
Aa is a genus of plants of the family Orchidaceae.

Cortaderia is a genus of South American and Central American plants in the Poaceae grass family.

Chusquea is a genus of evergreen bamboos in the grass family. Most of them are native to mountain habitats in Latin America, from Mexico to southern Chile and Argentina.

Oncidium, abbreviated as Onc. in the horticultural trade, is a genus that contains about 330 species of orchids from the subtribe Oncidiinae of the orchid family (Orchidaceae). As presently conceived, it is distributed across much of South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies, with one species (O. ensatum) extending into Florida. Common names for plants in this genus include dancing-lady orchid and golden shower orchid.
Harold Ernest Robinson was an American botanist and entomologist.

Aiphanes is a genus of spiny palms which is native to tropical regions of South and Central America and the Caribbean. There are about 26 species in the genus, ranging in size from understorey shrubs with subterranean stems to subcanopy trees as tall as 20 metres (66 ft). Most have pinnately compound leaves ; one species has entire leaves. Stems, leaves and sometimes even the fruit are covered with spines. Plants flower repeatedly over the course of their lifespan and have separate male and female flowers, although these are borne together on the same inflorescence. Although records of pollinators are limited, most species appear to be pollinated by insects. The fruit are eaten by several birds and mammals, including at least two species of amazon parrots.

Clethra is a genus of flowering shrubs or small trees described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753.
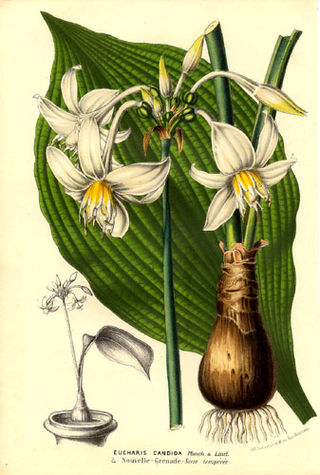
Eucharis is a genus of about 15–20 species of neotropical plants in the Amaryllis family, native to Central America and South America, from Guatemala south to Bolivia. Some species have become naturalized in Mexico, the West Indies, and scattered tropical islands. The English name Amazon lily is sometimes used for all species in the genus, but is particularly used for Eucharis amazonica and Eucharis × grandiflora, which are often confused.

Desmoncus is a genus of mostly climbing, spiny palms native to the Neotropics. The genus extends from Mexico in the north to Brazil and Bolivia in the south, with two species present in the southeastern Caribbean.

Oenocarpus is a genus of pinnate-leaved palms (Arecaceae) native to Trinidad, southern Central and tropical South America. With nine species and one natural hybrid, the genus is distributed from Costa Rica and Trinidad in the north to Brazil and Bolivia in the south.

Aequatorium is a genus of flowering plants in the aster family. It was described as a genus in 1978. It is a member of the tribe Senecioneae and native to South America.
Oblivia is a genus of flowering plant in the tribe Heliantheae within the family Asteraceae.

Pseudogynoxys is a genus of flowering plant in the groundsel tribe within the sunflower family, native to North and South America.
Wettinia is a palm genus, consisting of flowering plants in the family Arecaceae. The genus, established in 1837, contains some 20 species, but more seem to await discovery considering that 4 species - W. aequatorialis, W. lanata, W. minima and W. panamensis - were described as late as 1995. The genus is broadly divided into two groups. One group has the fruits tightly packed, while the other, formerly classified as genus Catoblastus, has fruits scattered along the inflorescence branches. It is not known whether these groups are both monophyletic. The genus is named after Frederick Augustus II of Saxony, of the House of Wettin.

Gustavia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lecythidaceae described by Linnaeus in 1775. It is native to tropical Central America and South America. Many of the species are threatened; some are critically endangered Gustavia superba, though, is actually abundant in re-growing secondary forests. It grows in northern South America, from Panama south through the Andes as far as Ecuador, and along the Caribbean coast and in the Amazon basin. Gustavia flowers have numerous stamens, in some species as many as 1,200 in a single flower.

Brunellia is a genus of trees. They are distributed in the mountainous regions of southern Mexico, Central America, West Indies, and South America. Brunellia is the only genus in the family Brunelliaceae. As of 2001 there were about 54 species.

Pholidostachys is a genus of palms found in Central America and northwestern South America.
Critoniella is a genus of South American flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.
Polyanthina is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Eupatorieae within the family Asteraceae.

Alloispermum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae described as a genus in 1807.














