
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus Carex with over 2,000 species.

Mer Bleue Bog is a 33.43 km2 (12.91 sq mi) protected area in Gloucester, Ontario, an eastern suburb of Ottawa in Eastern Ontario, Canada. Its main feature is a sphagnum bog that is situated in an ancient channel of the Ottawa River and is a remarkable boreal-like ecosystem normally not found this far south. Stunted black spruce, tamarack, bog rosemary, blueberry, and cottongrass are some of the unusual species that have adapted to the acidic waters of the bog.

Carex is a vast genus of nearly 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.
Yanal Bog is a 1.6 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest on the southern edge of the North Somerset Levels, just north of the village of Sandford, North Somerset. It was notified as an SSSI in 1988.

Lambert's Castle is an Iron Age hillfort in the county of Dorset in southwest England. Since 1981 it has been designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) on account of its geology, archaeology and ecology. The hillfort is designated a scheduled monument together with a bowl barrow, the sites of a post-medieval fair and a telegraph station. The site was on the Heritage at Risk Register but was removed in 2022 as a result of the Hillforts and Habitats Project.

Carex chordorrhiza, commonly called creeping sedge or string sedge, is a species of perennial plant in the family Cyperaceae with Holarctic distribution growing in acidic bogs.

Carex canescens L. is a perennial species of plants in the family Cyperaceae growing in damp forests and wetlands. It is widespread across much of Europe, Asia, Australia, New Guinea, North America, Greenland and southern South America.

Carex rossii, commonly known as Ross's sedge, is a hardy species of sedge that is often a pioneer species in areas with little or no established vegetation, or in places where disturbance has occurred. Ross's sedge grows in a variety of habitats throughout much of western North America, from Alaska to Ontario, south to New Mexico and California. It flowers in May and June.

Carex vesicaria is an essentially Holarctic species of sedge known as bladder sedge, inflated sedge, and blister sedge. It has been used to insulate footwear in Norway and among the Sami people, and for basketry in North America.

Carex riparia, the greater pond sedge, is a species of sedge found across Europe and Asia. It grows in a variety of wet habitats, and can be a dominant species in some swamps. It is Britain's largest Carex, growing up to 130 cm tall, with glaucous leaves up to 160 cm long. It hybridises with a number of other Carex species, including the closely related Carex acutiformis – the lesser pond sedge. A variegated cultivar is grown as an ornamental grass.

Carex binervis, the green-ribbed sedge, is a European species of sedge with an Atlantic distribution. It is found from Fennoscandia to the Iberian Peninsula, and occurs in heaths, moorland and other damp, acidic environments. It typically grows to a height of 15–120 cm (6–50 in), and has inflorescences comprising one male and several female spikes, each up to 45 mm (1.8 in) long. The utricles have two conspicuous green veins, which give rise to both the scientific name and the common name of the species. In the vegetative state, it closely resembles C. bigelowii, a species that usually grows at higher altitude. C. binervis was first described by James Edward Smith in 1800, and is classified in Carex sect. Spirostachyae; several hybrids with other Carex species are known.

Carex sect. Spirostachyae is a section of the genus Carex, containing 38 species of sedge. Species in Carex sect. Spirostachyae share a suite of features, including the short internodes of the primary rhizomes, the presence of an antiligule, the leaf-like, sheathing bract at the base of the inflorescence, the presence of three stigmas in female flowers, and the shape of the seeds.

Carex archeri, known as Archer's sedge, is a species of sedge in the genus Carex, endemic to south-eastern Australia.

Carex bicolor, the bicoloured sedge, is a species of sedge native to North America, Northern Europe and Northern Asia. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed the plant's conservation status as being of least concern because it has a widespread distribution and faces no particular threats.
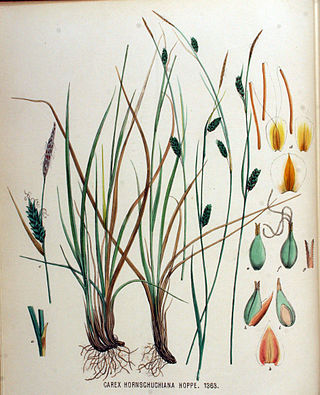
Carex hostiana, the tawny sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Europe and northeast Canada, and extinct in Massachusetts. It is a member of the Carex flava species complex.

Carex gravida, also known as heavy-fruited sedge, heavy sedge or long-awned bracted sedge, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to southern parts of Canada and parts of the United States.

Carex digitalis is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to south eastern parts of Canada as well as central and eastern parts of the United States.

Carex vestita, also commonly known as velvet sedge, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to eastern parts of the United States.















