
Protein YIF1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YIF1A gene.
C20orf96 is a protein-coding gene in humans. It codes for an unknown protein known as uncharacterized protein C20orf96, predicted to be a nuclear protein. The function and biological processes of the gene is not well understood by the scientific community yet.

C8orf48 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf48 gene. C8orf48 is a nuclear protein specifically predicted to be located in the nuclear lamina. C8orf48 has been found to interact with proteins that are involved in the regulation of various cellular responses like gene expression, protein secretion, cell proliferation, and inflammatory responses. This protein has been linked to breast cancer and papillary thyroid carcinoma.

PRR29 is a protein located on human chromosome 17 that in humans is encoded by the PRR29 gene.
Coiled-coil domain containing protein 180 (CCDC180) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC180 gene. This protein is known to localize to the nucleus and is thought to be involved in regulation of transcription as are many proteins containing coiled-coil domains. As it is expressed most highly in the testes and is regulated by SRY and SOX transcription factors, it could be involved in sex determination.

Uncharacterized protein C2orf73 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C2orf73 gene. The protein is predicted to be localized to the nucleus.

C17orf53 is a gene in humans that encodes a protein known as C17orf53, uncharacterized protein C17orf53. It has been shown to target the nucleus, with minor localization in the cytoplasm. Based on current findings C17orf53 is predicted to perform functions of transport, however further research into the protein could provide more specific evidence regarding its function.

Chromosome 21 Open Reading Frame 58 (C21orf58) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C21orf58 gene.

Chromosome 18 open reading frame 63 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the C18orf63 gene. This protein is not yet well understood by the scientific community. Research has been conducted suggesting that C18orf63 could be a potential biomarker for early stage pancreatic cancer and breast cancer.
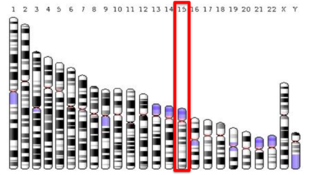
C15orf39 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the Chromosome 15 open reading frame 15 (C15orf39) gene.

Chromosome 9 open reading frame 25 (C9orf25) is a domain that encodes the FAM219A gene. The terms FAM219A and C9orf25 are aliases and can be used interchangeably. The function of this gene is not yet completely understood.

Uncharacterized protein C16orf86 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the C16orf86 gene. It is mostly made of alpha helices and it is expressed in the testes, but also in other tissues such as the kidney, colon, brain, fat, spleen, and liver. For the function of C16orf86, it is not well understood, however it could be a transcription factor in the nucleus that regulates G0/G1 in the cell cycle for tissues such as the kidney, brain, and skeletal muscles as mentioned in the DNA microarray data below in the gene level regulation section.

Testis expressed 55 (TEX55) is a human protein that is encoded by the C3orf30 gene located on the forward strand of human chromosome three, open reading frame 30 (3q13.32). TEX55 is also known as Testis-specific conserved, cAMP-dependent type II PK anchoring protein (TSCPA), and uncharacterized protein C3orf30.

Single-pass membrane and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 3 is a protein that is encoded in humans by the SMCO3 gene.

Chromosome 1 open reading frame 185, also known as C1orf185, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C1orf185 gene. In humans, C1orf185 is a lowly expressed protein that has been found to be occasionally expressed in the circulatory system.

C5orf46 is a protein coding gene located on chromosome 5 in humans. It is also known as sssp1, or skin and saliva secreted protein 1. There are two known isoforms known in humans, with isoform 2 being the longer of the two. The protein encoded is predicted to have one transmembrane domain, and has a predicted molecular weight of 9,692 Da, and a basal isoelectric point of 4.67.

C16orf90 or chromosome 16 open reading frame 90 produces uncharacterized protein C16orf90 in homo sapiens.. C16orf90's protein has four predicted alpha-helix domains and is mildly expressed in the testes and lowly expressed throughout the body. While the function of C16orf90 is not yet well understood by the scientific community, it has suspected involvement in the biological stress response and apoptosis based on expression data from microarrays and post-translational modification data.

C20orf202 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C20orf202 gene. In humans, this gene encodes for a nuclear protein that is primarily expressed in the lung and placenta.

ProteinFAM89A is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FAM89A gene. It is also known as chromosome 1 open reading frame 153 (C1orf153). Highest FAM89A gene expression is observed in the placenta and adipose tissue. Though its function is largely unknown, FAM89A is found to be differentially expressed in response to interleukin exposure, and it is implicated in immune responses pathways and various pathologies such as atherosclerosis and glioma cell expression.
TMEM275 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM275 gene. TMEM275 has two, highly-conserved, helical trans-membrane regions. It is predicted to reside within the plasma membrane or the endoplasmic reticulum's membrane.






















