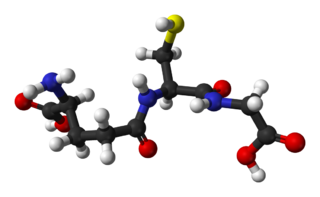
Glutathione is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.

A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups from one molecule to another. They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes.

Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, are a family of eukaryotic and prokaryotic phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to catalyze the conjugation of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) to xenobiotic substrates for the purpose of detoxification. The GST family consists of three superfamilies: the cytosolic, mitochondrial, and microsomal—also known as MAPEG—proteins. Members of the GST superfamily are extremely diverse in amino acid sequence, and a large fraction of the sequences deposited in public databases are of unknown function. The Enzyme Function Initiative (EFI) is using GSTs as a model superfamily to identify new GST functions.
The peptidyl transferase is an aminoacyltransferase as well as the primary enzymatic function of the ribosome, which forms peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids using tRNAs during the translation process of protein biosynthesis. The substrates for the peptidyl transferase reaction are two tRNA molecules, one bearing the growing peptide chain and the other bearing the amino acid that will be added to the chain. The peptidyl chain and the amino acids are attached to their respective tRNAs via ester bonds to the O atom at the CCA-3' ends of these tRNAs. Peptidyl transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the addition of an amino acid residue in order to grow the polypeptide chain in protein synthesis. It is located in the large ribosomal subunit, where it catalyzes the peptide bond formation. It is composed entirely of RNA. The alignment between the CCA ends of the ribosome-bound peptidyl tRNA and aminoacyl tRNA in the peptidyl transferase center contribute to its ability to catalyze these reactions. This reaction occurs via nucleophilic displacement. The amino group of the aminoacyl tRNA attacks the terminal carboxyl group of the peptidyl tRNA. Peptidyl transferase activity is carried out by the ribosome. Peptidyl transferase activity is not mediated by any ribosomal proteins but by ribosomal RNA (rRNA), a ribozyme. Ribozymes are the only enzymes which are not made up of proteins, but ribonucleotides. All other enzymes are made up of proteins. This RNA relic is the most significant piece of evidence supporting the RNA World hypothesis.
Guanylyl transferases are enzymes that transfer a guanosine mono phosphate group, usually from GTP to another molecule, releasing pyrophosphate. Many eukaryotic guanylyl transferases are capping enzymes that catalyze the formation of the 5' cap in the co-transcriptional modification of messenger RNA. Because the 5' end of the RNA molecule ends in a phosphate group, the bond formed between the RNA and the GTP molecule is an unusual 5'-5' triphosphate linkage, instead of the 3'-5' linkages between the other nucleotides that form an RNA strand. In capping enzymes, a highly conserved lysine residue serves as the catalytic residue that forms a covalent enzyme-GMP complex.
N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase is a transferase enzyme.

Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituents of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates. The general reaction of transferring a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from A to B, can be written as:
In enzymology, a mycothiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.306) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Arsenate reductase (glutaredoxin) (EC 1.20.4.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mycothione reductase (EC 1.8.1.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Bacillithiol is a thiol compound found in Bacillus species. It is likely involved in maintaining cellular redox balance and plays a role in microbial resistance to the antibiotic fosfomycin.
Arsenic biochemistry refers to biochemical processes that can use arsenic or its compounds, such as arsenate. Arsenic is a moderately abundant element in Earth's crust, and although many arsenic compounds are often considered highly toxic to most life, a wide variety of organoarsenic compounds are produced biologically and various organic and inorganic arsenic compounds are metabolized by numerous organisms. This pattern is general for other related elements, including selenium, which can exhibit both beneficial and deleterious effects. Arsenic biochemistry has become topical since many toxic arsenic compounds are found in some aquifers, potentially affecting many millions of people via biochemical processes.

In molecular biology, the ars operon is an operon found in several bacterial taxon. It is required for the detoxification of arsenate, arsenite, and antimonite. This system transports arsenite and antimonite out of the cell. The pump is composed of two polypeptides, the products of the arsA and arsB genes. This two-subunit enzyme produces resistance to arsenite and antimonite. Arsenate, however, must first be reduced to arsenite before it is extruded. A third gene, arsC, expands the substrate specificity to allow for arsenate pumping and resistance. ArsC is an approximately 150-residue arsenate reductase that uses reduced glutathione (GSH) to convert arsenate to arsenite with a redox active cysteine residue in the active site. ArsC forms an active quaternary complex with GSH, arsenate, and glutaredoxin 1 (Grx1). The three ligands must be present simultaneously for reduction to occur.
Mycoredoxin is an enzyme with systematic name arseno-mycothiol:mycoredoxin oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Mycothiol synthase is an enzyme with systematic name acetyl-CoA:desacetylmycothiol O-acetyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-inositol-3-phosphate glycosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:1D-myo-inositol 3-phosphate alpha-D-glycosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-acetyl-1-D-myo-inositol-2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranoside deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.103, MshB) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-1D-myo-inositol acetylhydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
L-cysteine:1D-myo-inositol 2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranoside ligase is an enzyme with systematic name L-cysteine:1-O-(2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-1D-myo-inositol ligase (AMP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Arsenate-reducing bacteria are bacteria which reduce arsenates. Arsenate-reducing bacteria are ubiquitous in arsenic-contaminated groundwater (aqueous environment). Arsenates are salts or esters of arsenic acid (H3AsO4), consisting of the ion AsO43−. They are moderate oxidizers that can be reduced to arsenites and to arsine. Arsenate can serve as a respiratory electron acceptor for oxidation of organic substrates and H2S or H2. Arsenates occur naturally in minerals such as adamite, alarsite, legrandite, and erythrite, and as hydrated or anhydrous arsenates. Arsenates are similar to phosphates since arsenic (As) and phosphorus (P) occur in group 15 (or VA) of the periodic table. Unlike phosphates, arsenates are not readily lost from minerals due to weathering. They are the predominant form of inorganic arsenic in aqueous aerobic environments. On the other hand, arsenite is more common in anaerobic environments, more mobile, and more toxic than arsenate. Arsenite is 25–60 times more toxic and more mobile than arsenate under most environmental conditions. Arsenate can lead to poisoning, since it can replace inorganic phosphate in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate --> 1,3-biphosphoglycerate step of glycolysis, producing 1-arseno-3-phosphoglycerate instead. Although glycolysis continues, 1 ATP molecule is lost. Thus, arsenate is toxic due to its ability to uncouple glycolysis. Arsenate can also inhibit pyruvate conversion into acetyl-CoA, thereby blocking the TCA cycle, resulting in additional loss of ATP.







