
Cnidaria is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, including jellyfish, hydroids, sea anemone, corals and some of the smallest marine parasites. Their distinguishing features are a decentralized nervous system distributed throughout a gelatinous body and the presence of cnidocytes or cnidoblasts, specialized cells with ejectable flagella used mainly for envenomation and capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick.

Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.

Anthozoa is a class of marine invertebrates which includes the sea anemones, stony corals and soft corals. Adult anthozoans are almost all attached to the seabed, while their larvae can disperse as part of the plankton. The basic unit of the adult is the polyp; this consists of a cylindrical column topped by a disc with a central mouth surrounded by tentacles. Sea anemones are mostly solitary, but the majority of corals are colonial, being formed by the budding of new polyps from an original, founding individual. Colonies are strengthened by calcium carbonate and other materials and take various massive, plate-like, bushy or leafy forms.

Antipatharians, also known as black corals or thorn corals, are an order of soft deep-water corals. These corals can be recognized by their jet-black or dark brown chitin skeletons, which are surrounded by their colored polyps. Antipatharians are a cosmopolitan order, existing in nearly every oceanic location and depth, with the sole exception of brackish waters. However, they are most frequently found on continental slopes under 50 m (164 ft) deep. A black coral reproduces both sexually and asexually throughout its lifetime. Many black corals provide housing, shelter, food, and protection for other animals.

Zoanthids are an order of cnidarians commonly found in coral reefs, the deep sea and many other marine environments around the world. These animals come in a variety of different colonizing formations and in numerous different colors. They can be found as individual polyps, attached by a fleshy stolon or a mat that can be created from small pieces of sediment, sand and rock. The term "zoanthid" refers to all animals within this order Zoantharia, and should not be confused with "Zoanthus", which is one genus within Zoantharia.

Hexacorallia is a class of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are colonial and reef-forming, as well as all sea anemones, and zoanthids, arranged within five extant orders. The hexacorallia are distinguished from another class of Anthozoa, Octocorallia, in having six or fewer axes of symmetry in their body structure; the tentacles are simple and unbranched and normally number more than eight. These organisms are formed of individual soft polyps which in some species live in colonies and can secrete a calcite skeleton. As with all Cnidarians, these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile planktonic phase and a later characteristic sessile phase. Hexacorallia also include the significant extinct order of rugose corals.

Sea anemones are a group of predatory marine invertebrates constituting the order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the Anemone, a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemones are classified in the phylum Cnidaria, class Anthozoa, subclass Hexacorallia. As cnidarians, sea anemones are related to corals, jellyfish, tube-dwelling anemones, and Hydra. Unlike jellyfish, sea anemones do not have a medusa stage in their life cycle.

Discosoma is a genus of cnidarians in the order Corallimorpharia. Common names for the genus include mushroom anemone, disc anemone and elephant ear mushroom.

Tubastraea, also known as sun coral or sun polyps, is a genus of coral in the phylum Cnidaria. It is a cup coral in the family Dendrophylliidae.

Antipathidae is a family of corals in the order Antipatharia, commonly known as black corals. They are generally considered a deep-water taxon; however, some of the most diverse communities are known from tropical shallow waters.

Umimayanthus parasiticus, commonly known as the sponge zoanthid, is a species of coral in the order Zoantharia which grows symbiotically on several species of sponge. It is found in shallow waters in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico.

Millepora platyphylla is a species of fire coral, a type of hydrocoral, in the family Milleporidae. It is also known by the common names blade fire coral and plate fire coral. It forms a calcium carbonate skeleton and has toxic, defensive polyps that sting. It obtains nutrients by consuming plankton and via symbiosis with photosynthetic algae. The species is found from the Red Sea and East Africa to northern Australia and French Polynesia. It plays an important role in reef-building in the Indo-Pacific region. Depending on its environment, it can have a variety of different forms and structures.
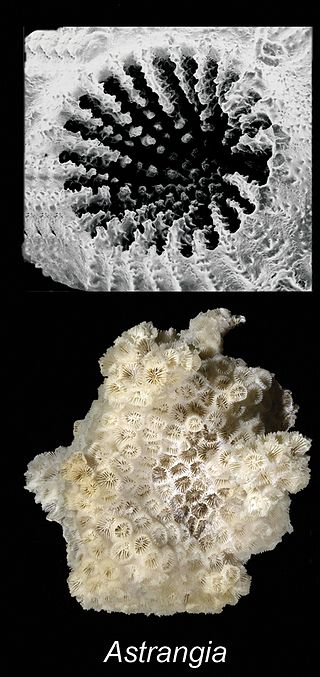
Astrangia poculata, the northern star coral or northern cup coral, is a species of non-reefbuilding stony coral in the family Rhizangiidae. It is native to shallow water in the western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. It is also found on the western coast of Africa. The International Union for Conservation of Nature lists this coral as being of "least concern". Astrangia poculata is an emerging model organism for corals because it harbors a facultative photosymbiosis, is a calcifying coral, and has a large geographic range. Research on this emerging model system is showcased annually by the Astrangia Research Working Group, collaboratively hosted by Roger Williams University, Boston University, and Southern Connecticut State University

Isozoanthus sulcatus is a species of zoanthid in the family Parazoanthidae.

Aphanipathes is a diverse genus of black corals in the family Aphanipathidae, typified by large polypar spines. However, there are some disagreement in the correct taxonomic classification of this genus. The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) classifies Aphanipathes as being a genus of the family Aphanipathidae while the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS) classifies it as a genus of the family Antipathidae.

Blastomussa merleti, commonly known as pineapple coral, is a species of large polyp stony coral. It is unclear in which family the genus Blastomussa belongs. This coral is native to the west and central Indo-Pacific region and is sometimes used in reef aquaria.

Porites cylindrica, commonly known as hump coral, is a stony coral belonging to the subclass Hexacorallia in the class Anthozoa. Hexacorallia differ from other subclasses in that they have 6 or fewer axes of symmetry. Members of this class possess colonial polyps which can be reef-building, secreting a calcium carbonate skeleton. They are dominant in both inshore reefs and midshelf reefs.
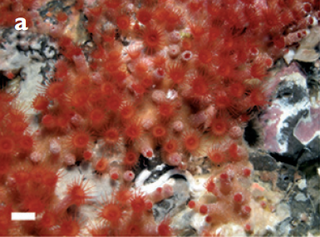
Terrazoanthus onoi is a species of uncertain validity of macrocnemic zoanthid first found in the Galapagos. It is potentially a junior synonym of Terrazoanthus patagonichus. It can be distinguished by its bright red oral disk colour, having about 32–40 tentacles, and having only basitrichs and mastigophores present in its pharynx.

Leiopathes glaberrima is a species of black coral of the order Antipatharia found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Seas deep water habitats. A very slow-growing species, it is among the oldest living animals on the planet.

Antipathella fiordensis is a species of colonial coral in the order Antipatharia, the black corals, so named because their calcareous skeletons are black. It was first described as Antipathes fiordensis by the New Zealand zoologist Ken R. Grange in 1990, from material collected in the steep-sided fiords of Fiordland in the southeastern South Island, New Zealand. A 2001 revision of the Antipatheria put this species in the newly-created genus Antipathella.



















