
Vicia villosa, known as the hairy vetch, fodder vetch or winter vetch, is a plant native to some of Europe and western Asia. It is a legume, grown as a forage crop, fodder crop, cover crop, and green manure. Although non-native, it occurs in all US states and is considered invasive by some states, such as Alaska, Florida, Georgia, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Oregon, and Washington state — as well as in Japan and some parts of Europe where it is not native. It is also found in most Canadian provinces.

Portulaca grandiflora is a succulent flowering plant in the family Portulacaceae, native to southern Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay and often cultivated in gardens. It has many common names, including rose moss, eleven o'clock, Mexican rose, moss rose, sun rose, rock rose, and moss-rose purslane.

Miconia crenata, commonly called soapbush, clidemia or Koster's curse, is a perennial shrub. It is an invasive plant species in many tropical regions of the world, creating serious damage.

Thunbergia alata, commonly called black-eyed Susan vine, is a herbaceous perennial climbing plant species in the family Acanthaceae. It is native to Eastern Africa, and has been naturalized in other parts of the world.

Wikstroemia villosa, the hairy wikstroemia or hairy false ohelo, is a tropical species of plant in the Thymelaeaceae family.

Abronia villosa is a species of sand-verbena known by the common names desert sand-verbena and chaparral sand-verbena. It is in the four o'clock plant family (Nyctaginaceae). It is native to sandy areas in the deserts of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico, associated with creosote-bush and coastal-sage scrub habitats.
Monardella siskiyouensis is an uncommon species of flowering plant in the mint family known by the common name Siskiyou monardella.

Microsteris is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the phlox family containing the single species Microsteris gracilis, known by the common name slender phlox.

Quincula is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. The sole species it contains, Quincula lobata, is commonly known as Chinese lantern, lobed groundcherry, or purple groundcherry.
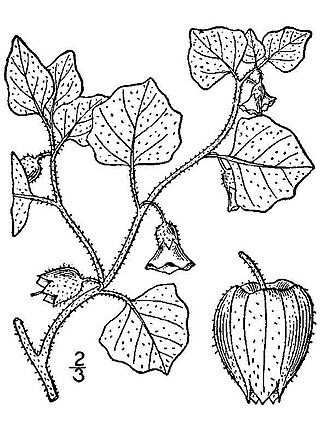
Physalis pubescens is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family known by many common names, including husk tomato, low ground-cherry and hairy groundcherry in English, and muyaca and capulí in Spanish. It is native to the Americas, including the southern half of the United States, Mexico, Central and much of South America. It can be found elsewhere as an introduced species and sometimes a weed. It can grow in many types of habitat, including disturbed areas. This is an annual herb producing a glandular, densely hairy stem up to about 60 cm (24 in) in maximum height from a taproot. The oval or heart-shaped leaves are 3–9 cm (1.2–3.5 in) long and have smooth or toothed edges. The flowers blooming from the leaf axils are bell-shaped and about a centimeter long. They are yellow with five dark spots in the throats, and have five stamens tipped with blue anthers. The five-lobed calyx of sepals at the base of the flower enlarges as the fruit develops, becoming an inflated, ribbed, lanternlike structure 2–4 cm (0.79–1.57 in) long which contains the berry.

Spergularia villosa is a species of flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae known by the common name hairy sandspurry. It is native to southern South America, and it is known in the southwestern United States and Baja California as an introduced species and casual weed. It grows in a wide variety of habitat types. It is a small perennial herb producing a sprawling stem up to 30 centimeters long with a woody base. It is coated in glandular hairs. The leaves are generally linear in shape and measure a few centimeters long. They are accompanied by dull white lance-shaped stipules. The flowers have hairy, glandular sepals and five oval whitish petals.

Sphaeralcea coulteri is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family known by the common name Coulter's globemallow. It is native to the Sonoran Desert, its distribution extending from northern Mexico north into California and Arizona. It is an annual herb, its slender, hairy stems sprawling or growing erect to a maximum height near 1.5 meters. The thin, gray-green leaf blades are wide and short, heart-shaped or triangular in shape, and measure up to about 5 centimeters long. They have a few wide lobes along the edges which may have teeth or smaller lobes. The leafy inflorescence bears clusters of flowers each with five wedge-shaped orange petals around a centimeter long, and yellow anthers.

Potentilla villosa is a species of flowering plant in the rose family, Rosaceae. Its common names include villous cinquefoil, northern cinquefoil, and hairy cinquefoil. It is native to northwestern North America, where its distribution extends from Alaska to Alberta to Oregon. There are records from eastern Asia.

Pyrrocoma clementis is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name tranquil goldenweed. It is native to Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming in the United States.

Thapsia villosa, commonly known as the villous deadly carrot, is a species of poisonous herbaceous plants in the genus Thapsia. It grows to about 70 to 190 cm in height. It has pinnate hairy leaves with sheath-like petioles. The flowers are yellow in color and borne on compound umbels. They develop into fruits with four wings characteristic of the genus. It is native to southwestern Europe and northwestern Africa surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. The plant was used extensively for traditional medicine since around the 3rd century BC.

Gagea villosa, common name hairy star of Bethlehem, is a Eurasian and North African plant species in the lily family.

Heterotheca villosa, called the hairy goldenaster, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae found in central and western North America.

Mairia crenata is a perennial herbaceous plant of mostly 2–15 cm (1–6 in) high that is assigned to the family Asteraceae. It has a woody rootstock of up to 5 cm (2 in) long, from which brown, fleshy roots develop. The five to eighteen, hard and leathery, spoon-shaped leaves are in one to three rosettes, have a distinct main vein, blunt or pointy tip, often dark red or blackish margins with rounded teeth and a ½–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) long stalk-like foot, often initially somewhat woolly hairy, on particularly the lower surface and the main vein, but this is easily rubbed off the shiny surfaces. Each rosette produces mostly one, sometimes up to four, mostly rusty or whitish woolly hairy, brown or dark red inflorescence stalks, usually 1½–15 cm long, each with two to eight, initially woolly, line-shaped to oval bracts, the lowest up to 3 cm (1.2 in), decreasing size further up, and carrying mostly one, rarely up to three flower heads. The flower heads have a bell-shaped involucre with about 40 bracts, sixteen to thirty three violet to white ray florets of about 1¼–1⅞ cm long, and many yellow disc florets. The species flowers anywhere between February and December but only after a fire has destroyed the overhead biomass or serious disturbance. It is an endemic species that is restricted to the Eastern Cape and Western Cape provinces of South Africa.
Salix crenata is a cushion-shaped growing shrub from the genus of willow (Salix) with about 8 millimeter long leaf blades. The natural range of the species is in China.

Babiana villosa is a species of geophyte of 10–20 cm (3.9–7.9 in) high that is assigned to the family Iridaceae. It has mauve-pink, purple or scarlet star-symmetrical wide chalice-shaped flowers with narrow tube, large, blackish or dark purple anthers, and velvety hairy, lance-shaped, laterally compressed leaves, set in a fan. Flowers occur during August and September. Its grows between Malmesbury and Wellington in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is commonly called red babiana in English and rooibobbejaantjie in Afrikaans.


















