Down bow
Three notes with down-bow marks
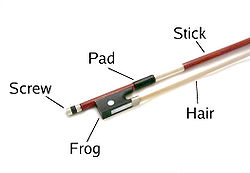
A down-bow is a type of stroke used when bowing a musical instrument, most often a string instrument. The player performs the indicated note by drawing the bow downward or to the right across the instrument, moving its point of contact from the frog toward the tip of the bow. This technique is indicated by a notated symbol resembling a small bracket over the note. [1] [2]
Instruments
How the down-bow is achieved varies depending on the shape and orientation of the instrument. On violin and viola, the player pulls the bow down, away from the left shoulder. On cello and double bass, the player pulls the bow to the right, away from the left elbow.
Uses
String players can exert stronger pressure when bowing near the frog than when bowing near the tip, due to the bowing hand's proximity to the bow's contact point with the string. Down-bows, which begin near the frog, are therefore often used to play the downbeat (strong beat) within musical phrases. Notes that begin loudly and diminuendo are ideally down-bowed — from frog to tip — allowing pressure on the string to decrease naturally.
Up bow
Three notes with up-bow marks
An up-bow is a type of stroke used when bowing a musical instrument, most often a string instrument. The player draws the bow upward or to the left across the instrument, moving the point of contact from the bow's tip toward the frog (the end of the bow held by the player). [3] [2]
Instruments
How the up-bow is achieved varies depending on the shape and orientation of the instrument. On violin and viola, the player pushes the bow up, toward the left shoulder. On cello and double bass, the player pushes the bow to the left, toward the left elbow.
Uses
String players can exert stronger pressure on the string when bowing near the frog than when bowing near the tip, due to the bowing hand's proximity to the bow's contact point with the string. Up-bows, which begin near the tip, are therefore often used to play the upbeats (weaker beats) within a musical phrase. Notes that begin quietly and crescendo are also ideally up-bowed — from tip to frog — allowing pressure on the string to increase naturally.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.