The Bristol Aeroplane Company, originally the British and Colonial Aeroplane Company, was both one of the first and one of the most important British aviation companies, designing and manufacturing both airframes and aircraft engines. Notable aircraft produced by the company include the 'Boxkite', the Bristol Fighter, the Bulldog, the Blenheim, the Beaufighter, and the Britannia, and much of the preliminary work which led to Concorde was carried out by the company. In 1956 its major operations were split into Bristol Aircraft and Bristol Aero Engines. In 1959, Bristol Aircraft merged with several major British aircraft companies to form the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC) and Bristol Aero Engines merged with Armstrong Siddeley to form Bristol Siddeley.

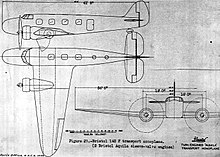
The Bristol Blenheim is a British light bomber designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company, which was used extensively in the first two years of the Second World War, with examples still being used as trainers until the end of the war. Development began with the Type 142, a civil airliner, after a challenge from the newspaper proprietor Lord Rothermere to produce the fastest commercial aircraft in Europe. The Type 142 first flew in April 1935, and the Air Ministry, ordered a modified design as the Type 142M for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a bomber.

The Bristol Bombay was a British troop transport aircraft adaptable for use as a medium bomber flown by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the Second World War.

The Bristol Buckmaster was an advanced British training aircraft operated by the Royal Air Force during the 1950s.

The Bristol Bulldog is a British Royal Air Force single-seat biplane fighter designed during the 1920s by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. More than 400 Bulldogs were produced for the RAF and overseas customers, and it was one of the most famous aircraft used by the RAF during the inter-war period.
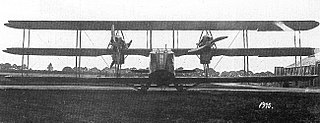
The Bristol Braemar was a British heavy bomber aircraft developed at the end of the First World War for the Royal Air Force. Only two prototypes were constructed.

The Bristol Pullman was a British prototype passenger aircraft developed from the Braemar triplane heavy bomber.
The Bristol Tramp was a British steam-powered passenger and airmail transport aircraft designed by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. It was built but never flew.

The Bristol Type 138 High Altitude Monoplane was a British high-altitude single-engine, low-wing monoplane research aircraft developed and produced by the Bristol Aeroplane Company during the 1930s. It set nine world altitude records, with the maximum altitude achieved being 53,937 ft (16,440 m) on 30 June 1937, during a 2¼-hour flight.

The Bristol M.1 Monoplane Scout was a British monoplane fighter of the First World War. It holds the distinction of being the only British monoplane fighter to reach production during the conflict.

The Bristol T.B.8, or Bristol-Coanda T.B.8 was an early British biplane built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company and designed by the Romanian Henri Coandă. Fifty four Bristol T.B.8s were built, being mainly used as a trainer. A small number of Bristol T.B.8s were briefly used as bombers at the start of the World War I by the Royal Naval Air Service.

The Bristol Ten-seater and Bristol Brandon were British single-engine biplane transport aircraft built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in the early 1920s. Only three were built, two of which were used as civil transports and one of which served with the Royal Air Force.

The Bristol Bloodhound was a British two-seat reconnaissance/fighter aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company as a possible replacement for the Bristol F.2 Fighter for the Royal Air Force. It was unsuccessful, only four prototypes being built.
The Bristol Type 91 Brownie was a light sports aircraft produced in the United Kingdom by the Bristol Aeroplane Company in 1924. It was a low-wing cantilever monoplane aircraft of conventional configuration with fixed tailskid undercarriage. The pilot and passenger sat in tandem open cockpits. It won the £1,000 pound prize for second place at the Lympne light aircraft trials in October 1924.

The Bristol Bullfinch was an experimental British military aircraft first flown in 1922. Variants were built as both parasol wing monoplanes and biplanes, but both versions proved unsuccessful, and only the three prototypes were built.

The Bristol Type 107 Bullpup was a British fighter aircraft built in the 1920s. It was not selected for squadron service and only the single prototype was built
Sir Archibald Russell, CBE, FRS was a British aerospace engineer who worked most of his career at the Bristol Aeroplane Company, before becoming managing director of the Filton Division when Bristol merged into British Aircraft Corporation in 1960. He also served as the vice-chairman of the BAC-Sud Aviation Concorde Committee that produced the Concorde, working alongside Morien Morgan. His designs include the Blenheim, Britannia, Type 188 and many others. He was known throughout his career as a perfectionist, as well as his criticism for those who did not measure up – criticisms that included ministers, civil servants, the Brabazon Committee and BOAC.

The Bristol Babe was a British-built light single-seat biplane, intended for the private flyer and produced immediately after the First World War. Only two flew.

The Bristol B.R.7 was a Romanian-designed single-engine two-seat biplane built by Bristol to a Spanish government order in 1913. It failed to meet its specifications and the order was cancelled.

The Bristol Scout E and F were a British single-seat biplane fighters built in 1916 to use newer and more powerful engines. It was initially powered by the Sunbeam Arab, but the third prototype was used as a testbed for the Cosmos Mercury, marking the start of Roy Fedden's association with the Bristol Aeroplane Company. The Armistice ended hopes of production.