Related Research Articles

Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in the Central American region of North America. Costa Rica is bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of 51,060 km2 (19,710 sq mi). An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area.

The economy of Costa Rica has been very stable for some years now, with continuing growth in the GDP and moderate inflation, though with a high unemployment rate: 11.49% in 2019. Costa Rica's economy emerged from recession in 1997 and has shown strong aggregate growth since then. The estimated GDP for 2023 is US$78 billion, up significantly from the US$52.6 billion in 2015 while the estimated 2023 per capita is US$26,422.

A free trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and to increase trade of goods and services with each other. If natural persons are also free to move between the countries, in addition to a free trade agreement, it would also be considered an open border. It can be considered the second stage of economic integration.
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is a legal agreement between many countries, whose overall purpose was to promote international trade by reducing or eliminating trade barriers such as tariffs or quotas. According to its preamble, its purpose was the "substantial reduction of tariffs and other trade barriers and the elimination of preferences, on a reciprocal and mutually advantageous basis."

The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that govern international trade. It officially commenced operations on 1 January 1995, pursuant to the 1994 Marrakesh Agreement, thus replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) that had been established in 1948. The WTO is the world's largest international economic organization, with 164 member states representing over 98% of global trade and global GDP.

The Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA) was a proposed agreement to eliminate or reduce the trade barriers among all countries in the Americas, excluding Cuba. Negotiations to establish the FTAA ended in failure, however, with all parties unable to reach an agreement by the 2005 deadline they had set for themselves.

Central America is commonly said to include Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. This definition matches modern political borders. Central America begins geographically in Mexico, at the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico's narrowest point, and the former country of Yucatán (1841–1848) was part of Central America. At the other end, before its independence in 1903 Panama was part of South America, as it was a Department of Colombia. At times Belize, a British colony until 1981, where English instead of Spanish is spoken, and where the population is primarily of African origin, has been considered not part of (Spanish-speaking) Central America.

The Cairns Group is an interest group of 19 agricultural exporting countries, composed of Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Indonesia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, the Philippines, South Africa, Thailand, Uruguay, and Vietnam.

The Dominican Republic–Central America–United States Free Trade Agreement is a free trade agreement. Originally, the agreement encompassed the United States and the Central American countries of Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua, and was called CAFTA. In 2004, the Dominican Republic joined the negotiations, and the agreement was renamed CAFTA-DR.
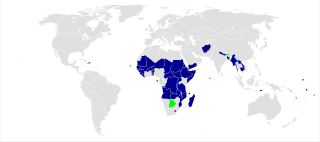
Everything but Arms (EBA) is an initiative of the European Union under which all imports to the EU from the Least Developed Countries are duty-free and quota-free, with the exception of armaments. EBA entered into force on 5 March 2001. There were transitional arrangements for bananas, sugar and rice until January 2006, July 2009 and September 2009 respectively. The EBA is part of the EU Generalized System of Preferences (GSP). The up-to-date list of all countries benefiting from such preferential treatment is given in Annex IV of the consolidated text of Regulation (EU) 978/2012.
A free-trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occur when two countries agree to loosen trade restrictions between the two of them, generally to expand business opportunities. Multilateral trade agreements are agreements among three or more countries, and are the most difficult to negotiate and agree.
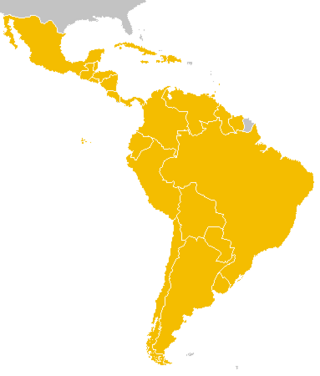
The Latin American and the Caribbean Economic System, officially known as Sistema Económico Latinoamericano y del Caribe (SELA), is an organization founded in 1975 to promote economic cooperation and social development between Latin American and the Caribbean countries. In the early 1990s, its representatives consisted of members from 28 countries and took part in the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) negotiations, which led to a new global agreement on restrictions on trade and established the World Trade Organization (WTO).

Historically speaking, bilateral relations between the various countries of Latin America and the United States of America have been multifaceted and complex, at times defined by strong regional cooperation and at others filled with economic and political tension and rivalry. Although relations between the U.S. government and most of Latin America were limited prior to the late 1800s, for most of the past century, the United States has unofficially regarded parts of Latin America as within its sphere of influence, and for much of the Cold War (1947–1991), actively vied with the Soviet Union for influence in the Western Hemisphere.

The Central American Integration System has been the economic and political organization of Central American states since 1 February 1993. On 13 December 1991, the ODECA countries signed the Protocol of Tegucigalpa, extending earlier cooperation for regional peace, political freedom, democracy and economic development. SICA's General Secretariat is in El Salvador.

The Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries(G.S.T.P) is a preferential trade agreement, currently encompassing 42 members (“participants”), signed on 13 April 1988 with the aim of increasing trade between developing countries. It was negotiated within the framework of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). The Agreement entered into force on 19 April 1989 and was notified to the then General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), predecessor of the World Trade Organization (WTO), on 25 September 1989. The 42 members of GSTP include as well 7 LDCs.

The free trade agreements of Canada represents Canada's cooperation in multinational trade pacts and plays a large role in the Canadian economy. Canada is regularly described as a trading nation, considering its total trade is worth more than two-thirds of its GDP. Of that total trade, roughly 75% is done with countries that are part of free trade agreements with Canada—primarily the United States through the Canada–United States–Mexico Agreement (CUSMA), and its predecessor the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). By the end of 2014, Canadas bilateral trade hit Can$1 trillion for the first time. Canada is a signatory to 15 free trade agreements with 51 different countries.

Costa Rica–Mexico relations are the diplomatic relations between Costa Rica and Mexico. Both nations are members of the Association of Caribbean States, Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.

The economy of Central America is the eleventh-largest economy in Latin America, behind Brazil, Mexico, Argentina and Colombia. According to the World Bank, the nominal GDP of Central America reached 204 billion US dollar in 2010, as recovery from the crisis of 2009, where gross domestic product (GDP) suffered a decline to 3.8%. The major economic sectors are agriculture and tourism, although the industrial sector has shown strong growth, mainly in Panama.

The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization which regulates international trade. The WTO officially commenced on 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement, signed by 123 nations on 15 April 1994, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which commenced in 1948. The WTO deals with regulation of trade between participating countries by providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements and a dispute resolution process aimed at enforcing participants' adherence to WTO agreements, which is signed by representatives of member governments and ratified by their parliaments. Most of the issues that the WTO focuses on derive from previous trade negotiations, especially from the Uruguay Round (1986–1994).
References
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/world/1999/mar/05/eu.wto3
- ↑ UNCTAD (2009), The EC banana regime, GATT/WTO challenges, and the evolving policy framework Archived 2009-09-26 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Official Journal of the European Union, Geneva Agreement on Trade in Bananas, 9 June 2010
