
The Airspeed AS.57 Ambassador is a British twin piston-engined airliner that was designed and produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Airspeed Ltd. It was one of the first postwar airliners to be produced.

The Bristol Type 170 Freighter is a British twin-engine aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company as both a freighter and airliner. Its best known use was as an air ferry to carry cars and their passengers over relatively short distances. A passenger-only version was also produced, known as the Wayfarer.

The Aviation Traders ATL-98 Carvair is a retired large transport aircraft powered by four radial engines. It was a Douglas DC-4-based air ferry conversion developed by Freddie Laker's Aviation Traders (Engineering) Limited (ATL), with a capacity generally of 22 passengers in a rear cabin, and five cars loaded in at the front.

The Avro 691 Lancastrian was a British and Canadian passenger and mail transport aircraft of the 1940s and 1950s developed from the Avro Lancaster heavy bomber. The Lancastrian was basically a modified Lancaster bomber without armour or armament and with the gun turrets replaced by streamlined metal fairings, including a new nose section. The initial batch was converted directly from Lancasters; later batches were new builds.

The Zivko Edge 540 manufactured by Zivko Aeronautics is a highly aerobatic aircraft. Capable of a 420 degree per second roll rate and a 3,700 foot per minute climb rate, it has been flown to victory on the international Unlimited aerobatics circuit several times since the mid-1990s. A tandem-seat version is sold as the Edge 540T.

The SAI KZ III Lærke ("lark") was a Danish light utility aircraft used by the Danish Air Ambulance Service and Danish Air Force.

The Noorduyn Norseman, also known as the C-64 Norseman, is a Canadian single-engine bush plane designed to operate from unimproved surfaces. Distinctive stubby landing gear protrusions from the lower fuselage make it easily recognizable.

The Handley Page HPR.7 Dart Herald is a British turboprop passenger aircraft, designed in the 1950s as a DC-3 replacement, but only entering service in the 1960s by which time it faced stiff competition from Fokker and Avro. Sales were disappointing, contributing in part to the demise of Handley Page in 1970.

The de Havilland DH.91 Albatross was a four-engined British transport aircraft of the 1930s manufactured by de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited. Seven aircraft were built between 1938 and 1939.
British United Air Ferries (BUAF) was a wholly private, British independent car and passenger ferry airline based in the United Kingdom during the 1960s. It specialised in cross-Channel ferry flights carrying cars and their owners between its numerous bases in Southern England, the Channel Islands and Continental Europe. All-passenger and all-cargo flights were operated as well. Following several identity and ownership changes, it went out of business in 2001.
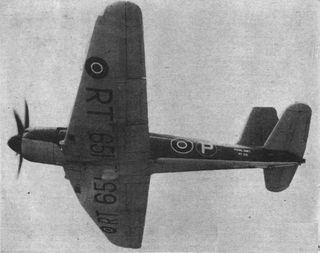
The Blackburn B.48 Firecrest, given the SBAC designation YA.1, was a single-engine naval strike fighter built by Blackburn Aircraft for service with the British Fleet Air Arm during the Second World War. It was a development of the troubled Firebrand, designed to Air Ministry Specification S.28/43, for an improved aircraft more suited to carrier operations. Three prototypes were ordered with the company designation of B-48 and the informal name of "Firecrest", but only two of them actually flew. The development of the aircraft was prolonged by significant design changes and slow deliveries of components, but the determination by the Ministry of Supply in 1946 that the airframe did not meet the requirements for a strike fighter doomed the aircraft. Construction of two of the prototypes was continued to gain flight-test data and the third was allocated to strength testing. The two flying aircraft were sold back to Blackburn in 1950 for disposal and the other aircraft survived until 1952.

The Piaggio P.166 is an Italian twin-engine pusher-type utility aircraft developed by Piaggio Aero. The aircraft model name was Portofino, and is also known as Albatross in South African military service.
The Auster Avis was a four-seat light aircraft developed from the Auster Autocrat. It featured a redesigned fuselage incorporating four doors and a circular cross-section towards the tail, new undercarriage, and new wing flaps. It was planned in two versions, the Mk 1 for civil use, and the Mk 2 for military and air ambulance duties. However, only two prototypes were built, and Auster abandoned the project in favour of the Auster J-5 Autocar.

The Zlin Z-526 Akrobat is a Czech sports plane used in aerobatics.

The M 17 was a German single-engine high-wing sports monoplane. It was designed by Willy Messerschmitt in 1925 in Bamberg. This aircraft won many competitions and allowed Willy Messerschmitt to build his first factory.

The HAL HT-2 is an Indian two-seat primary trainer designed and built by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The HT-2 was the first company design to enter production in 1953 for the Indian Air Force and Navy, where it replaced the de Havilland Tiger Moth. The HT-2 is a low-wing cantilever monoplane with a fixed tailwheel landing gear. Powered by a 155 hp (116 kW) Cirrus Major III piston engine, the aircraft has enclosed tandem cockpits with dual controls. Apart from military use, the aircraft was also used by Indian flying schools.

The SAI KZ VII Lærke was a light utility aircraft built in Denmark shortly after the Second World War. Based on the SAI KZ III air ambulance, the KZ VII was a strut-braced, high-wing monoplane of conventional design with an enclosed cabin for four seats. Fifty-six aircraft were built, and another 22 partially completed aircraft were destroyed in a factory fire in 1947. The Danish Air Force operated 10 of the type as trainers between 1950 and 1977.
The Harmon Der Donnerschlag is an American homebuilt aircraft that was designed and produced by Harmon Engineering of Howe, Texas. The aircraft was intended for amateur construction.
The Bagalini Colombo is an Italian homebuilt aircraft that was designed by Marino Bagalini. The aircraft is supplied in the form of plans for amateur construction.

The Tri-R KIS TR-1 is an American homebuilt aircraft that was designed by Rich Trickel and produced by Tri-R Technologies of Oxnard, California, introduced in the 1990s. When it was available the aircraft was supplied as a kit for amateur construction.

















