
The Squaliformes are an order of sharks that includes about 126 species in seven families.

Batrachoididae is the only family in the ray-finned fish order Batrachoidiformes. Members of this family are usually called toadfish or frogfish: both the English common name and scientific name refer to their toad-like appearance.

A midshipman fish is any species of toadfish belonging to the genus Porichthys. Historically, there have been two common names. Porichthys refers to the well developed pores on the fish, and this led to the common name "Porous Catfish". The other common name, "Midshipman" is based on the pattern of button-like luminous spots (photophores) which resemble the buttons on the uniforms of young naval officers known as Midshipmen.
Chelon is a genus of mullets found in coastal marine waters, estuaries and rivers in the Atlantic Ocean and Arabian Sea.

Batrachoides is a genus of toadfishes.

Tetractenos is a genus of Tetraodontidae. The genus can be found throughout the Indo-West Pacific and Australia's southern and eastern coastlines.

The smooth toadfish is a species of fish in the pufferfish family Tetraodontidae. It is native to shallow coastal and estuarine waters of southeastern Australia, where it is widespread and abundant. French naturalist Christophe-Paulin de La Poix de Fréminville described the species in 1813, though early records confused it with its close relative, the common toadfish. The two are the only members of the genus Tetractenos after going through several taxonomic changes since discovery.

Allenbatrachus is a genus of toadfishes found in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans. The generic name honours the Humboldt State University ichthyologist George Allen (1923-2011), who introduced David Greenfield, who coined the name, to ichthyology.

The banded toadfish is a species of toadfish found along the Pacific coast of South America where it is found in Chile, Ecuador and Peru. This species grows to a length of 28 centimetres (11 in) TL. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Aphos. Unlike the other genus, Porichthys in this subfamily the banded toadfish lacks photophores.
Austrobatrachus is a genus of toadfishes found in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans off the coast of South Africa.
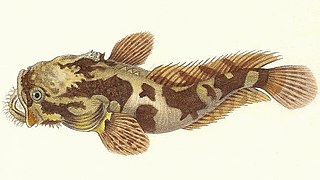
Batrichthys is a genus of toadfishes.

Colletteichthys is a genus of toadfishes found in the western Indian Ocean. The generic name is a compound of the surname Collette, in honour of the American ichthyologist Bruce Baden Collette to recognise his contribution to the study of toadfish, and the Greek ichthys meaning "fish".

Opsanus is a genus of toadfishes found in the western Atlantic Ocean. It currently has six recognised species, with the latest one described in 2005.
The broadbodied toadfish is a species of toadfish only known from the coasts of South Africa. This species grows to a length of 29 centimetres (11 in) TL. Its binomial name honours two people: the generic name honours Dr. C. Riekert who sent J. L. B. Smith "many specimens", while the specific name honours P. V. Ellis who collected the type specimen.

Thalassophryne is a genus of toadfishes found in the western Atlantic Ocean with one species found in the Amazon River and some of its tributaries.

Ambophthalmos is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Psychrolutidae. These fishes are found in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
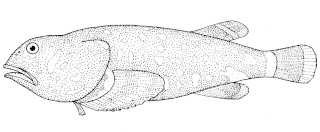
Neophrynichthys is a small genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Psychrolutidae, the fatheads. These fishes are found in the southwestern Pacific Ocean waters around New Zealand.

The Halophryninae is a largely Old World subfamily of toadfish, part of the family Batrachoididae.

Thalassophryne maculosa, the Cano toadfish, is a species of toadfish which is common along the Caribbean coasts of South America from Colombia to Trinidad and Venezuela. It occurs on the sandy bottoms of reef flats, lagoons, and seaward edges of reefs where it sits partially buried in the substrate. It is a venomous species with the venom being delivered through spines and wounds from the spines have been known to cause severe symptoms of pain and illness that may persist for up to a week. A study of the holotype of Batrachus uranoscopus, said to be a freshwater toadfish from Madagascar, in the Muséum national d’Histoire Naturelle in Paris found that it was most probably a misslabelled specimen of Thalassophryne maculosa and that subsequent records of Batrachus uranoscopus were attributable to Allenbatrachus meridionalis, a species found in Madagascar. T. maculosa is the type species of the genus Thalassophryne, the generic name translates from Greek as "sea toad" while the specific name is Latin for "spotted".
The toadfish goby is a species of bony fish in the family Gobiidae which is found in areas of sandy substrates among coral reefs. It occurs in the western Atlantic Ocean from the Bahamas south through the Caribbean Sea as well as along the Central and South American coast from Belize to Santa Marta, Colombia. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Cryptopsilotris, although it was formerly classified under Psilotris and its generic name means "hidden Pilotris", meaning that it was hidden within that genus.













