
The South Florida Railroad was a railroad from Sanford, Florida, to Tampa, Florida, becoming part of the Plant System in 1893 and the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad in 1902. It served as the southernmost segment of the Atlantic Coast Line's main line. The line remains in service today and is now part of the Central Florida Rail Corridor in the Orlando metro area. The rest of the line remains under the ownership of CSX Transportation as part of their A Line.
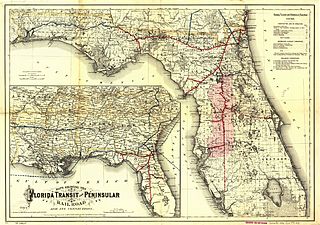
The Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad was the final name of a system of railroads throughout Florida, becoming part of the Seaboard Air Line Railway in 1900. The system, including some of the first railroads in Florida, stretched from Jacksonville west through Tallahassee and south to Tampa. Much of the FC&P network is still in service under the ownership of CSX Transportation.

The Atlantic and Western Railway is a Class III short-line railroad operating about 10 miles (16 km) of track in Lee County, North Carolina. Atlantic and Western is part of Genesee & Wyoming Inc. and formerly part of Rail Management and Consulting. It was reorganized in 1927 from the Atlantic and Western Railroad.
The Atlantic and Yadkin Railway was a short line railroad within North Carolina from 1899 to 1950. It ran from Mount Airy southeast to Sanford, primarily serving the Piedmont region. Some of the rails are still in use as of 2006 as parts of the Yadkin Valley Railroad.
The Wilmington and Weldon Railroad (W&W) name began use in 1855, having been originally chartered as the Wilmington and Raleigh Railroad in 1834. When it opened in 1840, the line was the longest railroad in the world with 161.5 miles (259.9 km) of track. It was constructed in 4 ft 8 in gauge. At its terminus in Weldon, North Carolina, it connected with the Seaboard and Roanoke Railroad and the Petersburg Railroad. The railroad also gave rise to the city of Goldsboro, North Carolina, the midpoint of the W&W RR and the railroad intersection with the North Carolina Railroad.

The Yadkin Valley Railroad is the trade name of the Piedmont and Atlantic Railroad and is a shortline railroad operating two lines leased from the Norfolk Southern Railway originating out of Rural Hall, North Carolina for a distance of 93 miles (150 km). The railroad began operation in 1989 and is currently a subsidiary of Gulf and Ohio Railways.
The South Carolina Pacific Railway was a shortline railroad operation that existed in eastern South Carolina in the late 19th century and much of the 20th century.
The Wilmington and Manchester Railroad was a railroad that served South Carolina and North Carolina before, during and after the American Civil War. It received its charter in 1846 and began operation in 1853 from Wilmington, North Carolina, extending west to the now-defunct town of Manchester, South Carolina. The track gauge was 5 ft.
The Pee Dee River Railway is a South Carolina railroad that serves the far eastern portion of the state.
The Red Springs & Northern Railroad is a 13-mile short-line railroad extending from Parkton to Red Springs, in southeastern North Carolina. It connects with major carrier CSX Transportation in Parkton. The line was originally constructed by the Cape Fear & Yadkin Valley Railroad to the South Carolina state line near McColl, South Carolina, in 1883-1885. The trackage became the Atlantic Coast Line's "Bennettsville Branch" in 1898. The portion of the route from Red Springs to McColl was removed in 1973. ACL-successor CSX abandoned the remainder of the line in the 1980s.
The W&W Subdivision is a railroad line owned by CSX Transportation in the U.S. state of North Carolina. The line today runs from just south of Wilson, North Carolina, to Wallace, North Carolina, for a total of 69.1 miles. At its north end the line connects to CSX's A Line. The line's name stands for the Wilmington and Weldon Railroad, the company that originally built the line.

Wilmington Union Station was a union station in Wilmington, North Carolina. Opened in 1913, it was designed by architect Joseph F. Leitner. Construction by Boyle-Robertson contractors began in 1912. It was located at Front Street and Red Cross Street in downtown Wilmington.
The Fayetteville Cutoff was a railroad line in North Carolina and South Carolina built by predecessors of the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad connecting Wilson, North Carolina with Pee Dee, South Carolina. Its main purpose was to shorten the Atlantic Coast Line's main line.

The CSX A Line forms the backbone of the historic Atlantic Coast Line Railroad Main Line, the backbone of their network in the southeastern United States. The main line runs from Richmond, Virginia to Port Tampa just southwest of Tampa, Florida, a distance of nearly 900 miles. Along its route it passes through Petersburg, Rocky Mount, Florence, Charleston, Savannah, Jacksonville, and Orlando. With the exception of a short 61-mile segment in Greater Orlando, the entire line is owned by CSX Transportation.

The Carolina Central Railroad, was a railway company in the United States. It was incorporated in 1855 as the Wilmington and Charlotte Railroad and was renamed the Wilmington, Charlotte and Rutherford Railroad shortly after. It was reorganized as the Carolina Central Railway in 1873. It built 152 miles (245 km) of track, in two unconnected sections, in the southern part of North Carolina. The company was again reorganized as the Carolina Central Railroad in 1880. In 1900, the Carolina Central Railroad was merged into the Seaboard Air Line Railroad. Its lines are now owned by CSX Transportation.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Florence—Robbins Line was one of the company's secondary main lines that ran from Florence, South Carolina to Robbins. It was built in the late 1800s and large parts of it were built by the Atlantic Coast Line's predecessor companies. Parts of the line are still in service.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Wilmington—Pee Dee Line was a railroad line running from Wilmington, North Carolina west to Pee Dee, South Carolina. Running in an east–west trajectory, it notably passed through Lake Waccamaw, Chadbourn, Nichols, and Mullins. Some of the line is still operating today.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Parkton—Sumter Line was one of the company's secondary main lines running between Parkton, North Carolina and Sumter, South Carolina.
The Atlantic Coast Line Railroad's Norfolk—Rocky Mount Line was one of the company's secondary main lines running from the company's main line in Rocky Mount, North Carolina northeast to a point just outside of Norfolk, Virginia. Despite its name, it terminated at Pinners Point in Portsmouth, Virginia. Bus and ferry service connected passengers to Norfolk.










