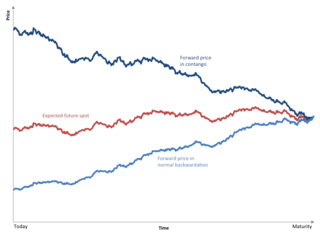
Contango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.
In finance, a put or put option is a derivative instrument in financial markets that gives the holder the right to sell an asset, at a specified price, by a specified date to the writer of the put. The purchase of a put option is interpreted as a negative sentiment about the future value of the underlying stock. The term "put" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "put up for sale" the stock or index.
In finance, a straddle strategy involves two transactions in options on the same underlying, with opposite positions. One holds long risk, the other short. As a result, it involves the purchase or sale of particular option derivatives that allow the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying security moves, regardless of the direction of price movement.
In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the forward price or delivery price. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the delivery date. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative.
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.

Volatility smiles are implied volatility patterns that arise in pricing financial options. It is a parameter that is needed to be modified for the Black–Scholes formula to fit market prices. In particular for a given expiration, options whose strike price differs substantially from the underlying asset's price command higher prices than what is suggested by standard option pricing models. These options are said to be either deep in-the-money or out-of-the-money.
In finance, volatility arbitrage is a term for financial arbitrage techniques directly dependent and based on volatility.

In options trading, a box spread is a combination of positions that has a certain payoff, considered to be simply "delta neutral interest rate position". For example, a bull spread constructed from calls combined with a bear spread constructed from puts has a constant payoff of the difference in exercise prices assuming that the underlying stock does not go ex-dividend before the expiration of the options. If the underlying asset has a dividend of X, then the settled value of the box will be 10 + x. Under the no-arbitrage assumption, the net premium paid out to acquire this position should be equal to the present value of the payoff.
The iron condor is an options trading strategy utilizing two vertical spreads – a put spread and a call spread with the same expiration and four different strikes. A long iron condor is essentially selling both sides of the underlying instrument by simultaneously shorting the same number of calls and puts, then covering each position with the purchase of further out of the money call(s) and put(s) respectively. The converse produces a short iron condor.
In options trading, a bear spread is a bearish, vertical spread options strategy that can be used when the options trader is moderately bearish on the underlying security.
In finance, a spread trade is the simultaneous purchase of one security and sale of a related security, called legs, as a unit. Spread trades are usually executed with options or futures contracts as the legs, but other securities are sometimes used. They are executed to yield an overall net position whose value, called the spread, depends on the difference between the prices of the legs. Common spreads are priced and traded as a unit on futures exchanges rather than as individual legs, thus ensuring simultaneous execution and eliminating the execution risk of one leg executing but the other failing.
In finance an iron butterfly, also known as the ironfly, is the name of an advanced, neutral-outlook, options trading strategy that involves buying and holding four different options at three different strike prices. It is a limited-risk, limited-profit trading strategy that is structured for a larger probability of earning smaller limited profit when the underlying stock is perceived to have a low volatility.
Option strategies are the simultaneous, and often mixed, buying or selling of one or more options that differ in one or more of the options' variables. Call options, simply known as Calls, give the buyer a right to buy a particular stock at that option's strike price. Opposite to that are Put options, simply known as Puts, which give the buyer the right to sell a particular stock at the option's strike price. This is often done to gain exposure to a specific type of opportunity or risk while eliminating other risks as part of a trading strategy. A very straightforward strategy might simply be the buying or selling of a single option; however, option strategies often refer to a combination of simultaneous buying and or selling of options.
A Ratio spread is a, multi-leg options position. Like a vertical, the ratio spread involves buying and selling options on the same underlying security with different strike prices and the same expiration date. In this spread, the number of option contracts sold is not equal to a number of contracts bought. An unequal number of options contracts gives this spread certain unique properties compared to a regular vertical spread. A typical ratio spread would be where twice as many option contracts are sold, thus forming a 1:2 ratio.
The backspread is the converse strategy to the ratio spread and is also known as reverse ratio spread. Using calls, a bullish strategy known as the call backspread can be constructed and with puts, a strategy known as the put backspread can be constructed.
Pin risk occurs when the market price of the underlier of an option contract at the time of the contract's expiration is close to the option's strike price. In this situation, the underlier is said to have pinned. The risk to the writer (seller) of the option is that they cannot predict with certainty whether the option will be exercised or not. So the writer cannot hedge their position precisely and may end up with a loss or gain. There is a chance that the price of the underlier may move adversely, resulting in an unanticipated loss to the writer. In other words, an option position may result in a large, undesired risky position in the underlier immediately after expiration, regardless of the actions of the writer.
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the holder, the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in over-the-counter (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts.
In finance, a credit spread, or net credit spread is an options strategy that involves a purchase of one option and a sale of another option in the same class and expiration but different strike prices. It is designed to make a profit when the spreads between the two options narrows.
A jelly roll, or simply a roll, is an options trading strategy that captures the cost of carry of the underlying asset while remaining otherwise neutral. It is often used to take a position on dividends or interest rates, or to profit from mispriced calendar spreads.

In finance, a ladder, also known as a Christmas tree, is a combination of three options of the same type at three different strike prices. A long ladder is used by traders who expect low volatility, while a short ladder is used by traders who expect high volatility. Ladders are in some ways similar to strangles, vertical spreads, condors, or ratio spreads.



