeroma quoyanum have invaded California, and I. californica was first described from Sausalito, California. Nine species are recognised:

The Idoteidae are a family of isopod crustaceans. It includes these genera:

The Cirolanidae are a family of isopod crustaceans, including these genera:

Paracerceis is a genus of isopod crustacean in the family Sphaeromatidae. It contains the following species:

The Leptanthuridae are a family of isopod crustaceans, containing the following genera:

Sphaeromatidea is a suborder of isopod crustaceans.

Gnathia is a genus of isopod crustaceans, containing the following species:

The Chaetiliidae are a family of isopod crustaceans in the suborder Valvifera, comprising these genera:
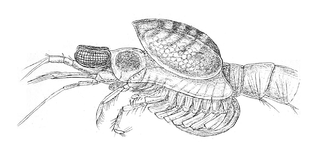
The Dajidae are a family of marine isopod crustaceans in the suborder Cymothoida. The original description was made by Giard and Bonnier in 1887. Members of this family are ectoparasites of krill. They resemble a fleshy growth on the krill's back, and make the host look as if it is wearing a rucksack. These genera are included in the family Dajidae:

Platyarthridae is a family of woodlice, containing the following genera:
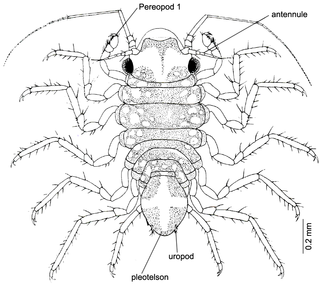
Uromunna sheltoni is a species of isopod first described by Brian Kensley in 1977. U. sheltoni is included in the genus Uromunna and family Munnidae. No subspecies are listed. The species was first collected by Peter Shelton of the University of Cape Town, for whom it is named.

Cirolana is a genus of isopod crustaceans.

Aega is a genus of isopods in the family Aegidae, containing the following species:

Glyptidotea is a monotypic genus of isopod in the family Idoteidae. Its sole member is Glyptidotea lichtensteini, the keeled isopod, a medium-sized isopod found on the coast of southern Africa.
Holidoteidae is a family of marine isopods belonging to the suborder Valvifera.

Leptanthura is a genus of isopod crustaceans in the family Leptanthuridae. It was first described in 1897 by Georg Ossian Sars and the type species is Paranthura tenuis. It is found in coastal waters throughout the world, and contains the following species:














