
Tulbaghia is a genus of monocotyledonous herbaceous perennial bulbs native to Africa, belonging to the amaryllis family. It is one of only two known genera in the society garlic tribe within the onion subfamily. The genus was named for Ryk Tulbagh (1699–1771), one time governor of The Cape of Good Hope.

Cussonia spicata, known as spiked cabbage tree, lowveld cabbage tree or common cabbage tree, is a tree in the family Araliaceae, which is native to the moister regions of Sub-Saharan Africa. It is cultivated as a garden plant in areas without extreme degrees of frost. It is one of the favorite foods of wild elephants.

Vachellia tortilis, widely known as Acacia tortilis but now attributed to the genus Vachellia, is the umbrella thorn acacia, also known as umbrella thorn and Israeli babool, a medium to large canopied tree native to most of Africa, primarily to the savanna and Sahel of Africa, but also occurring in the Middle East.

Vachellia erioloba, the camel thorn, giraffe thorn, or Kameeldoring in Afrikaans, still more commonly known as Acacia erioloba, is a tree of southern Africa in the family Fabaceae. Its preferred habitat is the deep dry sandy soils in parts of South Africa, Botswana, the western areas of Zimbabwe and Namibia. It is also native to Angola, south-west Mozambique, Zambia and Eswatini. The tree was first described by Ernst Heinrich Friedrich Meyer and Johann Franz Drège in 1836. The camel thorn is a protected tree in South Africa.

Omphalocarpum is a genus of plants belonging to the family Sapotaceae. It was first described in 1800 by Palisot de Beauvois. The genus is endemic to tropical Africa.

Rhaphidophora is a genus in the family Araceae, occurring from tropical Africa eastwards through Malesia and Australasia to the Western Pacific. The genus consists of approximately 100 species.

Widdringtonia nodiflora is a species of Widdringtonia native to Southern Africa. It usually grows at high altitudes, typically among rocks on mountainsides. Its foliage and wood are highly flammable while its natural habitat is prone to fire. To compensate, the species will coppice from its roots after being burnt down.

Pleiospilos nelii, the split rock, splitrock or living granite, is a species of flowering plant in the family Aizoaceae, native to South Africa. It grows in semi-arid areas with rainfall of between 150mm and 300mm, in the Karoo of South Africa.

Atkinsonia is a hemi-parasitic shrub with oppositely set, entire leaves and yellowish, later rusty-red colored flowers, that is found in Eastern Australia. It is a monotypic genus, the only species being Atkinsonia ligustrina, and is assigned to the showy mistletoe family, Loranthaceae. It is sometimes called Louisa's mistletoe.
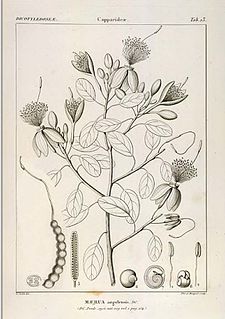
Maerua angolensis is a 10m tall, occasionally deciduous tree of the Capparaceae or caper family, often growing on termitaria and in thickets fringing seasonal watercourses, up to 1800m. Though never common, it is widespread in tropical Africa and arid regions, being absent from high-rainfall regions.

Clausena anisata (Willd.) Hook.f. ex Benth. is a deciduous shrub or small tree, belonging to the Rutaceae or Citrus family, and widespread in the Afrotropical realm or Sub-Saharan Africa, but absent from the drier regions. It is also found in tropical and South-East Asia, growing in India and Sri Lanka and extending as far as Queensland in north-eastern Australia and some Pacific islands. It is cultivated in Malaysia and Indonesia. As with other plants useful to mankind its large range of medicinal properties has led to a global distribution and its growth wherever the climate is suitable. It grows in higher-rainfall regions in savanna, thickets, riverine forest, disturbed areas and secondary forest, up to an altitude of 3000 m. The leaves, which are foetid when bruised, give rise to the common name 'Horsewood' or the more descriptive Afrikaans common name 'Perdepis', meaning 'horse urine'.

Eucomis zambesiaca is a bulbous plant in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, native to southern Africa, from Zimbabwe through Malawi to the Limpopo Province of South Africa. One of the smaller species in the genus, it has a rosette of leaves about 45 cm (18 in) across and white flowers in a spike to about 30 cm (12 in) tall.
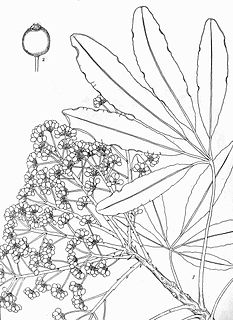
Schefflera umbellifera is an evergreen to semi-deciduous Southern African tree of 15-20m growing in escarpment and coastal forest in Malawi, through eastern Zimbabwe and Mozambique along the east coast to South Africa, as far south as the Garden Route. It belongs to the Araliaceae or Cabbage Tree family and is one of some 600 species in the genus Schefflera, created by J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. in 1776 to honour the 18th century German physician and botanist Johann Peter Ernst von Scheffler of Danzig, and not to be confused with writer and physician Jacob Christoph Scheffler (1698-1745) of Altdorf bei Nürnberg.
Iris zaprjagajevii is a species in the genus Iris, it is also in the subgenus Scorpiris. It is a bulbous perennial from Central Asia. It has greyish-green leaves, short stem and white flowers with a yellow crest.

Hymenodictyon parvifolium Oliv. is a small rubiaceous African tree and is one of some 24 species in the genus, with a tropical African and Asian distribution. This species grows as a small tree to some 5 metres tall, or sometimes a liane or scrambler to 10.5 m, and is found in low-altitude woodland.

Pteleopsis myrtifolia is one of some 10 African species in this genus in the family of Combretaceae. It is the only Pteleopsis species to occur in Southern Africa. Its flowers are strongly scented and perceived by humans to be either 'honey-like' or 'cloying' or even 'stinky'. The timber is red, hard and durable, and used for furniture and construction.
Odyssea paucinervis is a species of African plants in the grass family. The genus is named after the ancient Greek tale the "Odyssey", in allusion to the long journey the type species has taken through nine genera before settling in this one. The specific name means "few veined".

Boscia foetida, commonly known as the stink shepherd's tree and the smelly shepherd's bush, is an evergreen shrub or tree that is native to the warmer and drier parts southern Africa. It is found in semi-desert and arid bushveld, and in the west it occurs commonly in areas which are otherwise sparsely wooded. It is known for the particularly unpleasant smell of its flowers which appear during early spring, to which its specific name foetida alludes. Its freshly cut wood likewise has an unpleasant smell, and has traditional medicinal and magical uses, for instance as a protection against lightning. In central Botswana the village of Mopipi is named after this species.

Barthlottia madagascariensis is the only species in the genus Barthlottia of flowering plants in the family Scrophulariaceae. The large shrub with conspicuous purple flowers is native to a very restricted area in southeast Madagascar and was described in 1996.

Exomis is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Amaranthaceae. It just contains one species, Exomis microphylla(Thunb.) Aellen It is also in the Chenopodioideae subfamily.






















