
Prince Edward Island is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation". Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces.

The American bison or simply bison, is an American species of bison that once roamed North America in vast herds. Bison are often mistakenly called buffalo, but the two are separate and distinct animals. There are two types of bison: the American bison and the European bison; and two types of buffalo: the African buffalo, native to Africa, and the water buffalo, native to Asia. Its historical range, by 9000 BC, is described as the great bison belt, a tract of rich grassland that ran from Alaska to the Gulf of Mexico, east to the Atlantic Seaboard as far north as New York and south to Georgia and, according to some sources, further south to Florida, with sightings in North Carolina near Buffalo Ford on the Catawba River as late as 1750. It nearly became extinct by a combination of commercial hunting and slaughter in the 19th century and introduction of bovine diseases from domestic cattle. With a population in excess of 60 million in the late 18th century, the species was down to just 541 animals by 1889. Recovery efforts expanded in the mid-20th century, with a resurgence to roughly 31,000 wild bison today, largely restricted to a few national parks and reserves. Through multiple reintroductions, the species is now also freely roaming wild in some regions in the United States, Canada, and Mexico, with it also being introduced to Yakutia in Russia.

Prince Edward Island National Park is a National Park of Canada located in the province of Prince Edward Island. Situated along the island's north shore, fronting the Gulf of St. Lawrence, the park measures approximately 60 km (37 mi) in length and ranges from several hundred metres to several kilometres in width. Established in 1937, the park's mandate includes the protection of many broad sand beaches, sand dunes and both freshwater wetlands and saltmarshes. The park's protected beaches provide nesting habitat for the endangered piping plover; the park has been designated a Canadian Important Bird Area.

Elk Island National Park is a national park in Alberta, Canada, that played an important part in the conservation of the Plains bison. The park is administered by the Parks Canada Agency. This "island of conservation" is 35 km (22 mi) east of Edmonton, along the Yellowhead Highway, which goes through the park. It is Canada's eighth smallest in area but largest fully enclosed national park, with an area of 194 km2 (75 sq mi).

Wood Buffalo National Park is the largest national park of Canada at 44,807 km2 (17,300 sq mi). It is located in northeastern Alberta and the southern Northwest Territories. Larger in area than Switzerland, it is the second-largest national park in the world. The park was established in 1922 to protect the world's largest herd of free-roaming wood bison. They became hybridized after the introduction of plains bison. The population is currently estimated at about 3,000. It is one of two known nesting sites of whooping cranes.
Patrick George Binns, is a Canadian diplomat, the 30th premier of Prince Edward Island from 1996 to 2007 and Canadian Ambassador to Ireland from 2007 to 2010.

Grasslands National Park is a Canadian national park located near the village of Val Marie, Saskatchewan, and one of 44 national parks and park reserves in Canada's national park system. This national park is north of the U.S. state of Montana and lies adjacent to the international boundary.

Holland College is the provincial community college for the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island (PEI). It is named after British Army engineer and surveyor Captain Samuel Holland. It was formed by the Government of Prince Edward Island in 1969 as a result of an education reform policy undertaken as part of the Prince Edward Island Comprehensive Development Plan which saw the closure of the province's two post-secondary institutions structured on religious lines, St. Dunstan's University and Prince of Wales College, and the creation of the non-denominational University of Prince Edward Island (UPEI) and Holland College.

Antelope Island, with an area of 42 square miles (109 km2), is the largest of ten islands located within the Great Salt Lake in the US state of Utah. The island lies in the southeastern portion of the lake, near Salt Lake City and Davis County, and becomes a peninsula when the lake is at extremely low levels. It is protected as Antelope Island State Park.

The wood bison or mountain bison, is a distinct northern subspecies or ecotype of the American bison. Its original range included much of the boreal forest regions of Alaska, Yukon, western Northwest Territories, northeastern British Columbia, northern Alberta, and northwestern Saskatchewan.

The Plains bison is one of two subspecies/ecotypes of the American bison, the other being the wood bison. A natural population of Plains bison survives in Yellowstone National Park and multiple smaller reintroduced herds of bison in many places in the United States as well as southern portions of the Canadian Prairies.

Brudenell River Provincial Park is a provincial park in Prince Edward Island, Canada. It lies on the north side of the Brudenell River. Brudenell River is the largest provincial park in eastern Prince Edward Island. Some of its land is used by Rodd Brudenell Resort. It has two public 18-hole golf courses, Brudenell River Golf Course and Dundarave Golf Course.

Green Park Provincial Park is a provincial park in Prince Edward Island, Canada. It is located on the western shore of Malpeque Bay. It is the site of a former shipyard; in the 19th century, ship building was a major industry on Prince Edward Island. The province acquired the land in the 1960s. It is home to the Green Park Shipbuilding Museum and Yeo House, the historic home of a shipping magnate.

Panmure Island Provincial Park is a provincial park in Prince Edward Island, Canada. It is located along a causeway connecting Prince Edward Island with Panmure Island. The Native Council of Prince Edward Island hosts their annual Abegweit Pow Wow in the park.
The politics of Prince Edward Island are centred on a provincial government resembling that of the other Canadian provinces. The capital of the province of Prince Edward Island is Charlottetown, where the lieutenant governor and the premier reside, and the provincial legislature, and cabinet are located.

Buffalo National Park was created near the town of Wainwright in east central Alberta on June 5, 1909. It was closed in 1940 and delisted in 1947 when the land was transferred to the Department of National Defence. The 583 km2 (225 sq mi) park land was developed for use by Canadian Forces Base Wainwright and comprises the majority of its space. The first Park Warden was Bud Cotton, who served from 1912 through 1940.

Baseball PEI is the provincial governing body for baseball in Prince Edward Island. It is a member of Baseball Canada and Baseball Atlantic.

The Wind Cave bison herd is a herd of 250–400 American bison in Wind Cave National Park, South Dakota, United States. As an active participant in the conservation of American bison, it is believed to be one of only seven free-roaming and genetically pure herds on public lands in North America. The other six herds are in Yellowstone Park, Theodore Roosevelt National Park, Henry Mountains, Blue Mounds State Park (Minnesota), Minneopa State Park (Minnesota), and Elk Island National Park. The Wind Cave herd are of the Plains bison subspecies.
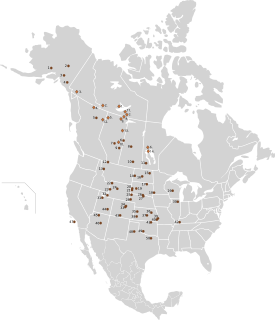
Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, the plains bison and wood bison in Canada were hunted by nomadic indigenous hunters and white hunters alike. By the 1850s, the bison was nearly extinct, spurring a movement to save the few herds that remained. Federal government wildlife policy evolved from preservation of wilderness to utilitarian, scientific conservation and management of bison populations. The goals of these policies were often contradictory: to simultaneously preserve wildlife, promote recreation, commercialize the bison, and assert state control over Aboriginal Canadians. Bison conservation efforts were shaped by the federal government's colonialist and modernist approach to Canada's North, the management of national parks and reserves, and the influence of scientific knowledge.
The conservation of bison in North America is an ongoing, diverse effort to bring American bison back from the brink of extinction. Plains bison, a subspecies, are a keystone species in the North American Great Plains. Bison are a species of conservation concern in part because they suffered a severe population bottleneck at the end of the 19th century. The near decimation of the species during the 1800s unraveled fundamental ties between bison, grassland ecosystems, and indigenous peoples’ cultures and livelihoods. English speakers used the word buffalo for this animal when they arrived. Bison was used as the scientific term to distinguish them from the true buffalo. Buffalo is commonly used as it continues to hold cultural significance, particularly for Indigenous people. Recovery began in the late 1800s with a handful of individuals independently saving the last surviving bison. Dedicated restoration efforts in the 1900s bolstered bison numbers though they still exist in mostly small and isolated populations. Expansion of the understanding of bison ecology and management is ongoing.
The buffalo that reside at Buffaloland park in the Kings county region of PEI were originally a gift from the province of Alberta in the 1970s. Currently there are between 50 and 60 buffalo that roam the 40 hectare fenced area. The park was run by the provincial government but is now run by the Moonlight Society, a buddhist organization.
















