Related Research Articles

The human reproductive system includes the male reproductive system which functions to produce and deposit sperm; and the female reproductive system which functions to produce egg cells, and to protect and nourish the fetus until birth. Humans have a high level of sexual differentiation. In addition to differences in nearly every reproductive organ, there are numerous differences in typical secondary sex characteristics.
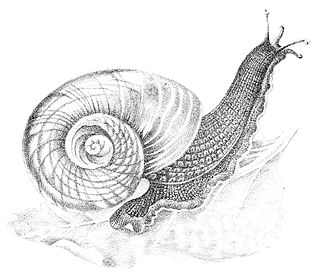
Paryphanta busbyi is a species of large predatory land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Rhytididae.

Catinella arenaria is a species of land snail in the family Succineidae, the amber snails. It is known commonly as the sandbowl snail.

Amphidromus is a genus of tropical air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Camaenidae. The shells of Amphidromus are relatively large, from 25 mm (0.98 in) to 75 mm (3.0 in) in maximum dimension, and particularly colorful. During the 18th century, they were among the first Indonesian land snail shells brought to Europe by travelers and explorers. Since then, the genus has been extensively studied: several comprehensive monographs and catalogs were authored by naturalists and zoologists during the time period from the early 19th to the mid 20th centuries. Modern studies have focused on better understanding the evolutionary relationships within the group, as well as solving taxonomic problems.

Tandonia nigra is a species of air-breathing land slug, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Milacidae.

Tandonia is a genus of air-breathing, keeled, land slugs. These are shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusks in the family Milacidae.

Lehmannia is a genus of air-breathing land slugs in the family Limacidae, the keelback slugs. The genus is distributed in Europe and North Africa.

Tandonia rustica is a species of air-breathing, keeled, land slug, a shell-less terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Milacidae.

Anostoma depressum is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Odontostomidae.

Indrella is a monotypic genus containing the single species Indrella ampulla, a tropical terrestrial air-breathing gastropod mollusk in the family Ariophantidae. It is endemic to the Western Ghats of India.

Tomigerus clausus is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Odontostomidae.

The reproductive system of gastropods varies greatly from one group to another within this very large and diverse taxonomic class of animals. Their reproductive strategies also vary greatly, see Mating of gastropods.
Tandonia serbica is a species of keeled air-breathing land slug, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Milacidae.

Perrottetia is a genus of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Streptaxidae.

Corona pfeifferi is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Orthalicidae.

Leptacme cuongi is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Clausiliidae, the door snails.

Oospira smithi is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial gastropod mollusk in the family Clausiliidae, the door snails.

Marstonia comalensis is a species of minute freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Hydrobiidae. It is found in south central Texas, United States.

Lymnaea meridensis is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Lymnaeidae, the pond snails.

Pseudorhabdosynochus americanus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of groupers. It was described as Diplectanum americanum by Price in 1937 and transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky and Beverley-Burton in 1986. The species was redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015.
References
This article incorporates public domain text from the reference. [2]
- ↑ Wagner A. J. (1895). "Die Arten des Genus Daudebardia Hartmann in Europa und Westasien. Eine kritische Studie." Denkschriften der kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften, mathematisch-naturwissenschaftliche Classe62: 609-626, Taf. I-V [= 1-5]. Wien.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 "Genus summary for Carpathica". AnimalBase, last modified 13 January 2009, accessed 4 September 2010.
- ↑ Grossu A. V. (1983). Gastropoda Romaniae 4. Ordo Stylommatophora. Suprafam.: Arionacea, Zonitacea, Ariophantacea şi Helicacea. pp. 1–564. București. (Editura Litera).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Species in genus Carpathica". [n=10] AnimalBase, accessed 4 September 2010.