
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver and are a major component of human skin oils.

Heptane or n-heptane is the straight-chain alkane with the chemical formula H3C(CH2)5CH3 or C7H16. When used as a test fuel component in anti-knock test engines, a 100% heptane fuel is the zero point of the octane rating scale (the 100 point is 100% iso-octane). Octane number equates to the anti-knock qualities of a comparison mixture of heptane and iso-octane which is expressed as the percentage of iso-octane in heptane, and is listed on pumps for gasoline (petrol) dispensed globally.

Propionic acid is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH
3CH
2CO
2H. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion CH
3CH
2CO−
2 as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates.

A drying oil is an oil that hardens to a tough, solid film after a period of exposure to air, at room temperature. The oil hardens through a chemical reaction in which the components crosslink by the action of oxygen. Drying oils are a key component of oil paint and some varnishes. Some commonly used drying oils include linseed oil, tung oil, poppy seed oil, perilla oil, castor oil and walnut oil. The use of natural drying oils has declined over the past several decades, as they have been replaced by alkyd resins and other binders.

Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually.

Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).

The bioconversion of biomass to mixed alcohol fuels can be accomplished using the MixAlco process. Through bioconversion of biomass to a mixed alcohol fuel, more energy from the biomass will end up as liquid fuels than in converting biomass to ethanol by yeast fermentation.

In fire protection, an accelerant is any substance or mixture that accelerates or speeds the development and escalation of fire. Accelerants are often used to commit arson, and some accelerants may cause an explosion. Some fire investigators use the term "accelerant" to mean any substance that initiates and promotes a fire without implying intent or malice. The accelerant works by burning rapidly. As such, the accelerant itself is consumed in the process, and should not be considered as a catalyst. In Arson investigation, the significance of accelerant is to detect the presence of a such substance in order to proved that the fire is classified as an arson.
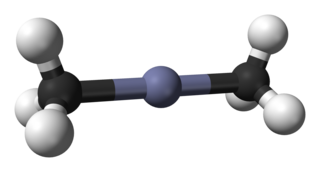
Dimethylzinc, also known as zinc methyl, DMZ, or DMZn, is a toxic organozinc compound with the chemical formula Zn(CH3)2. It belongs to the large series of similar compounds such as diethylzinc.
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC.
Propyl propanoate (also known as propyl propionate and n-propyl propionate) is the organic compound with the molecular formula C6H12O2. It is the ester of propanol and propionic acid. Like most esters, propyl propanoate is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor. The scent of propyl propionate is described as a chemically tinged pineapple or pear. It is used in perfumery and as a solvent. The refractive index at 20 °C is 1.393.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.

Ethyl propionate is an organic compound with formula C2H5O2CCH2CH3. It is the ethyl ester of propionic acid. It is a colorless volatile liquid with a pineapple-like odor. Some fruits such as kiwis and strawberries contain ethyl propionate in small amounts.
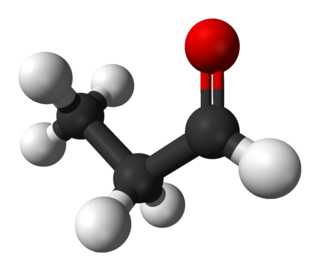
Propionaldehyde or propanal is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CHO. It is the 3-carbon aldehyde. It is a colourless, flammable liquid with a pungent and fruity odour. It is produced on a large scale industrially.

Methyl propionate, also known as methyl propanoate, is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CH2CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid with a fruity, rum-like odor.

Dibutyltin dilaurate is an organotin compound with the formula (CH310CO2)2Sn(CH2CH2CH2CH3)2. It is a colorless viscous and oily liquid. It is used as a catalyst.
Butyl acrylate is an organic compound with the formula C4H9O2CCH=CH2. A colorless liquid, it is the butyl ester of acrylic acid. It is used commercially on a large scale as a precursor to poly(butyl acrylate). Especially as copolymers, such materials are used in paints, sealants, coatings, adhesives, fuel, textiles, plastics, and caulk.

Vinyl propionate is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CO2CH=CH2. This colorless liquid is the ester of propionic acid and vinyl alcohol. It is used to produce poly(vinyl propionate) as well as copolymers with acrylate esters, vinyl chloride, and vinyl acetate, some of which are used in paints. The compound resembles vinyl acetate.

















