
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig, also known as the cavy or domestic cavy, is a species of rodent belonging to the genus Cavia, family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the name "cavy" for the animal, but "guinea pig" is more commonly used in scientific and laboratory contexts. Despite their name, guinea pigs are not native to Guinea, nor are they closely related to pigs. Instead, they originated in the Andes region of South America, where wild guinea pigs can still be found today. Studies based on biochemistry and DNA hybridization suggest they are domesticated animals that do not exist naturally in the wild, but are descendants of a closely related cavy species such as C. tschudii. Originally, they were domesticated as livestock in the Andean region and are still consumed in some parts of the world.

Promissum is an extinct genus of conodonts, primitive chordates, that lived during the Upper Ordovician period.

Sivatherium is an extinct genus of giraffid that ranged throughout Africa and Eurasia. The species Sivatherium giganteum is, by weight, one of the largest giraffids known, and also one of the largest ruminants of all time.
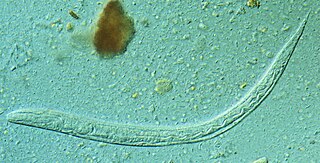
Strongyloides, anguillula, or threadworm is a genus of small nematode parasites, belonging to the family Strongylidae, commonly found in the small intestine of mammals, that are characterized by an unusual lifecycle that involves one or several generations of free-living adult worms.
Gorgopithecus is an extinct genus of primate in the Old World monkey family Cercopithecidae, closely related to the baboons. There is only one known species, Gorgopithecus major. It has been found at sites from the Pliocene and Early Pleistocene Epoch in South Africa and Tanzania. It was first discovered at the Kromdraai A site in South Africa. It has since been found from Swartkrans, South Africa. Most recently, it has been recognized from the DKI site in Bed I of Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania, which has been dated to 1.8 million years old.
Tetraconodontinae is an extinct subfamily of the pig family (Suidae). Fossils have been found in Africa and Asia.
Rhadalognathus was a prehistoric crocodile-like amphibian that belongs to the Mastodonsauridae family. Not much is known about this creature but it lived in the Triassic period. Rhadalognathus is also the name of the genus in which the organism belongs within. Rhadalognathus was found in northern Arizona, US, by S. P. Welles in 1947. The size of the organism is unknown but its skull is about 17in long and weighs 7lbs.

Listriodon is an extinct genus of pig-like animals that lived in Eurasia during the Miocene.
Sinohyus was a genus of ground dwelling omnivorous even toed ungulates that existed in Asia during the Pliocene.
Sivahyus was a genus of ground dwelling omnivorous even toed ungulates that existed in Asia during the Pliocene.
Cainochoerinae was a subfamily of even-toed ungulates that existed during the Miocene and Pliocene in Asia and Africa.
Albanohyus was an extinct genus of even-toed ungulates which lived during the Miocene in Eurasia and possibly Africa.

Hyotheriinae was a subfamily of even-toed ungulates that existed during the Miocene and Pliocene in Europe, Asia, and Africa.

Aureliachoerus was an extinct genus of suids that existed during the Miocene in Europe.
Nguruwe was an extinct genus of even-toed ungulates that existed during the Miocene in Africa. It was formerly considered a member of the subfamily Listriodontinae, but has since been placed in Hyotheriinae.
Xenohyus was an extinct genus of suids that existed during the Miocene in Europe.
Parachleuastochoerus was an extinct genus of even-toed ungulates that existed during the Miocene in Europe. It was a smaller descendant of the Conohyus genus, with narrower cheek teeth and reduced premolars.

Florida hosts many types of fauna. From coral reefs of the Florida Keys to the cypress swamps of the Panhandle, the state's diverse habitats are home to a variety of wildlife. Florida is among the top five states in terms of endemic species. There are over 700 terrestrial animals, 200 freshwater fish species, 1,000 marine fish and thousands of terrestrial insects and other invertebrates that inhabit the state. Florida's peninsular geography spans from subtropical to tropical zones, which, combined with its distinctive geology and climate, contribute to habitat diversity and an array of species. The native wildlife that exists in the state are of temperate and tropical origin.
Azabbaremys is an extinct genus of bothremydid pleurodiran turtle that was discovered in the Teberemt Formation of Mali. It was described in 2001, based on a skull that had been recovered in an expedition in 1981. The genus consists solely of the type species Azabbaremys moragjonesi. The genus name is derived from Azabbar, a monster in Tamasheq folk stories. The species is named for Morag Jones, a research student who participated in the discovery of the specimen and died in the expedition. Azabbaremys is most closely related to another Paleocene side-necked turtle, Acleistochelys.

Redlichia chinensis is an extinct species of trilobite that existed from 526 million years ago to 513 million years ago in the early Cambrian period.









