The south-east coast drainage division is the very long, narrow area of southern Australia between the Great Dividing Range and the Coral and Tasman seas, and the Bass Strait. It includes the small part of south-eastern South Australia which lies to the east of the Murray-Darling Basin, and all of coastal Victoria and coastal New South Wales. While the southern, eastern, and western boundaries are clearly defined by geography, the northern boundary is arbitrarily defined as the New South Wales - Queensland border. The distinguishing feature of the drainage basin is the Great Dividing Range and the associated Australian Alps.

The Avoca River, an inland intermittent river of the north–central catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower Riverina bioregion and Central Highlands and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The headwaters of the Avoca River rise on the northern slopes of the Pyrenees Range and descend to flow into the ephemeral Kerang Lakes.
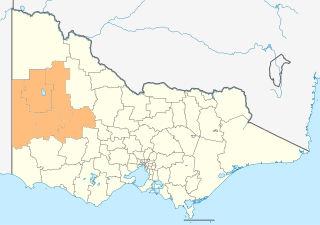
The Victorian government's Wimmera Southern Mallee subregion is part of the Grampians region in western Victoria. It includes most of what is considered the Wimmera, and part of the southern Mallee region. The subregion is based on the social catchment of Horsham, its main settlement.

Soil salinity and dryland salinity are two problems degrading the environment of Australia. Salinity is a concern in most states, but especially in the south-west of Western Australia.

North Central Victoria is a rural region in the Australian state of Victoria. The region lies to the south of the Victorian/New South Wales border as defined by the Murray River, to the southwest of the Hume region, to the west of the Great Dividing Range contained within the Central Highlands and Victorian Alps, to the north of Greater Melbourne, to the northeast of the Wimmera, and to the east of the Mallee region.

The Avon River is a perennial river of the West Gippsland catchment, located in the West Gippsland region, of the Australian state of Victoria. The Avon, forms an important part of the Latrobe sub-catchment, draining the south eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, to form the Gippsland Lakes.

The Wimmera River, an inland intermittent river of the Wimmera catchment, is located in the Grampians and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. Rising in the Pyrenees, on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the Wimmera River flows generally north by west and drains into Lake Hindmarsh and Lake Albacutya, a series of ephemeral lakes that, whilst they do not directly empty into a defined watercourse, form part of the Murray River catchment of the Murray-Darling basin.
The 1909 Western Victorian floods consisted of widespread flooding on rivers of the western half of the State of Victoria during the middle of August that year.

Victoria is the southernmost mainland state of Australia. With an area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi), it is Australia's sixth largest state/territory, comparable in size to the island of Great Britain or the U.S. state of Utah. It is bound to the northwest by South Australia, directly north by New South Wales, and also shares a maritime border with Tasmania across the Bass Strait to the south. Most of Victoria's northern border lies along the Murray River. The eastern half of the state is dominated by the Australian Alps and the surrounding highlands of the Great Dividing Range, which also to a lesser extent extend far into the west of the state and ease off after The Grampians. By comparison the north and northwest of the state is extremely flat with little prominence.
The regions of Victoria vary according to the different ways that the Australian state of Victoria is divided into distinct geographic regions. The most commonly used regions are those created by the state government for the purposes of economic development.
The Timbarra River is a perennial river of the Mitchell River catchment, located in the East Gippsland region of the Australian state of Victoria.

Trust for Nature is a not-for-profit organisation in the Australian state of Victoria which protects native plants and wildlife in co-operation with private landowners. The Trust was established under the Victorian Conservation Trust Act 1972 to enable people to contribute permanently to nature conservation by donating land or money. Trust for Nature has since evolved into one of Victoria's primary private land conservation organisations.
Bowls Victoria, established in 1880 is the governing body for the sport of bowls in the State of Victoria. In addition to its specific responsibility for governing the sport and the development of the game at all levels, it also has a social objective to enhance existing bowling communities and to position bowls clubs and the sport in the wider community.
The Avon River, an inland intermittent river of the Wimmera catchment, located in the Grampians and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. Rising on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the Avon River flows north-westerly to reach its confluence with the Richardson River. The rivers of the Wimmera catchment drain into a series of ephemeral lakes that, whilst they do not directly empty into a defined watercourse, form part of the Murray River catchment of the Murray-Darling basin.

The Richardson River, an inland intermittent river of the Wimmera catchment, located in the Grampians and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. Rising on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the Richardson River flows generally north and drains into Lake Buloke, one of a series of ephemeral lakes that, whilst they do not directly empty into a defined watercourse, form part of the Murray River catchment of the Murray-Darling basin.

Water management in Victoria deals with the management of water resources in and by the Australian State of Victoria.









