
The Western Interior Seaway was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses for 34 million years. The ancient sea, which existed from the early Late Cretaceous to the earliest Paleocene, connected the Gulf of Mexico to the Arctic Ocean. The two land masses it created were Laramidia to the west and Appalachia to the east. At its largest extent, it was 2,500 feet (760 m) deep, 600 miles (970 km) wide and over 2,000 miles (3,200 km) long.

Charles Hazelius Sternberg was an American fossil collector and paleontologist. He was active in both fields from 1876 to 1928, and collected fossils for Edward Drinker Cope and Othniel C. Marsh, and for the British Museum, the San Diego Natural History Museum and other museums.

Enchodus is an extinct genus of aulopiform ray-finned fish related to lancetfish and lizardfish. Species of Enchodus flourished during the Late Cretaceous, and there is some evidence that they may have survived to the Paleocene or Eocene; however, this may just represent reworked Cretaceous material.

Microsauria is an extinct, possibly polyphyletic order of tetrapods from the late Carboniferous and early Permian periods. It is the most diverse and species-rich group of lepospondyls. Recently, Microsauria has been considered paraphyletic, as several other non-microsaur lepospondyl groups such as Lysorophia seem to be nested in it. Microsauria is now commonly used as a collective term for the grade of lepospondyls that were originally classified as members of Microsauria.
Raymond Cecil Moore was an American geologist and paleontologist. He is known for his work on Paleozoic crinoids, bryozoans, and corals. Moore was a member of US Geological Survey from 1913 until 1949. In 1919 he became professor at the University of Kansas (Lawrence). In 1953 Professor Moore organized the launch and became the first editor of the still ongoing multi-volume work Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology. Contributors to the Treatise have included the world's specialists in the field. He served as president of the Geological Society of America in 1958. In 1970 he was awarded the Mary Clark Thompson Medal from the National Academy of Sciences.

Dolichorhynchops is an extinct genus of polycotylid plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America, containing the species D. osborni and D. herschelensis, with two previous species having been assigned to new genera. Definitive specimens of D. osborni have been found in the late Coniacian to early Campanian rocks, while those of D. herschelensis have been found in the late Campanian to early Maastrichtian rocks. Dolichorhynchops was a prehistoric marine reptile measuring around 3 metres (9.8 ft) long. Its Greek generic name means "long-nosed face".

Acanthohoplites is an extinct genus of ammonites in the family Parahoplitidae that lived in the Aptian and Early Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous.
Aulacosphinctes is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopod that lived during the Late Jurassic and had a widespread distribution.

Styxosaurus is a genus of plesiosaur of the family Elasmosauridae. Styxosaurus lived during the Campanian age of the Cretaceous period. Three species are known: S. snowii, S. browni, and S. rezaci.

The Pierre Shale is a geologic formation or series in the Upper Cretaceous which occurs east of the Rocky Mountains in the Great Plains, from Pembina Valley in Canada to New Mexico.

Toxochelys is an extinct genus of marine turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It is the most commonly found fossilized turtle species in the Smoky Hill Chalk, in western Kansas.
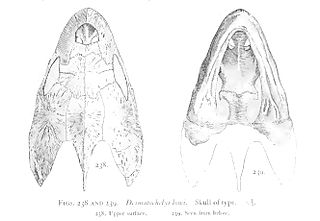
Desmatochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtles belonging to the family Protostegidae. This genus contains two known species, D. lowii and D. padillai. D. lowii was first discovered in 1895, followed by D. padillai in 2015. Having been estimated at over 120 million years old, D. padillai is currently the oldest known species of sea turtle.

Dakotasuchus is a genus of goniopholidid mesoeucrocodylian. Its fossils have been recovered from the Cenomanian-age Upper Cretaceous Dakota Sandstone of Kansas. The type specimen was found in an iron-cemented sandstone concretion near Salina. This concretion was broken into two large pieces; more of the specimen was probably present originally, but by the time it was found only the torso and short portions of the neck and tail remained. Twenty pairs of bony scutes ran down the midline of the back. The vertebrae lacked the procoelous articulation of more derived crocodyliforms. Dakotasuchus had short broad shoulder blades, suggesting it had stout powerful forelimbs and perhaps terrestrial habits. M. G. Mehl, who described the genus, estimated the length of the type individual when complete to have been 3–4 metres (9.8–13.1 ft). The type species is D. kingi, named for Professor King, a former dean of Kansas Wesleyan University. Mehl did not classify his new genus to a more inclusive group than Mesosuchia. Robert Carroll assigned Dakotasuchus to Goniopholididae in 1988. In 2017, fossils of Dakotasuchus kingi which consisted of a coracoid, scutes, a dorsal vertebrate and postcranial bones were found in Utah, specifically in the Cedar Mountain Formation's Mussentuchit Member.

Coroniceras is a genus in the Arietitidae, a family in the ammonitid superfamily Psiloceratoidea, from the lower Sinermurian stage in the Lower Jurassic. It is a sub zone ammonite of the Arnioceras semicostatum Zone.

The Carlile Shale is a Turonian age Upper/Late Cretaceous series shale geologic formation in the central-western United States, including in the Great Plains region of Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming.

During most of the Late Cretaceous the eastern half of North America formed Appalachia, an island land mass separated from Laramidia to the west by the Western Interior Seaway. This seaway had split North America into two massive landmasses due to a multitude of factors such as tectonism and sea-level fluctuations for nearly 40 million years. The seaway eventually expanded, divided across the Dakotas, and by the end of the Cretaceous, it retreated towards the Gulf of Mexico and the Hudson Bay.

Paleontology in Iowa refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Iowa. The paleozoic fossil record of Iowa spans from the Cambrian to Mississippian. During the early Paleozoic Iowa was covered by a shallow sea that would later be home to creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, cephalopods, corals, fishes, and trilobites. Later in the Paleozoic, this sea left the state, but a new one covered Iowa during the early Mesozoic. As this sea began to withdraw a new subtropical coastal plain environment which was home to duck-billed dinosaurs spread across the state. Later this plain was submerged by the rise of the Western Interior Seaway, where plesiosaurs lived. The early Cenozoic is missing from the local rock record, but during the Ice Age evidence indicates that glaciers entered the state, which was home to mammoths and mastodons.

Paleontology in Oklahoma refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Oklahoma has a rich fossil record spanning all three eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Oklahoma is the best source of Pennsylvanian fossils in the United States due to having an exceptionally complete geologic record of the epoch. From the Cambrian to the Devonian, all of Oklahoma was covered by a sea that would come to be home to creatures like brachiopods, bryozoans, graptolites and trilobites. During the Carboniferous, an expanse of coastal deltaic swamps formed in areas of the state where early tetrapods would leave behind footprints that would later fossilize. The sea withdrew altogether during the Permian period. Oklahoma was home a variety of insects as well as early amphibians and reptiles. Oklahoma stayed dry for most of the Mesozoic. During the Late Triassic, carnivorous dinosaurs left behind footprints that would later fossilize. During the Cretaceous, however, the state was mostly covered by the Western Interior Seaway, which was home to huge ammonites and other marine invertebrates. During the Cenozoic, Oklahoma became home to creatures like bison, camels, creodonts, and horses. During the Ice Age, the state was home to mammoths and mastodons. Local Native Americans are known to have used fossils for medicinal purposes. The Jurassic dinosaur Saurophaganax maximus is the Oklahoma state fossil.

Lytoceras is an ammonite genus that was extant during most of the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and is the type genus for the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores.

The Fort Hays Limestone is a member of the Niobrara Formation of the Colorado Group exposed in Colorado, Kansas, Nebraska, and South Dakota and is named for the bluffs near the old Fort Hays, a well-known landmark in western Kansas.

















