
Lygodium is a genus of about 40 species of ferns, native to tropical regions across the world, with a few temperate species in eastern Asia and eastern North America. It is the sole genus in the family Lygodiaceae in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016. Alternatively, the genus may be placed as the only genus in the subfamily Lygodioideae of a more broadly defined family Schizaeaceae, the family placement used in Plants of the World Online as of November 2019. Per recent molecular evidence, Lygodiaceae is thought to have diverged relatively early from the other members of the Schizaeales due to the relatively high level of synonymous sequence divergence between the families within the Schizaeales.

Carmichaelia is a genus of 24 plant species belonging to Fabaceae, the legume family. All but one species are native to New Zealand; the exception, Carmichaelia exsul, is native to Lord Howe Island and presumably dispersed there from New Zealand.

Ruppia, also known as the widgeonweeds, ditch grasses or widgeon grass, is the only extant genus in the family Ruppiaceae, with eight known species. These are aquatic plants widespread over much of the world. The genus name honours Heinrich Bernhard Rupp, a German botanist (1688–1719). They are widespread outside of frigid zones and the tropics.

Clianthus, commonly known as kakabeak, is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae, comprising two species of shrubs endemic to the North Island of New Zealand. They have striking clusters of red flowers which resemble the beak of the kākā, a New Zealand parrot. The plants are also known as parrot's beak, parrot's bill and lobster claw – all references to the distinctive flowers. There is also a variety with white to creamy coloured flowers called: "Albus," and a variety with rosy pink flowers called: "Roseus."

Streblorrhiza was a monotypic genus of legumes in the family Fabaceae. Its only species was Streblorrhiza speciosa, a perennial shrub endemic to Phillip Island. It is now presumed extinct.

Sporobolus is a nearly cosmopolitan genus of plants in the grass family. The name Sporobolus means "seed-thrower", and is derived from Ancient Greek word σπόρος (spóros), meaning "seed", and the root of βάλλειν (bállein) "to throw", referring to the dispersion of seeds. Members of the genus are usually called dropseeds or sacaton grasses. They are typical prairie and savanna plants, occurring in other types of open habitat in warmer climates. At least one species is threatened with extinction, and another is extinct.

The Papuan mountain pigeon is a species of bird in the pigeon family, Columbidae. It is found in the Bacan Islands, New Guinea, the D'Entrecasteaux Islands, and the Bismarck Archipelago, where it inhabits primary forest, montane forest, and lowlands. It is a medium-sized species of pigeon, being 33–36 cm (13–14 in) long and weighing 259 g (9.1 oz) on average. Adult males have slate-grey upperparts, chestnut-maroon throats and bellies, whitish breasts, and a pale grey terminal tail band. The lores and orbital region are bright red. Females are similar, but have grayish breasts and grey edges to the throat feathers.

The Antarctic floristic kingdom, also the Holantarctic kingdom, is a floristic kingdom that includes most areas of the world south of 40°S latitude. It was first identified by botanist Ronald Good, and later by Armen Takhtajan. The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom is a classification in phytogeography, different from the Antarctic realm classification in biogeography, and from Antarctic flora genera/species classifications in botany.

Posidonia is a genus of flowering plants. It contains nine species of marine plants ("seagrass"), found in the seas of the Mediterranean and around the south coast of Australia.

The flora of Australia comprises a vast assemblage of plant species estimated to over 21,000 vascular and 14,000 non-vascular plants, 250,000 species of fungi and over 3,000 lichens. The flora has strong affinities with the flora of Gondwana, and below the family level has a highly endemic angiosperm flora whose diversity was shaped by the effects of continental drift and climate change since the Cretaceous. Prominent features of the Australian flora are adaptations to aridity and fire which include scleromorphy and serotiny. These adaptations are common in species from the large and well-known families Proteaceae (Banksia), Myrtaceae, and Fabaceae.

Adenanthos macropodianus, commonly known as gland flower, or Kangaroo Island gland flower, is a species of shrub in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to Kangaroo Island in South Australia. First published as a variety of A. sericeus in 1870, it was promoted to species rank in 1978.
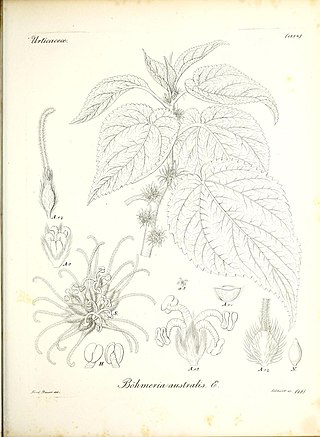
Pouzolzia australis, synonyms including Boehmeria australis and Boehmeria calophleba, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant family Urticaceae. It is endemic to small islands belonging to Australia and New Zealand – Norfolk Island, Lord Howe Island, and the Kermadec Islands. The population on Norfolk island, sometimes treated as a distinct subspecies, is critically endangered. In the Kermadec Islands, it was described in 2018 as "threatened – nationally endangered".
Hollandaea is a small genus of plants in the family Proteaceae containing four species of Australian rainforest trees. All four species are endemic to restricted areas of the Wet Tropics of northeast Queensland.

Carmichaelia muritai, common name coastal tree broom, is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in the South Island of New Zealand.

Eucalyptus effusa, commonly known as rough-barked gimlet, is a species of mallee or small tree that is endemic to Western Australia. It has thin, rough bark on the base of the trunk, smooth bark above, linear to narrow lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds arranged in groups of seven, white flowers and cup-shaped to conical fruit.

Carmichaelia petriei is a species of New Zealand broom in the genus Carmichaelia. It is endemic to New Zealand. C. petrieis is possibly a host plant for the critically endangered fungus weevil Cerius otagensis.

Carmichaelia astonii is a species of pea in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in South Island of New Zealand. Its conservation status (2018) is "Nationally vulnerable" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System.

Carmichaelia appressa is a species of pea in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in the South Island of New Zealand. Its conservation status (2018) is "At Risk - Naturally Uncommon" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System.
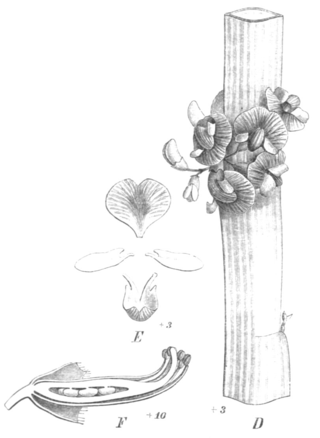
Carmichaelia australis, commonly known as the New Zealand common broom or mākaka, is a shrub of the Fabaceae family. It is native to New Zealand and found in both the North and South Islands.

Carmichaelia nana is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found in both the North and South Islands of New Zealand. Its conservation status in 2013 was assessed as "At Risk (declinining)" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System, but in 2018 its risk under the same system became "Threatened-Nationally Vulnerable".


















