
The Hypocreales are an order of fungi within the class Sordariomycetes. In 2008, it was estimated that it contained some 237 genera, and 2647 species in seven families. Since then, a considerable number of further taxa have been identified, including an additional family, the Stachybotryaceae. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more families and genera to the order. According to the Catalog of Life, As of April 2021 the Hypocreales contains 6 families, 137 genera, and 1411 species. Hyde et al. (2020a) listed 14 families under Hypocreales, while, Wijayawardene et al. (2022) accepted 15 families in the order, where Cylindriaceae was additionally added. Earlier, Hyde et al. (2020a) had placed Cylindriaceae in class Xylariomycetidae. Samarakoon et al. (2022) agreed. Hence, Cylindriaceae should have been excluded from Hypocreales and placed in Xylariomycetidae. Xiao et al. (2022) recently introduced a new family Polycephalomycetaceae to Hypocreales.

The Nectriaceae comprise a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. It was circumscribed by brothers Charles and Louis René Tulasne in 1865. In 2020, an Outline of fungi was produced and listed 70 genera and about 1,336 species.

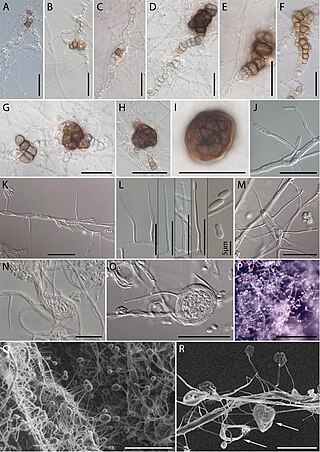
Stachybotrys is a genus of molds, hyphomycetes or asexually reproducing, filamentous fungi, now placed in the family Stachybotryaceae. The genus was erected by August Carl Joseph Corda in 1837. Historically, it was considered closely related to the genus Memnoniella, because the spores are produced in slimy heads rather than in dry chains. Recently, the synonymy of the two genera is generally accepted. Most Stachybotrys species inhabit materials rich in cellulose. The genus has a widespread distribution and contained about 50 species in 2008. There are 88 records of Stachybotrys on Species Fungorum, of which 33 species have DNA sequence data in GenBank. Species in the genus are commonly found in soil, plant litter and air and a few species have been found from damp paper, cotton, linen, cellulose-based building materials water-damaged indoor buildings, and air ducts from both aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
Clonostachys rosea f. rosea, also known as Gliocladium roseum, is a species of fungus in the family Bionectriaceae. It colonizes living plants as an endophyte, digests material in soil as a saprophyte and is also known as a parasite of other fungi and of nematodes. It produces a wide range of volatile organic compounds which are toxic to organisms including other fungi, bacteria, and insects, and is of interest as a biological pest control agent.

The Bionectriaceae are a family of fungi in the order Hypocreales. A 2008 estimate places 35 genera and 281 species in the family. Species in the family tend to grow on plant material, including woody debris, while some species associate with algae, bryophytes, or other fungi.

Bionectria is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. The genus was described in 1919 by mycologist Carlos Luigi Spegazzini to include species of Nectria that grew on living plant material.
Hydropisphaera is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. It consisted of 18 species in 2008, and 32 species in 2023.
Ijuhya is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. It consisted of seven species in 2008, and 21 species in 2023.

Lasionectria is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. It consisted of six species in 2008, and 16 in 2023.

Nectriopsis is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. The number of species in this genus varies between sources. The Dictionary of Fungi lists only 58 species, but the Catalogue of Life includes 72 species.
Protocreopsis is a genus of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. It consisted of nine species in 2008, and up to 11 species in 2023.
Niesslia is a genus of fungi in the family Niessliaceae. It was circumscribed by German mycologist Bernhard Auerswald in 1869, with Niesslia chaetomium assigned as the type species.

Corallomycetella is a genus of ascomycete fungi in the family Nectriaceae. Species of Corallomycetella are tropical, and are characterized by the formation of brightly colored rhizomorphs of their rhizostilbella-like asexual morphs. These fungi causes a number of plant diseases including 'violet root rot' of Theobroma cacao, root rot of Carica papaya, and 'stinking root disease' of several tropical woody plants. Two species of Corallomycetella are recognized: Corallomycetella elegans C. Herrera & P. Chaverri and Corallomycetella repens Rossman & Samuels. Corallomycetella jatrophae is now classified under Corallonectria.

Cosmospora is a genus of ascomycete fungi in the family Nectriaceae. The genus, as circumscribed by Rossman et al. (1998), included all the nectrioid species with small, reddish, non-ornamented sexual fruiting bodies that collapse laterally when dry. However, the genus was shown to be polyphyletic, and the majority of species were re-classified into revived or recently established genera that are monophyletic. Cosmosporasensu Rossman housed members of the following genera: Chaetopsina, Cylindrocladiella, Fusicolla, Macroconia, Mariannaea, Microcera, Pseudocosmospora, Stylonectria, and Volutella. Cosmospora was restricted to species having acremonium-like asexual morphs that grow on polypores and xylariaceous fungi by Gräfenhan in 2011. About 20 species are accepted in the genus.

Neonectria is a genus of fungi in the family Nectriaceae.

Corallonectria is a genus of ascomycete fungi in the family Nectriaceae. Species of Corallonectria are Neotropical. These fungi are characterized by the formation of brightly colored rhizomorphs and of copulated synnematous fusarium-like asexual morphs in culture. The asexual morph in nature has been rarely observed. The sexual fruiting bodies are furfuraceous and usually seated at the base of a reddish synnemata. It is a monotypic genus containing the sole species Corallonectria jatrophae. This species was formerly classified under Corallomycetella.
Gliomastix is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Bionectriaceae.
Volutella is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Nectriaceae.

Mariannaea is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Nectriaceae.












