
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy drupe.

An apricot is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus Prunus.

A plum is a fruit of some species in Prunus subg. Prunus. Dried plums are most often called prunes, though in the United States they may be labeled as simply 'dried plums', especially during the 21st century.

Prunus is a genus of trees and shrubs in the flowering plant family Rosaceae that includes plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots, and almonds. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, being native to the North American temperate regions, the neotropics of South America, and temperate and tropical regions of Asia and Africa, There are 340 accepted species. Many members of the genus are widely cultivated for their fruit and for decorative purposes. Prunus fruit are drupes, or stone fruits. The fleshy mesocarp surrounding the endocarp is edible while the endocarp itself forms a hard, inedible shell called the pyrena. This shell encloses the seed, which is edible in some species, but poisonous in many others. Besides being eaten off the hand, most Prunus fruit are also commonly used in processing, such as jam production, canning, drying, and the seeds for roasting.
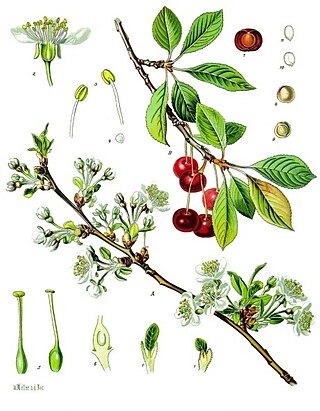
Prunus cerasus is a species of Prunus in the subgenus Cerasus (cherries), native to much of Europe, North Africa and West Asia. It is closely related to the sweet cherry, but has a fruit that is more acidic. Its sour pulp is edible.

The cherry blossom, or sakura, is the flower of trees in Prunus subgenus Cerasus. "Sakura" usually refers to flowers of ornamental cherry trees, such as cultivars of Prunus serrulata, not trees grown for their fruit. Cherry blossoms have been described as having a vanilla-like smell, which is mainly attributed to coumarin.

Prunus mume is a Chinese tree species classified in the Armeniaca section of the genus Prunus subgenus Prunus. Its common names include Chinese plum,Japanese plum, and Japanese apricot. The flower, long a beloved subject in the traditional painting and poetry of Sinospheric countries, is usually called plum blossom. This distinct tree species is related to both the plum and apricot trees. Although generally referred to as a plum in English, it is more closely related to the apricot. In East Asian cuisine, the fruit of the tree is used in juices, as a flavouring for alcohol, as a pickle, and in sauces. It is also used in traditional medicine.

Prunus laurocerasus, also known as cherry laurel, common laurel and sometimes English laurel in North America, is an evergreen species of cherry (Prunus), native to regions bordering the Black Sea in southwestern Asia and southeastern Europe, from Albania and Bulgaria east through Turkey to the Caucasus Mountains and northern Iran.

Prunus virginiana, commonly called bitter-berry, chokecherry, Virginia bird cherry, and western chokecherry, is a species of bird cherry native to North America.

Prunus subg. Padus is a subgenus of Prunus, characterised by having racemose inflorescences. Padus was originally a distinct genus, but genetic and morphological studies have shown that Padus is polyphyletic. It has been proposed that all the racemose taxa within Prunus are incorporated into a broad-sense Prunus subg. Padus.

Prunus serotina, commonly called black cherry, wild black cherry, rum cherry, or mountain black cherry, is a deciduous tree or shrub in the rose family Rosaceae. Despite being called black cherry, it is not very closely related to the commonly cultivated cherries such as sweet cherry, sour cherry and Japanese flowering cherries which belong to Prunus subg. Cerasus. Instead, P. serotina belongs to Prunus subg. Padus, a subgenus also including Eurasian bird cherry and chokecherry. The species is widespread and common in North America and South America.

Prunus × yedoensis is a hybrid cherry tree between Prunus speciosa as father plant and Prunus pendula f. ascendens as mother. It is a hybrid born in Japan and one of its cultivars, Prunus × yedoensis 'Somei-yoshino' or Yoshino cherry, is one of the most popular and widely planted cherry cultivars in temperate regions around the world today. 'Somei-yoshino' is a clone from a single tree, and has been propagated by grafting all over the world. 'Somei-yoshino' inherits Edo higan's quality of blooming before the leaves unfold and it growing into a large-sized tree. It also inherits the characteristics of the Oshima cherry, which grows rapidly and has white flowers. These characteristics are favored and have become one of the most popular cultivars of cherry trees.

Prunus campanulata is a species of cherry native to Japan, Taiwan, southern and eastern China, and Vietnam. It is a large shrub or small tree, growing 3–8 m (10–26 ft) tall. It is widely grown as an ornamental tree, and a symbol of Nago in the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. It is variously known in English as the Taiwan cherry, Formosan cherry, or bellflower cherry. It was described in 1883 by Carl Johann Maximowicz.

Prunus sargentii, commonly known as Sargent's cherry or North Japanese hill cherry, is a species of cherry native to Japan, Korea, and Sakhalin (Russia).

Prunus domestica is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae. A deciduous tree, it includes many varieties of the fruit trees known as plums in English, though not all plums belong to this species. The greengages and damsons also belong to subspecies of P. domestica.

Prunus avium, commonly called wild cherry, sweet cherry or gean is a species of cherry, a flowering plant in the rose family, Rosaceae. It is native to Europe, Anatolia, Maghreb, and Western Asia, from the British Isles south to Morocco and Tunisia, north to the Trondheimsfjord region in Norway and east to the Caucasus and northern Iran, with a small isolated population in the western Himalaya. The species is widely cultivated in other regions and has become naturalized in North America, New Zealand and Australia.

Phyllonorycter cerasicolella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from all of Europe, except northern Scandinavia.

Prunus rivularis, known variously by the common names creek plum, hog plum, or wild-goose plum is a thicket-forming shrub. It prefers calcareous clay soil or limestone-based woodland soils. This deciduous plant belongs to the rose family, Rosaceae, and is found mainly in the central United States. It is a shrub consisting of slender stems with umbel clusters of white blossoms. The fruit is a drupe that resembles a large berry; though it has a bitter taste, it serves as a source of food for birds and other wildlife. "Prunus" is Latin for plum, whereas "rivularis" means being near a stream.

Prunus subg. Prunus is a subgenus of Prunus. This subgenus includes plums, apricots and bush cherries. Some species conventionally included in Prunus subg. Amygdalus are clustered with plum/apricot species according to molecular phylogenetic studies. Shi et al. (2013) has incorporated subg. Amygdalus into subg. Prunus, thereby including almonds and peaches in this subgenus. The species in this subgenus have solitary flowers or 2–3 in a fascicle.

Prunus subg. Cerasus is a subgenus of Prunus. Species of the subgenus have a single winter bud per axil. The flowers are usually in small corymbs or umbels of several together, but some species have short racemes. The fruit is a drupe and has no obvious groove along the side. The subgenus is native to the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, with two species in North America, four in Europe, two in North Africa, and the remainder in Asia.



















