
The family Pandalidae is a taxon of caridean shrimp. These species are commonly called pandalid shrimp. They are edible and have high economic value. They are characterised by the subdivided carpus of the second pereiopod and, mainly, by the lack of the chelae (claws) on the first pereiopod. This is a cold-water family, and their representation in tropical areas is made by deep-sea shrimp. The genus Physetocaris, sometimes placed in this family, is now considered to be in its own family, Physetocarididae.

Crangonidae is a family of shrimp, of the superfamily Crangonoidea, including the commercially important species Crangon crangon. Its type genus is Crangon. Crangonid shrimps' first pair of pereiopods have partially chelate claws that they use to capture their prey. They burrow shallowly into sediment on the sea floor, and feed on bivalves, crustaceans, polychaetes, and some small fish.

Alpheidae is a family of caridean snapping shrimp, characterized by having asymmetrical claws, the larger of which is typically capable of producing a loud snapping sound. Other common names for animals in the group are pistol shrimp or alpheid shrimp.

Alpheopsis is a genus of shrimp of the family Alpheidae. Several species of the genus have been known to share the same burrows with members of different species. They are inhabitants of the eastern Pacific Ocean.

Athanas is a genus of shrimp of the family Alpheidae. These are small shrimp measuring 2 cm in length. Females have smaller chelae than males.

Salmoneus is a genus of shrimps of the family Alpheidae. Understanding of the genus has grown rapidly, with only 19 known species before 2000, to over 60 species as of 2023.

Macrophthalmus is a genus of crabs which are widespread across the Indo-Pacific. It contains the following species :

Callianassidae is a family of ghost shrimp crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Axiidea, within the order Decapoda.

Pagurus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Paguridae. Like other hermit crabs, their abdomen is not calcified and they use snail shells as protection. These marine decapod crustaceans are omnivorous, but mostly prey on small animals and scavenge carrion. Trigonocheirus and Pagurixus used to be considered subgenera of Pagurus, but the former is nowadays included in Orthopagurus, while the latter has been separated as a distinct genus.

Palaemon is a genus of caridean shrimp in the family Palaemonidae.

Axiidae is a family of crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Axiidea, within the order Decapoda.
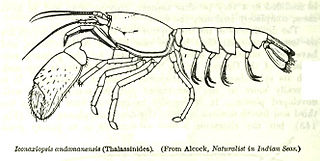
Eiconaxius is a genus of mud lobster that includes the following species:

Paguristes is a genus of hermit crab in the family Diogenidae. It includes the following species :

Lebbeus is a genus of shrimp in the family Thoridae. It includes a species whose name was auctioned in 2009 to raise funds for conservation; Luc Longley won with a bid of A$3,600. He named the shrimp Lebbeus clarehannah. The following species are included:

Diogenes is a genus of hermit crabs.

Macrobrachium is a genus of freshwater prawns or shrimps characterised by the extreme enlargement of the second pair of pereiopods, at least in the male.

Pandalus is a genus of shrimp in the family Pandalidae. Members of the genus are medium-sized and live on or near the seabed. Some species are the subject of commercial fisheries and are caught by trawling. One species, Pandalus montagui, lives in association with the reef-building polychaete worm, Sabellaria spinulosa.

Hermatobates is a genus of wingless marine bugs placed as the sole genus in the family Hermatobatidae that are sometimes known as coral-treaders. They are quite rare and known only from coral reefs in the Indo-Pacific region. During low tide, they move over the water surface not unlike the more familiar water-striders around coral atolls and reefs and stay submerged in reef crevices during high tide.
















