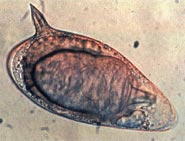
Schistosoma is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed schistosomiasis, which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease, with hundreds of millions infected worldwide.

Schistosoma mansoni is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (Schistosoma). The adult lives in the blood vessels near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis. Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 251.4 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to S. mansoni. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname.

Biomphalaria is a genus of air-breathing freshwater snails, aquatic pulmonates belonging to the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails and their allies.
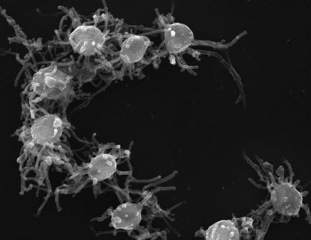
Capsaspora is a monotypic genus containing the single species Capsaspora owczarzaki. C. owczarzaki is a single-celled eukaryote that occupies a key phylogenetic position in our understanding of the origin of animal multicellularity, as one of the closest unicellular relatives to animals. It is, together with Ministeria vibrans, a member of the Filasterea clade. This amoeboid protist has been pivotal to unravel the nature of the unicellular ancestor of animals, which has been proved to be much more complex than previously thought.

Biomphalaria glabrata is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Biomphalaria tenagophila is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.
Biomphalaria smithi is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Biomphalaria straminea is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Biomphalaria pfeifferi is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic animal pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.
Biomphalaria andecola is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Biomphalaria peregrina is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.
Biomphalaria stanleyi is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Angiostrongylus vasorum, also known as French heartworm, is a species of parasitic nematode in the family Metastrongylidae. It causes the disease canine angiostrongylosis in dogs. It is not zoonotic, that is, it cannot be transmitted to humans.

Biomphalaria havanensis, common name the ghost rams-horn, is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Biomphalaria sudanica is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod belonging to the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails. Biomphalaria sudanica has a discoidal, brown shell with an approximate shell diameter of 9–11mm. Biomphalaria sudanica is a medically important pest, due to it being an intermediate host of the intravascular trematode genus, Schistosoma.
Biomphalaria kuhniana is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.

Indoplanorbis is a genus of air-breathing freshwater snail. Its only member species is Indoplanorbis exustus, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails. The species is widely distributed across the tropics. It serves as an important intermediate host for several trematode parasites. The invasive nature and ecological tolerance of Indoplanorbis exustus add to its importance in veterinary and medical science.
FMRFamide, a neuropeptide involved in cardiac activity regulation, is found in Biomphalaria glabrata, a species of a freshwater snail best known for its role as the intermediate host for the human-infecting trematode parasite Schistosoma mansoni.

Biomphalaria choanomphala is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails. Biomphalaria choanomphala has a discoidal, brownish-yellow shell with an approximate shell diameter of 6–10 mm. Biomphalaria choanomphala is a medically important pest, due to it being an intermediate host of the intravascular trematode genus, Schistosoma.












