
Sorrel, also called common sorrel or garden sorrel, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Polygonaceae. Other names for sorrel include spinach dock and narrow-leaved dock.

Chenopodium album is a fast-growing annual plant in the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae. Though cultivated in some regions, the plant is elsewhere considered a weed. Common names include lamb's quarters, melde, goosefoot, wild spinach and fat-hen, though the latter two are also applied to other species of the genus Chenopodium, for which reason it is often distinguished as white goosefoot.

Basella alba is an edible perennial vine in the family Basellaceae. It is found in tropical Asia and Africa where it is widely used as a leaf vegetable. It is native to the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and New Guinea. It is naturalized in China, tropical Africa, Brazil, Belize, Colombia, the West Indies, Fiji and French Polynesia.

Amaranthus blitum, commonly called purple amaranth or Guernsey pigweed, is an annual plant species in the economically important plant family Amaranthaceae.

Celosia argentea, commonly known as the plumed cockscomb or silver cock's comb, is a herbaceous plant of tropical origin in the family Amaranthaceae from India and Nepal. The plant is known for its very bright colors. In India and China it is known as a troublesome weed.

Amaranthus viridis is a cosmopolitan species in the botanical family Amaranthaceae and is commonly known as slender amaranth or green amaranth.

Alepidea peduncularis is an edible perennial herb native to the montane grasslands of East and South Africa.

Alternanthera sessilis is a flowering plant known by several common names, including sissoo spinach, Brazilian spinach, sessile joyweed, dwarf copperleaf. It is cultivated as a vegetable worldwide.

Allium moly, also known as yellow garlic, golden garlic and lily leek, Is a species of flowering plant in the genus Allium, which also includes the flowering and culinary onions and garlic. A bulbous herbaceous perennial from the Mediterranean. It is edible and used as a medicinal and ornamental plant. Allium moly is a bulb type flower, with the size of the bulb affecting the flowering period and the time of the flowering.

Astragalus canadensis is a common and widespread member of the milkvetch genus in the legume family, known commonly as Canadian milkvetch. The plant is found throughout Canada and the United States in many habitats including wetlands, woodlands, and prairies.

Commelina diffusa, sometimes known as the climbing dayflower or spreading dayflower, is a pantropical herbaceous plant in the dayflower family. It has been introduced to the southeastern United States where it is most common in wet disturbed soils. There are two recognised varieties, one being the type and the other being C. diffusa var. gigas, which is native to Asia and has been introduced to Florida. It flowers from spring to fall and is most common in disturbed situations, moist places and forests. In China the plant is used medicinally as a febrifuge and a diuretic. A blue dye is also extracted from the flower for paints. In the Hawaiian Islands, it is known as "honohono grass", although it is technically not a grass. "Honohono" refers to the alternating structure of the leaves. At least one publication lists it as an edible plant in New Guinea.

Astragalus lentiginosus Astragalus lentiginosus is a species of legume native to western North America where it grows in a range of habitats. Common names include spotted locoweed and freckled milkvetch. There are a great number of wild varieties. The flower and the fruit of an individual plant are generally needed to identify the specific variety.
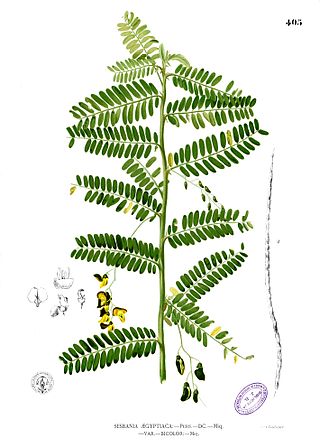
Sesbania sesban, the Egyptian riverhemp, is a species of plant in the legume family, a fast growing species, it has four varieties that are currently recognized.

Astragalus trichopodus is a species of legume known by the common name Santa Barbara milk vetch. It is native to southern California and Baja California, where it grows in several types of open habitat, including in the Transverse Ranges and Mojave Desert.

Astragalus cimae is a species of milkvetch known by the common name Cima milkvetch. It is native to the Mojave Desert and its sky island woodlands of eastern California western Nevada, especially on calcareous soils, including the Cima Dome area in the Mojave National Preserve.

Astragalus oophorus is a species of milkvetch known by the common name egg milkvetch. It is native to the western United States, mainly California and Nevada, though one variety can be found as far east as Colorado. It is a plant of sagebrush and other dry habitat.

Ceratotheca sesamoides is an annual flowering plant in the genus Ceratotheca. It is indigenous to Africa, and grows both as a wild and locally-cultivated species, and is colloquially referred to as false sesame owing to its marked similarities with common sesame. The plant is most commonly cultivated in the African savannah and other semi-arid areas on the continent, and is found across Africa in both tropical and sub-tropical latitudes, usually growing in sandier soils south of the Sahara. It can be identified by numerous hairs on the stem; its pinkish flowers, often showing brown and purple markings; and a sub-erect growth habit. The leaves and flowers are often consumed as a vegetable or used in sauces. The leaves are thought to have medicinal properties, while the seeds can be used to produce cooking oil. Despite its many uses and increasing domestication at a local level, the plant remains predominantly underused and undervalued.

Lippia abyssinica, or koseret, is a species of flowering plant in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. It is endemic to Ethiopia but cultivated throughout tropical African countries. The specific epithet abyssinica derives from Latin and means 'of or from Ethiopia (Abyssinia)'.

Dracaena surculosa, called the gold dust dracaena and spotted dracaena, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, native to west and west-central tropical Africa, from Guinea to the Republic of the Congo. Its cultivar 'Florida Beauty' has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.

Aspilia kotschyi is a species ofherbaceous plant in the family Asteraceae. It has ovate to narrowly lanceolate leaves and dark red-purple flowers commonly found Tropical Africa. It has a variety, Aspilia kotschyi var. alba which has white flowers.




















