
Herring are various species of forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.

The Ganges river dolphin is a species of freshwater dolphin classified in the family Platanistidae. It lives in the Ganges and related rivers of South Asia, namely in the countries of India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. It is related to the much smaller Indus river dolphin which lives in the Indus River in Pakistan and the Beas River of northwestern India.

Sprat is the common name applied to a group of forage fish belonging to the genus Sprattus in the family Clupeidae. The term also is applied to a number of other small sprat-like forage fish. Like most forage fishes, sprats are highly active, small, oily fish. They travel in large schools with other fish and swim continuously throughout the day.

The Ganges shark is a critically endangered species of requiem shark found in the Ganges River and the Brahmaputra River of India and Bangladesh. It is often confused with the more common bull shark, which also inhabits the Ganges River and is sometimes incorrectly referred to as the Ganges shark. The genus is currently considered to contain three recent species; genetic evidence has shown that both the Borneo river shark and Irrawaddy river shark should be regarded as synonyms of the Ganges shark, expanding the range of the species to Pakistan, Myanmar, Borneo, and Java. While the other members of the genus Glyphis occur in coastal marine waters as well as rivers, the Ganges shark is found only in fresh water, making it the world's only exclusively freshwater shark. The species remains poorly known and very rare.

The ilish, also known as the ilishi, hilsa, hilsa herring or hilsa shad, is a species of fish related to the herring, in the family Clupeidae. It is a very popular and sought-after food in the Bengal region, and is the national fish of Bangladesh and state fish of the Indian state of West Bengal.
Indo-Pacific king mackerel, also known as the spotted seer fish or spotted Spanish mackerel, is a sea fish among the mackerel variety of fishes. It is found in around the Indian Ocean and adjoining seas. It is a popular game fish, growing up to 45 kg (99 lb), and is a strong fighter that has on occasion been seen to leap out of the water when hooked.

The European sprat, also known as brisling, brisling sardine, bristling, garvie, garvock, Russian sardine, russlet, skipper or whitebait, is a species of small marine fish in the herring family Clupeidae. Found in European, West Asian and North African waters, it has silver grey scales and white-grey flesh. Specific seas in which the species occurs include the Irish Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea and Sea of the Hebrides. The fish is the subject of fisheries, particularly in Scandinavia, and is made into fish meal, as well as being used for human consumption. When used for food it can be canned, salted, breaded, fried, boiled, grilled, baked, deep fried, marinated, broiled, and smoked.

The European seabass, also known as the branzino, European bass, sea bass, common bass, white bass, capemouth, white salmon, sea perch, white mullet, sea dace or loup de mer, is a primarily ocean-going fish native to the waters off Europe's western and southern and Africa's northern coasts, though it can also be found in shallow coastal waters and river mouths during the summer months and late autumn. It is one of only six species in its family, Moronidae, collectively called the temperate basses.

Botia dario is a species of fish in the loach family Botiidae found in the Brahmaputra and Ganges basins in Bangladesh, Bhutan and northern India. The species is overall widespread.

Oreichthys cosuatis is a small cyprinid fish found in India and Bangladesh.In India it is found along the ganga and brahmaputra river drainage in the states of West bengal and odisha It is also reported from Thailand and Myanmar.
Bagarius bagarius, also known as the giant devil catfish or goonch, is a species of catfish in the genus Bagarius. It is generally reported as being found in large and medium rivers in South Asia, and is likely synonymous with B. yarrelli.

Chitala chitala is a knifefish from Bangladesh, India, Nepal, and Pakistan, found in the Brahmaputra, Indus, Ganges and Mahanadi River basins. It is sometimes known as the Indian featherback or Indian knifefish. In the past, it frequently included several related Chitala species, but these are now regarded as separate species. The main species confused with this species is C. ornata ; a Southeast Asian species seen regularly in the aquarium trade. The true C. chitala is very rare in the aquarium trade.

Bagarius yarrelli, also known as the goonch catfish, giant devil catfish, or simply Goonch, is a very large species of catfish in the genus Bagarius found in rivers in the Indian subcontinent. The species reaches up to 2 m (6.6 ft) in length. It may be synonymous with B. bagarius.

Gymnostomus ariza, the Reba or ariza labeo, is a cyprinid fish found in India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.

Nemacheilus corica is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Nemacheilus. It occurs in the foothills of the Himalayas in the drainage of the Ganges in Nepal and the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar and West Bengal. Its reported presence in other areas need to be confirmed.

Osteobrama cotio is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Osteobrama. This species had three subspecies named O. cotio cotio, O. cotio cunma and O. cotio peninsularis but these are now considered separate species. This species is found in the drainage basins of the Ganges-Brahmaputra including Jiri River in Manipur, Barak River in Silchar, in Brahmaputra River, Uzan Bazaar in Assam, and in Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab in India, and in Bangladesh. The presence of O. cotio in southern India and from the Indus basin of India and Pakistan needs to be confirmed. This species is threatened by extensive loss of habitat caused by pollution and deforestation.

Corica is a small genus of sprats that occur in rivers in South Asia and Southeast Asia. Two described species are placed in the genus.

The rice-paddy eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton in 1822, originally in the genus Ophisurus. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-West Pacific, including Somalia, Tanzania, South Africa, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Polynesia, Australia, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Kenya, Madagascar, the Philippines, Malaysia, Mozambique, Seychelles, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan, China, Thailand, Vietnam, and southern Yemen. It is an anadromous species and spawns in freshwater, often in rice paddies during the rainy season, earning it its common name. It also spends time in lagoons, estuaries and coastal rivers, in which it lives in burrows in the river bottom and bank. Males can reach a maximum total length (TL) of 100 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 70 cm.
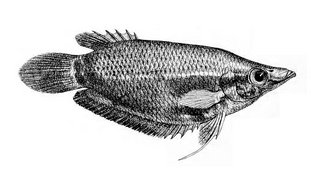
The frail gourami or noble gourami is a mouth brooding species of gourami native to northeastern India and Bangladesh. This species grows to a length of 10 cm (3.9 in). It is only seldom found in the aquarium trade, courtesy of its extreme sensitivity to shipping stress and high levels of aggression. This species is the only known member of its genus.

The corsula is a species of ray-finned fish from the mullet family Mugilidae. It is found in the rivers and estuaries of southern Asia, in India, Bangladesh, Nepal and Myanmar. It is presently regarded as the only species in the monospecific genus Rhinomugil.




















