Related Research Articles

The American National Standards Institute is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide.

Common Lisp (CL) is a dialect of the Lisp programming language, published in American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard document ANSI INCITS 226-1994 (S2018). The Common Lisp HyperSpec, a hyperlinked HTML version, has been derived from the ANSI Common Lisp standard.

Hypertext is text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typically activated by a mouse click, keypress set, or screen touch. Apart from text, the term "hypertext" is also sometimes used to describe tables, images, and other presentational content formats with integrated hyperlinks. Hypertext is one of the key underlying concepts of the World Wide Web, where Web pages are often written in the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). As implemented on the Web, hypertext enables the easy-to-use publication of information over the Internet.
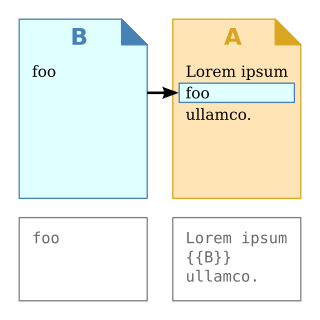
In computer science, transclusion is the inclusion of part or all of an electronic document into one or more other documents by reference via hypertext. Transclusion is usually performed when the referencing document is displayed, and is normally automatic and transparent to the end user. The result of transclusion is a single integrated document made of parts assembled dynamically from separate sources, possibly stored on different computers in disparate places.

Lisp is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in the late 1950s, it is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure.
Symbolics, Inc., was a privately held American computer manufacturer that acquired the assets of the former company and continues to sell and maintain the Open Genera Lisp system and the Macsyma computer algebra system.

In computer programming, an S-expression is an expression in a like-named notation for nested list (tree-structured) data. S-expressions were invented for and popularized by the programming language Lisp, which uses them for source code as well as data.
Kent M. Pitman (KMP) is a programmer who has been involved for many years in the design, implementation, and use of systems based on the programming languages Lisp and Scheme. Since 2010, he has been President of HyperMeta, Inc.

The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming in ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp.

Guy Lewis Steele Jr. is an American computer scientist who has played an important role in designing and documenting several computer programming languages and technical standards.
X3J13 is the name of a technical committee which was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards. The X3J13 committee was formed in 1986 to draw up an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Common Lisp standard based on the first edition of the book Common Lisp the Language, by Guy L. Steele Jr., which was formerly a de facto standard for the language. The primary output of X3J13 was an American National Standard for programming language Common Lisp (X3.226/1994), approved December 8, 1994. X3J13 later worked with International Organization for Standardization (ISO) working group SC22/WG16 on an internationally standardised dialect of Lisp named ISLISP.

Allegro Common Lisp is a programming language with an integrated development environment (IDE), developed by Franz Inc. It is a dialect of the language Lisp, a commercial software implementation of the language Common Lisp. Allegro CL provides the full American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Common Lisp standard with many extensions, including threads, CLOS streams, CLOS MOP, Unicode, SSL streams, implementations of various Internet protocols, OpenGL interface. The first version of Allegro Common Lisp was finished at the end of 1986, originally called Extended Common Lisp. Allegro CL is available for many operating systems including Microsoft Windows (32/64-bit), and many Unix and Unix-like, 32-bit or 64-bit, including macOS, Linux (32/64-bit), FreeBSD (32-bit), Solaris, UNICOS, and UTS. Internationalization and localization support is based on Unicode. It supports various external text encodings and provides string and character types based on Universal Coded Character Set 2 (UCS-2). Allegro CL can be used with and without its integrated development environment (IDE), which is available for Windows, Linux, and on macOS in version 8.2. The IDE includes development tools including an editor and an interface designer. Allegro CL can be used to deliver applications.
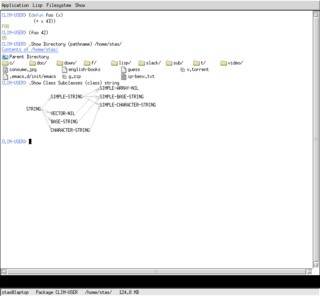
The Common Lisp Interface Manager (CLIM) is a Common Lisp-based programming interface for creating user interfaces, i.e., graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It provides an application programming interface (API) to user interface facilities for the programming language Lisp. It is a fully object-oriented programming user interface management system, using the Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) and is based on the mechanism of stream input and output. There are also facilities for output device independence. It is descended from the GUI system Dynamic Windows of Symbolics' Lisp machines between 1988 and 1993.
... you can check out Common Lisp Interface Manager (CLIM). A descendant of the Symbolics Lisp machines GUI framework, CLIM is powerful but complex. Although many commercial Common Lisp implementations actually support it, it doesn't seem to have seen a lot of use. But in the past couple years, an open-source implementation of CLIM, McCLIM – now hosted at Common-Lisp.net – has been picking up steam lately, so we may be on the verge of a CLIM renaissance. – From Practical Common Lisp
The Serial Item and Contribution Identifier (SICI) was a code used to uniquely identify specific volumes, articles or other identifiable parts of a serial. It was "intended primarily for use by those members of the bibliographic community involved in the use or management of serial titles and their contributions". Developed over 1993–1995, NISO adopted SICI as a standard in 1996, then reaffirmed it in 2002. It was withdrawn in 2012.
LispWorks is computer software, a proprietary implementation and integrated development environment (IDE) for the programming language Common Lisp. LispWorks was developed by the UK software company Harlequin Ltd., and first published in 1989. Harlequin ultimately spun off its Lisp division as Xanalys Ltd., which took over management and rights to LispWorks. In January 2005, the Xanalys Lisp team formed LispWorks Ltd. to market, develop, and support the software.
Common Lisp the Language is a reference book by Guy L. Steele about a set of technical standards and programming languages named Common Lisp.
AllegroGraph is a closed source triplestore which is designed to store RDF triples, a standard format for Linked Data. It also operates as a document store designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, in JSON-LD format. AllegroGraph is currently in use in commercial projects and a US Department of Defense project. It is also the storage component for the TwitLogic project that is bringing the Semantic Web to Twitter data.

OpenLisp is a programming language in the Lisp family developed by Christian Jullien from Eligis. It conforms to the international standard for ISLISP published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ISO/IEC 13816:1997(E), revised to ISO/IEC 13816:2007(E).

LISP is a university textbook on the Lisp programming language, written by Patrick Henry Winston and Berthold Klaus Paul Horn. It was first published in 1981, and the third edition of the book was released in 1989. The book is intended to introduce the Lisp programming language and its applications.
References
- ↑ "CLHS: About the Common Lisp HyperSpec". LispWorks. 1996–2005. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ↑ "Common Lisp HyperSpec". School of Computer Science. Carnegie Mellon University. 1996-07-23. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ↑ "CLHS: About the Common Lisp HyperSpec". LispWorks. 1996–2005. Retrieved 2013-10-05.
- ↑ Sirelkhatim, Mohammed. "[Guy Steele] Common LISP. The Language(BookZZ.org)".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)