
Callopistria is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. It was described by Jacob Hübner in 1821.
Erygia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae erected by Achille Guenée in 1852.

Serrodes is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852.

Sphingomorpha is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. Some species, such as Sphingomorpha chlorea, are notorious pests in orchards, and are known as fruitsucking or fruit-piercing moths.
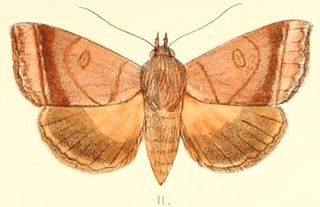
Ophiusa trapezium is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka to Queensland, the Bismarck Islands and New Caledonia. Adults are fruit piercers.

Ctenoplusia limbirena, the Scar Bank gem, or silver U-tail, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in south-western Europe, Africa, the Canary Islands, Arabia, the southern Himalayas, India, Sri Lanka, Indochina to south-eastern China, Taiwan, Sulawesi, Bali and Timor. In New Zealand, it has been established since 2011.

Sympis rufibasis is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka, Borneo east to New Guinea, the Solomons and Queensland.

Oruza divisa is a species of moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1862. It is found in Asia, including Hong Kong, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Taiwan, Japan and in Africa south of the Sahara, including Indian Ocean islands.

Ericeia inangulata, the sober tabby, is a moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in the Indo-Australian tropics of China, India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and the Marianas and Carolines, Fiji, Vanuatu, New Caledonia and Samoa.

Hipoepa fractalis is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1854. It is found in Taiwan, China, Japan, Kenya, Korea, India, Malaysia, Nigeria, Indonesia, the Philippines, Thailand, Cape Verde, Réunion, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Uganda, Yemen and Australia.

Polydesma umbricola, the monkeypod moth or large tabby, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. The species is found in southern Europe, Africa, Asia Minor to southern Asia, of India, Sri Lanka, Maldives, the Andaman Islands, including many Indian Ocean islands, like Coëtivy Island, Aldabra, Assumption Island, Madagascar and on Hawaii.

Scopula fibulata is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Achille Guenée in 1858. It is found in Kenya, Sri Lanka and China.

Thalassodes quadraria is a species of moth of the family Geometridae first described by Achille Guenée in 1857. It is found in Africa south of the Sahara and in India and Sri Lanka.

Nagia linteola is a species of moth in the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. This species occurs in South Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Yemen, the Comoros, Mauritius, Madagascar, Indonesia (Borneo), India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand and in Australia, where it has been recorded from Western Australia, the Northern Territory, Queensland and Victoria.
Racotis boarmiaria is a species of moth of the family Geometridae described by Achille Guenée in 1857. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Myanmar, China, Japan, Taiwan, Indonesia, Bhutan and Malaysia.

Erygia apicalis is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka to Japan, Australia and the Solomon Islands. The habitat consists of lowland areas, including dry heath forests and softwood plantations.

Hypopyra vespertilio is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1787. It is found in China, Korea, Honshu in Japan, India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, Taiwan, Malaysia, the Philippines, Java, Sumatra and Sulawesi.

Sphingomorpha chlorea, the sundowner moth, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae that is native to Africa and southern Asia. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1777. It is a fruit-piercing moth and a notorious pest in orchards. The fruit is pierced while performing a vertical and rhythmic movement of the head.

















