
Galls or cecidia are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to benign tumors or warts in animals. They can be caused by various parasites, from viruses, fungi and bacteria, to other plants, insects and mites. Plant galls are often highly organized structures so that the cause of the gall can often be determined without the actual agent being identified. This applies particularly to insect and mite plant galls. The study of plant galls is known as cecidology.

Plant diseases are diseases in plants caused by pathogens and environmental conditions. Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrates, or other pests that affect plant health by eating plant tissues and causing injury that may admit plant pathogens. The study of plant disease is called plant pathology.

Phytoplasmas are obligate intracellular parasites of plant phloem tissue and of the insect vectors that are involved in their plant-to-plant transmission. Phytoplasmas were discovered in 1967 by Japanese scientists who termed them mycoplasma-like organisms. Since their discovery, phytoplasmas have resisted all attempts at in vitro culture in any cell-free medium; routine cultivation in an artificial medium thus remains a major challenge. Phytoplasmas are characterized by the lack of a cell wall, a pleiomorphic or filamentous shape, a diameter normally less than 1 μm, and a very small genome.

Plant viruses are viruses that have the potential to affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses can be pathogenic to vascular plants.

Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are 522 species in this family, assigned to 15 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.

Dicistroviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Invertebrates, including aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, and silkworms, serve as natural hosts. There are 15 species in this family, assigned to three genera. Diseases associated with this family include: DCV: increased reproductive potential. extremely pathogenic when injected with high associated mortality. CrPV: paralysis and death.

Leafhopper is the common name for any species from the family Cicadellidae. These minute insects, colloquially known as hoppers, are plant feeders that suck plant sap from grass, shrubs, or trees. Their hind legs are modified for jumping, and are covered with hairs that facilitate the spreading of a secretion over their bodies that acts as a water repellent and carrier of pheromones. They undergo a partial metamorphosis, and have various host associations, varying from very generalized to very specific. Some species have a cosmopolitan distribution, or occur throughout the temperate and tropical regions. Some are pests or vectors of plant viruses and phytoplasmas. The family is distributed all over the world, and constitutes the second-largest hemipteran family, with at least 20,000 described species.

Phyllody is the abnormal development of floral parts into leafy structures. It is generally caused by phytoplasma or virus infections, though it may also be because of environmental factors that result in an imbalance in plant hormones. Phyllody causes the affected plant to become partially or entirely sterile, as it is unable to produce normal flowers.
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral species of the genus Closterovirus that causes the most economically damaging disease to its namesake plant genus, Citrus. The disease has led to the death of millions of Citrus trees all over the world and has rendered millions of others useless for production. Farmers in Brazil and other South American countries gave it the name "tristeza", meaning sadness in Portuguese and Spanish, referring to the devastation produced by the disease in the 1930s. The virus is transmitted most efficiently by the brown citrus aphid.

Maize streak virus (MSV) is a virus primarily known for causing maize streak disease (MSD) in its major host, and which also infects over 80 wild and domesticated grasses. It is an insect-transmitted pathogen of maize in the genus Mastrevirus of the family Geminiviridae that is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa and neighbouring Indian Ocean island territories such as Madagascar, Mauritius and La Reunion. The A-strain of MSV (MSV-A) causes sporadic maize streak disease epidemics throughout the maize-growing regions of Africa. MSV was first described by the South African entomologist Claude Fuller who referred to it in a 1901 report as "mealie variegation".
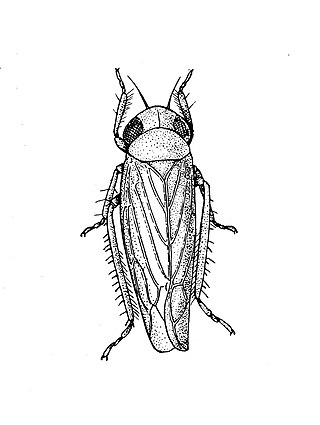
The beet leafhopper, also sometimes known as Neoaliturus tenellus, is a species of leafhopper which belongs to the family Cicadellidae in the order Hemiptera.

Beet curly top virus (BCTV) is a pathogenic plant virus of the family Geminiviridae, containing a single-stranded DNA. The family Geminiviridae consists of nine genera based on their host range, virus genome structure, and type of insect vector. BCTV is a Curtovirus affecting hundreds of plants. The only known vector is the beet leafhopper, which is native to the Western United States.

Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the family Bromoviridae. This virus has a worldwide distribution and a very wide host range, having the reputation of the widest host range of any known plant virus. It can be transmitted from plant to plant both mechanically by sap and by aphids in a stylet-borne fashion. It can also be transmitted in seeds and by the parasitic weeds, Cuscuta sp. (dodder).

Maize dwarf mosaic virus (MDMV) is a pathogenic plant virus of the family Potyviridae. Depending on the corn plant’s growth stage, the virus can have severe implications to the corn plant’s development which can also result in economic consequences to the producer of the crop.

Phytoreovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Reoviridae, in the subfamily Sedoreovirinae. They are non-turreted reoviruses that are major agricultural pathogens, particularly in Asia. Oryza sativa for RDV and RGDV, dicotyledonous for WTV, and leafhoppers serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: WTV: galls (tumor). RDV: dwarf disease of rice. RGDV: dwarfing, stunting, and galls.

Peregrinus maidis, commonly known as the corn planthopper, is a species of insect in the order Hemiptera and the family Delphacidae. It is widespread throughout most tropical and subtropical regions on earth, including southern North America, South America, Africa, Australia, Southeast Asia and China. P. maidis are a commercially important pest of maize and its relatives. In addition to physical plant damage, P. maidis is the vector for several species-specific maize viruses, including maize stripe virus, maize mosaic virus and the non-pathogenic Peregrinus maidis reovirus.

Macrostelini is a tribe in the Deltocephalinae subfamily of leafhoppers. Macrostelini contains 37 genera and over 300 species. The tribe has a cosmopolitan distribution. Some species in the genus Cicadulina are agricultural pests and transmit maize streak virus in Sub-saharan Africa.
Cicadulina mbila, the maize leafhopper, is a leafhopper species in the genus Cicadulina.

Corn stunt disease is a bacterial disease of corn and other grasses. Symptoms include stunted growth and leaves turning red. It is caused by the bacterium Spiroplasma kunkelii.














