
Common Lisp (CL) is a dialect of the Lisp programming language, published in American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard document ANSI INCITS 226-1994 (S2018). The Common Lisp HyperSpec, a hyperlinked HTML version, has been derived from the ANSI Common Lisp standard.

Lisp is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in the late 1950s, it is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure.

In computer programming, a macro is a rule or pattern that specifies how a certain input should be mapped to a replacement output. Applying a macro to an input is known as macro expansion. The input and output may be a sequence of lexical tokens or characters, or a syntax tree. Character macros are supported in software applications to make it easy to invoke common command sequences. Token and tree macros are supported in some programming languages to enable code reuse or to extend the language, sometimes for domain-specific languages.

Lua is a lightweight, high-level, multi-paradigm programming language designed mainly for embedded use in applications. Lua is cross-platform software, since the interpreter of compiled bytecode is written in ANSI C, and Lua has a relatively simple C application programming interface (API) to embed it into applications.

In computer science, an interpreter is a computer program that directly executes instructions written in a programming or scripting language, without requiring them previously to have been compiled into a machine language program. An interpreter generally uses one of the following strategies for program execution:
- Parse the source code and perform its behavior directly;
- Translate source code into some efficient intermediate representation or object code and immediately execute that;
- Explicitly execute stored precompiled bytecode made by a compiler and matched with the interpreter's virtual machine.
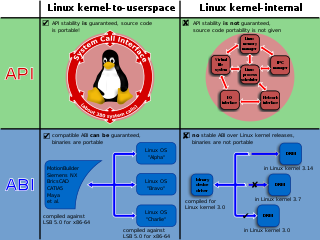
In computer software, an application binary interface (ABI) is an interface between two binary program modules. Often, one of these modules is a library or operating system facility, and the other is a program that is being run by a user.

Microsoft Visual C++ (MSVC) is a compiler for the C, C++, C++/CLI and C++/CX programming languages by Microsoft. MSVC is proprietary software; it was originally a standalone product but later became a part of Visual Studio and made available in both trialware and freeware forms. It features tools for developing and debugging C++ code, especially code written for the Windows API, DirectX and .NET.
Programming languages can be grouped by the number and types of paradigms supported.
The C preprocessor is the macro preprocessor for several computer programming languages, such as C, Objective-C, C++, and a variety of Fortran languages. The preprocessor provides inclusion of header files, macro expansions, conditional compilation, and line control.

D, also known as dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is now a very different language. As it has developed, it has drawn inspiration from other high-level programming languages. Notably, it has been influenced by Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel.

Factor is a stack-oriented programming language created by Slava Pestov. Factor is dynamically typed and has automatic memory management, as well as powerful metaprogramming features. The language has a single implementation featuring a self-hosted optimizing compiler and an interactive development environment. The Factor distribution includes a large standard library.
In computer science, a tail call is a subroutine call performed as the final action of a procedure. If the target of a tail is the same subroutine, the subroutine is said to be tail recursive, which is a special case of direct recursion. Tail recursion is particularly useful, and is often easy to optimize in implementations.

GNU Ubiquitous Intelligent Language for Extensions is the preferred extension language system for the GNU Project and features an implementation of the programming language Scheme. Its first version was released in 1993. In addition to large parts of Scheme standards, Guile Scheme includes modularized extensions for many different programming tasks.

Racket is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language. The Racket language is a modern dialect of Lisp and a descendant of Scheme. It is designed as a platform for programming language design and implementation. In addition to the core Racket language, Racket is also used to refer to the family of programming languages and set of tools supporting development on and with Racket. Racket is also used for scripting, computer science education, and research.
A foreign function interface (FFI) is a mechanism by which a program written in one programming language can call routines or make use of services written or compiled in another one. An FFI is often used in contexts where calls are made into a binary dynamic-link library.
Scheme 48 is a programming language, a dialect of the language Scheme, an implementation using an interpreter which emits bytecode. It has a foreign function interface for calling functions from the language C and comes with a library for regular expressions (regex), and an interface for Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX). It is supported by the portable Scheme library SLIB, and is the basis for the Scheme shell Scsh. It has been used in academic research. It is free and open-source software released under a BSD license.
Gambit, also called Gambit-C, is a programming language, a variant of the language family Lisp, and its variants named Scheme. The Gambit implementation consists of a Scheme interpreter, and a compiler which compiles Scheme into the language C, which makes it cross-platform software. It conforms to the standards R4RS, R5RS, and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and to several Scheme Requests for Implementations (SRFIs). Gambit was released first in 1988, and Gambit-C (Gambit with a C backend) was released first in 1994. They are free and open-source software released under a GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) 2.1, and Apache License 2.0.
SISC is an R5RS Scheme implementation, which includes a full number tower, hygienic macros, proper tail recursion, and first class continuations. SISC is short for Second Interpreter of Scheme Code, in reference to its predecessor LISC, the Lightweight Interpreter of Scheme Code.

Rust is a general-purpose programming language emphasizing performance, type safety, and concurrency. It enforces memory safety, meaning that all references point to valid memory. It does so without a traditional garbage collector; instead, both memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references at compile time.
Java bytecode is the instruction set of the Java virtual machine (JVM), the language to which Java and other JVM-compatible source code is compiled. Each instruction is represented by a single byte, hence the name bytecode, making it a compact form of data.











