Buckhorn Springs, Oregon | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 42°06′19″N122°31′54″W / 42.10528°N 122.53167°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Oregon |
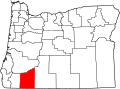
| County | Jackson |
| Elevation | 2,661 ft (811 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (Pacific (PST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| GNIS feature ID | 1637989 [1] |
| Coordinates and elevation from Geographic Names Information System [1] | |
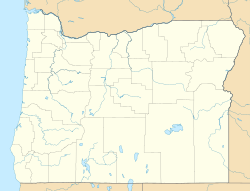
Buckhorn Springs is an unincorporated community in Jackson County, Oregon, United States. [1] It lies along Emigrant Creek in the Siskiyou Mountains southeast of Ashland. [2] Buckhorn Springs Road connects the community to Oregon Route 66 near Emigrant Lake. [3]
The springs at this location are known for their cold, highly carbonated water. James C. Tolman, who acquired the property around the springs in the 1890s, built a small hotel here called Tolman Springs. Subsequent owners used the property, springs, and buildings in various ways: as a hunting retreat called Buckhorn Lodge; as a picnic stop for tourists who sometimes used the carbonated water to make soda pop; as a retreat with overnight cabins and mineral mud baths; as a health spa, as a private residence; as an inn, and after 1998 as the Buckhorn Springs Retreat Center. [4]
Buckhorn Mineral Springs Resort was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989. The site covers 95 acres (38 ha) and includes many structures in addition to the main lodge. [5]