Related Research Articles
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), previously known as pseudotumor cerebri and benign intracranial hypertension, is a condition characterized by increased intracranial pressure without a detectable cause. The main symptoms are headache, vision problems, ringing in the ears, and shoulder pain. Complications may include vision loss.

Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure.
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide.
Primary aldosteronism (PA), also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, refers to the excess production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels and high blood pressure. This abnormality is a paraneoplastic syndrome. About 35% of the cases are caused by a single aldosterone-secreting adenoma, a condition known as Conn's syndrome.
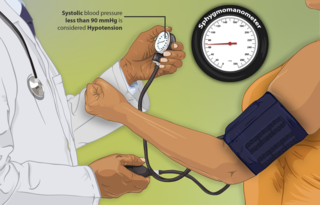
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure and the diastolic blood pressure, which are the maximum and minimum blood pressures within the cardiac cycle, respectively. A systolic blood pressure of less than 90 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or diastolic of less than 60 mmHg is generally considered to be hypotension. Different numbers apply to children. However, in practice, blood pressure is considered too low only if noticeable symptoms are present.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that a reduction of blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%. It can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers or antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fainting, tiredness, chest pain, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual. According to the definition at the 6th World Symposium of Pulmonary Hypertension in 2018, a patient is deemed to have pulmonary hypertension if the pulmonary mean arterial pressure is greater than 20mmHg at rest, revised down from a purely arbitrary 25mmHg, and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) greater than 3 Wood units.
Essential hypertension is a form of hypertension without an identifiable physiologic cause. It is the most common type affecting 85% of those with high blood pressure. The remaining 15% is accounted for by various causes of secondary hypertension. Essential hypertension tends to be familial and is likely to be the consequence of an interaction between environmental and genetic factors. Hypertension can increase the risk of cerebral, cardiac, and renal events.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. Because chlortalidone is effective in most patients with high blood pressure, it is considered a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days. Long-term treatment with chlortalidone is more effective than hydrochlorothiazide for prevention of heart attack or stroke.

Hypertensive kidney disease is a medical condition referring to damage to the kidney due to chronic high blood pressure. It manifests as hypertensive nephrosclerosis. It should be distinguished from renovascular hypertension, which is a form of secondary hypertension, and thus has opposite direction of causation.

Doxazosin, sold under the brand name Cardura among others, is a medication used to treat symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). For high blood pressure, it is a less preferred option. It is taken by mouth.
Alpha-1 blockers constitute a variety of drugs that block the effect of catecholamines on alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), hypertension and post-traumatic stress disorder. Alpha-1-adrenergic receptors are present in vascular smooth muscle, the central nervous system, and other tissues. When alpha blockers bind to these receptors in vascular smooth muscle, they cause vasodilation.

Arteriolosclerosis is a form of cardiovascular disease involving hardening and loss of elasticity of arterioles or small arteries and is most often associated with hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Types include hyaline arteriolosclerosis and hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis, both involved with vessel wall thickening and luminal narrowing that may cause downstream ischemic injury. The following two terms whilst similar, are distinct in both spelling and meaning and may easily be confused with arteriolosclerosis.

Renovascular hypertension is a condition in which high blood pressure is caused by the kidneys' hormonal response to narrowing of the arteries supplying the kidneys. When functioning properly this hormonal axis regulates blood pressure. Due to low local blood flow, the kidneys mistakenly increase blood pressure of the entire circulatory system. It is a form of secondary hypertension - a form of hypertension whose cause is identifiable.

Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a condition defined by an abnormal enlargement of the cardiac muscle surrounding the right ventricle. The right ventricle is one of the four chambers of the heart. It is located towards the right lower chamber of the heart and it receives deoxygenated blood from the right upper chamber and pumps blood into the lungs.
Medical terminology is a language used to precisely describe the human body including all its components, processes, conditions affecting it, and procedures performed upon it. Medical terminology is used in the field of medicine.
Prehypertension, also known as high normal blood pressure and borderline hypertensive (BH), is a medical classification for cases where a person's blood pressure is elevated above optimal or normal, but not to the level considered hypertension. Prehypertension is now referred to as "elevated blood pressure" by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA). The ACC/AHA define elevated blood pressure as readings with a systolic pressure from 120 to 129 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure under 80 mm Hg, Readings greater than or equal to 130/80 mm Hg are considered hypertension by ACC/AHA and if greater than or equal to 140/90 mm Hg by ESC/ESH. and the European Society of Hypertension defines "high normal blood pressure" as readings with a systolic pressure from 130 to 139 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure 85-89 mm Hg.

Alpha blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as antagonists on α-adrenergic receptors (α-adrenoceptors).
The modern history of hypertension begins with the understanding of the cardiovascular system based on the work of physician William Harvey (1578–1657), who described the circulation of blood in his book De motu cordis. The English clergyman Stephen Hales made the first published measurement of blood pressure in 1733. Descriptions of what would come to be called hypertension came from, among others, Thomas Young in 1808 and especially Richard Bright in 1836. Bright noted a link between cardiac hypertrophy and kidney disease, and subsequently kidney disease was often termed Bright's disease in this period. In 1850 George Johnson suggested that the thickened blood vessels seen in the kidney in Bright's disease might be an adaptation to elevated blood pressure. William Senhouse Kirkes in 1855 and Ludwig Traube in 1856 also proposed, based on pathological observations, that elevated pressure could account for the association between left ventricular hypertrophy to kidney damage in Bright's disease. Samuel Wilks observed that left ventricular hypertrophy and diseased arteries were not necessarily associated with diseased kidneys, implying that high blood pressure might occur in people with healthy kidneys; however, the first report of elevated blood pressure in a person without evidence of kidney disease was made by Frederick Akbar Mahomed in 1874 using a sphygmograph. The concept of hypertensive disease as a generalized circulatory disease was taken up by Sir Clifford Allbutt, who termed the condition "hyperpiesia". However, hypertension as a medical entity really came into being in 1896 with the invention of the cuff-based sphygmomanometer by Scipione Riva-Rocci in 1896, which allowed blood pressure to be measured in the clinic. In 1905, Nikolai Korotkoff improved the technique by describing the Korotkoff sounds that are heard when the artery is ausculted with a stethoscope while the sphygmomanometer cuff is deflated. Tracking serial blood pressure measurements was further enhanced when Donald Nunn invented an accurate fully automated oscillometric sphygmomanometer device in 1981.
Hypertensive disease of pregnancy, also known as maternal hypertensive disorder, is a group of high blood pressure disorders that include preeclampsia, preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, and chronic hypertension.
References
- ↑ McIver C (September 1964). "Blood pressure; a consideration of terminology". Can Med Assoc J. 91 (11): 578–80. PMC 1927435 . PMID 14175874.
- ↑ Beckman, Kenneth D. (March 2014). "How to document and code for hypertensive diseases in ICD-10". Family Practice Management. 21 (2): 5–9. ISSN 1531-1929. PMID 24693838.