Related Research Articles

Boron is a chemical element. It has the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride.
In materials science, a metal matrix composite (MMC) is a composite material with fibers or particles dispersed in a metallic matrix, such as copper, aluminum, or steel. The secondary phase is typically a ceramic or another metal. They are typically classified according to the type of reinforcement: short discontinuous fibers (whiskers), continuous fibers, or particulates. There is some overlap between MMCs and cermets, with the latter typically consisting of less than 20% metal by volume. When at least three materials are present, it is called a hybrid composite. MMCs can have much higher strength-to-weight ratios, stiffness, and ductility than traditional materials, so they are often used in demanding applications. MMCs typically have lower thermal and electrical conductivity and poor resistance to radiation, limiting their use in the very harshest environments.

A composite material is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called composite laminates.
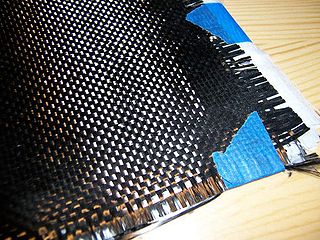
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres are fibers about 5 to 10 micrometers (0.00020–0.00039 in) in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber, basalt fibers, or plastic fibers.
Fiberglass or fibreglass is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic matrix may be a thermoset polymer matrix—most often based on thermosetting polymers such as epoxy, polyester resin, or vinyl ester resin—or a thermoplastic.

Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders, as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hardness of >30 GPa, it is one of the hardest known materials, behind cubic boron nitride and diamond.
A superhard material is a material with a hardness value exceeding 40 gigapascals (GPa) when measured by the Vickers hardness test. They are virtually incompressible solids with high electron density and high bond covalency. As a result of their unique properties, these materials are of great interest in many industrial areas including, but not limited to, abrasives, polishing and cutting tools, disc brakes, and wear-resistant and protective coatings.

Tantalum carbides (TaC) form a family of binary chemical compounds of tantalum and carbon with the empirical formula TaCx, where x usually varies between 0.4 and 1. They are extremely hard, brittle, refractory ceramic materials with metallic electrical conductivity. They appear as brown-gray powders, which are usually processed by sintering.

Maraging steels are steels that are known for possessing superior strength and toughness without losing ductility. Aging refers to the extended heat-treatment process. These steels are a special class of very-low-carbon ultra-high-strength steels that derive their strength not from carbon, but from precipitation of intermetallic compounds. The principal alloying element is 15 to 25 wt% nickel. Secondary alloying elements, which include cobalt, molybdenum and titanium, are added to produce intermetallic precipitates.
Basalt fibers are produced from basalt rocks by melting them and converting the melt into fibers. Basalts are rocks of igneous origin. The main energy consumption for the preparation of basalt raw materials to produce of fibers is made in natural conditions. Basalt fibers are classified into 3 types: Basalt continuous fibers (BCF), used for the production of reinforcing materials and composite products, fabrics, and non-woven materials; Basalt staple fibers, for the production of thermal insulation materials; and Basalt superthin fibers (BSTF), for the production of high quality heat- and sound-insulating and fireproof materials.
Specific modulus is a materials property consisting of the elastic modulus per mass density of a material. It is also known as the stiffness to weight ratio or specific stiffness. High specific modulus materials find wide application in aerospace applications where minimum structural weight is required. The dimensional analysis yields units of distance squared per time squared. The equation can be written as:

Filler materials are particles added to resin or binders that can improve specific properties, make the product cheaper, or a mixture of both. The two largest segments for filler material use is elastomers and plastics. Worldwide, more than 53 million tons of fillers are used every year in application areas such as paper, plastics, rubber, paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. As such, fillers, produced by more than 700 companies, rank among the world's major raw materials and are contained in a variety of goods for daily consumer needs. The top filler materials used are ground calcium carbonate (GCC), precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), kaolin, talc, and carbon black.

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter along with liquid, gas, and plasma. The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice, or irregularly. Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed.

Structural engineering depends on the knowledge of materials and their properties, in order to understand how different materials resist and support loads.

In materials science ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) are a subgroup of composite materials and a subgroup of ceramics. They consist of ceramic fibers embedded in a ceramic matrix. The fibers and the matrix both can consist of any ceramic material, including carbon and carbon fibers.
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers, carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic, also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications.
In materials science, advanced composite materials (ACMs) are materials that are generally characterized by unusually high strength fibres with unusually high stiffness, or modulus of elasticity characteristics, compared to other materials, while bound together by weaker matrices. These are termed "advanced composite materials" in comparison to the composite materials commonly in use such as reinforced concrete, or even concrete itself. The high strength fibers are also low density while occupying a large fraction of the volume.
Laser chemical vapor deposition (LCVD) is a chemical process used to produce high purity, high performance films, fibers, and mechanical hardware (MEMS). It is a form of chemical vapor deposition in which a laser beam is used to locally heat the semiconductor substrate, causing the vapor deposition chemical reaction to proceed faster at that site. The process is used in the semiconductor industry for spot coating, the MEMS industry for 3-D printing of hardware such as springs and heating elements,2,6,7,9 and the composites industry for boron and ceramic fibers. As with conventional CVD, one or more gas phase precursors are thermally decomposed, and the resulting chemical species 1) deposit on a surface, or 2) react, form the desired compound, and then deposit on a surface, or a combination of (1) and (2).
Advanced thermoplastic composites (ACM) have a high strength fibres held together by a thermoplastic matrix. Advanced thermoplastic composites are becoming more widely used in the aerospace, marine, automotive and energy industry. This is due to the decreasing cost and superior strength to weight ratios, over metallic parts. Advance thermoplastic composite have excellent damage tolerance, corrosion resistant, high fracture toughness, high impact resistance, good fatigue resistance, low storage cost, and infinite shelf life. Thermoplastic composites also have the ability to be formed and reformed, repaired and fusion welded.
Hy-Bor is a trademarked brand of hybrid composite materials that combines boron fiber and carbon fiber in a unidirectional prepreg. The portfolio was introduced to the commercial market in 1993 by Textron Specialty Materials and currently marketed by Specialty Materials. The material's unique combination of constituent properties for fiber-reinforced composites has led to adoption in aerospace, sporting goods, and space applications.
References
- ↑ Herring, H. W. (1966). "Selected Mechanical and Physical Properties of Boron Filaments" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved September 20, 2008.
- ↑ Layden, G. K. (1973). "Fracture behaviour of boron filaments". Journal of Materials Science. 8 (11): 1581–1589. Bibcode:1973JMatS...8.1581L. doi:10.1007/BF00754893. S2CID 136959123.
- ↑ "Boron fiber: The original high-performance fiber". www.compositesworld.com. Retrieved February 26, 2021.
- ↑ Kostick, Dennis S. (2006). "Mineral Yearbook: Boron" (PDF). United States Geological Survey . Retrieved September 20, 2008.
- ↑ Cooke, Theodore F. (1991). "Inorganic Fibers—A Literature Review". Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 74 (12): 2959–2978. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1991.tb04289.x.
- ↑ "Boron Fiber". Specialty Materials. Archived from the original on August 12, 2014.
- ↑ Johansson, S.; Schweitz, Jan-Åke; Westberg, Helena; Boman, Mats (1992). "Microfabrication of three-dimensional boron structures by laser chemical processing". Journal of Applied Physics. 72 (12): 5956–5963. Bibcode:1992JAP....72.5956J. doi:10.1063/1.351904.