This article is being considered for deletion in accordance with Wikipedia's deletion policy. |
| Bitcoin Private | |
|---|---|
| Ticker symbol | BTCP |
| Precision | 10−8 |
| Development | |
| Original author(s) | Bitcoin Private Community Jacob Brutman Christopher Sulmone Rhett Creighton |
| White paper | btcprivate |
| Initial release | 1.0.10 / 6 March 2018 |
| Latest release | 1.0.12-1 / 24 June 2018 |
| Code repository | github |
| Development status | Active |
| Forked from | Zclassic, Bitcoin |
| Written in | C++, Qt |
| Website | btcprivate |
| Ledger | |
| Ledger start | 2 March 2018 |
| Timestamping scheme | Proof-of-work |
| Hash function | Equihash |
| Issuance | Block reward |
| Block reward | 1.5625 BTCP, halving every 210,000 blocks or ~1 year [1] [2] |
| Block time | 2.5 minutes |
| Block explorer | explorer |
| Supply limit | 21,000,000 BTCP |
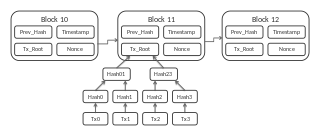
Bitcoin Private (BTCP) is an open-source, peer-to-peer cryptocurrency with the optional ability to keep the sender, receiver, and amount private in a given transaction. [1] [ non-primary source needed ] This is in contrast to many cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, which have a fully transparent transaction history. [3] [ irrelevant citation ] [4] [ irrelevant citation ] [5] [ irrelevant citation ]

Open-source software (OSS) is a type of computer software in which source code is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to study, change, and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes.

A cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses strong cryptography to secure financial transactions, control the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets. Cryptocurrencies use decentralized control as opposed to centralized digital currency and central banking systems.