
Brachypelma is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas). They may have bodies up to 6 cm long with legs of similar or greater lengths. Some species have brightly colored legs, with red or orange marks and rings.

Brachypelma klaasi is a tarantula endemic to Mexico and it is the rarest of the genus Brachypelma.

Brachypelma boehmei is a tarantula native to Mexico in Guerrero state. These long-lived tarantulas prefer burrowing and hiding in dry scrubland. As with all closely related tarantula species, they defend themselves with urticating hair when provoked.

Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. As of December 2023, 1,100 species have been identified, with 166 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although many other members of the same infraorder (Mygalomorphae) are commonly referred to as "tarantulas" or "false tarantulas". Some of the more common species have become popular in the exotic pet trade. Many New World species kept as pets have setae known as urticating hairs that can cause irritation to the skin, and in extreme cases, cause damage to the eyes.

Brachypelma albiceps is a species of spider in the tarantula family, Theraphosidae. It is known as the Mexican golden red rump tarantula or the Amula red rump tarantula. The carapace is a light golden color and the abdomen dark, covered with long red hairs. Females typically live for about 15 years. Males usually live about 5 years or up to 12 months after the last molt.
Cyclosternum is a genus of tarantulas that was first described by Anton Ausserer in 1871.
Brachypelma baumgarteni is a tarantula endemic to Pacific coast of Michoacan, Mexico.

The Stromatopelminae are a subfamily of tarantulas native to West Africa and part of Central Africa. The subfamily was first proposed by Günter Schmidt in 1993.
The Ischnocolinae are a problematic subfamily of tarantulas. In 1892, Eugène Simon based the group, which he noted was only weakly homogeneous, on the presence of divided tarsal scopulae. This feature was later considered to be plesiomorphic, and both morphological and molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that, as traditionally circumscribed, the subfamily is not monophyletic. A much more narrowly defined Ischnocolinae sensu stricto was proposed in 2014. One of the authors of that proposal subsequently said that no further taxonomic changes should be considered until there had been a more comprehensive sampling of the subfamily. As of January 2021, the status of the Ischnocolinae remains unresolved.

Davus, also known as the tiger rump tarantulas, is a genus of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas). It was formerly included in Cyclosternum. They are medium to large tarantulas, found in Central America and Mexico.
Crassicrus is a genus of Central and South American tarantulas that was first described by S. B. Reichling & R. C. West in 1996.
Hemirrhagus is a genus of Mexican tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1903. It is considered a senior synonym of Spelopelma. Species of the genus Hemirrhagus are 5 to 12 cm long, usually black in colour, the urticating hairs on the opisthosoma are arranged in one dorsomedian patch, two dorsal paramedian patches, or two lateral patches. It is unique amongst the theraphosine genera because of the retrolateral coxal heels, the shape of the male palpal bulb, and the urticating hairs on the abdomen are reduced or completely missing. It is the only genus with epigean, troglophile and troglobitic species.

Tliltocatl verdezi is a species of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas), found in Mexico.
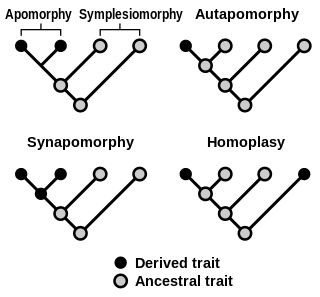
Homoplasy, in biology and phylogenetics, is the term used to describe a feature that has been gained or lost independently in separate lineages over the course of evolution. This is different from homology, which is the term used to characterize the similarity of features that can be parsimoniously explained by common ancestry. Homoplasy can arise from both similar selection pressures acting on adapting species, and the effects of genetic drift.

Avicularioidea is a clade of mygalomorph spiders, one of the two main clades into which mygalomorphs are divided. It has been treated at the rank of superfamily.

The Selenocosmiinae are a subfamily of tarantulas found throughout South-East Asia and Australia. This subfamily is defined by the presence of a lyra on the maxillae and strikers on the chelicerae, allowing these spiders to stridulate and produce a "hissing" sound. However some species within Phlogiellus may have secondary lost their lyra but retain their strikers. The monophyly of the subfamily has been only tested using genetic data with a handful of genera or species in a few studies. However, these studies found genera that had been previously placed in this subfamily were actual their own separate subfamily (Poecilotheria) and that Selenocosmiinae is most closely related to the Indian Thrigmopoeinae. As of 2021, Selenocosmiinae contains 11 genera.

Bonnetina cyaneifemur, also known as the Mexican blue femur, is a species of tarantula from the genus Bonnetina. It was first described in 2000 by Fabian Vol.

Tliltocatl is a genus of North American tarantulas that was split off from Brachypelma in 2020. They are also large burrowing tarantulas, but don't have the striking red leg markings of Brachypelma species. A female T. vagans can grow up to 50 mm (2.0 in) long and legs can get as long as 55 mm (2.2 in). They are found predominantly in Mexico, with some species native to Central America. The name is derived from two Nahuatl words, "tlil", meaning "black", and "tocatl", meaning "spider". Habitat destruction and collection for the pet trade has led to this and Brachypelma to be protected under International Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species rules, beginning with B. smithi.
Bonnetina minax also known as Mexican copperhead tarantula, is a tarantula which was first described by David Ortiz and Oscar F. Francke in 2017. It is found in Mexico, in the state of Michoacán, and is named after the Latin adjective "minax" that means menacing, as the red found in is carapace is usually aposematic coloration.













