
The Cuban cactus scrub is a xeric shrubland ecoregion that occupies 3,300 km2 (1,300 sq mi) on the leeward coast of Cuba. Most of it occurs in the southeastern part of the island in the provinces of Guantánamo and Santiago de Cuba. The ecoregion receives less than 800 mm (31 in) of rainfall annually. The principal soils are coastal rendzinas that were derived from coralline limestone. Cuban cactus scrub contains four vegetation zones: xerophytic coastal and subcoastal scrubland, coastal thorny semidesert, coastal sclerophyllous scrubland, and rocky coastal scrublands.

The Madagascar subhumid forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion that covers most of the Central Highlands of the island of Madagascar. They are included in the WWF's Global 200 list of outstanding ecoregions. Most of the original habitats have been lost due to human pressure.

Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location.

The Hawaiian tropical rainforests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Hawaiian Islands. They cover an area of 6,700 km2 (2,600 sq mi) in the windward lowlands and montane regions of the islands. Coastal mesic forests are found at elevations from sea level to 300 m (980 ft). Mixed mesic forests occur at elevations of 750 to 1,250 m, while wet forests are found from 1,250 to 1,700 m. Moist bogs and shrublands exist on montane plateaus and depressions. For the 28 million years of existence of the Hawaiian Islands, they have been isolated from the rest of the world by vast stretches of the Pacific Ocean, and this isolation has resulted in the evolution of an incredible diversity of endemic species, including fungi, mosses, snails, birds, and other wildlife. In the lush, moist forests high in the mountains, trees are draped with vines, orchids, ferns, and mosses. This ecoregion includes one of the world's wettest places, the slopes of Mount Waiʻaleʻale, which average 373 in (9,500 mm) of rainfall per year.

The Hispaniolan pine forests are a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion found on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, which is shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic. The ecoregion covers 11,600 km2 (4,500 sq mi), or about 15% of the island. It lies at elevations greater than 800 m (2,600 ft) in the mountains of Hispaniola, extending from the Cordillera Central of the Dominican Republic and into the Massif du Nord of Haiti. It is surrounded at lower elevations by the Hispaniolan moist forests and Hispaniolan dry forests ecoregions, which cover the remainder of the island. Annual rainfall is 1,000–2,000 mm (39–79 in).
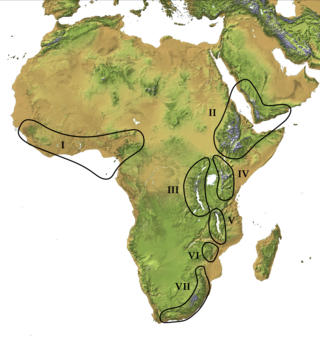
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

Cordillera Azul National Park is a protected area in Peru. It protects part of the Ucayali moist forests ecoregion.

The Araucaria moist forests, officially classified as mixed ombrophilous forest in Brazil, are a montane subtropical moist forest ecoregion. The forest ecosystem is located in southern Brazil and northeastern Argentina. The ecoregion is a southern portion of the Atlantic Forest. The ecoregion also includes select areas of open field called "campos de cima da serra" or "coxilhas".

The Talamancan montane forests ecoregion, in the tropical moist broadleaf forest biome, are in montane Costa Rica and western Panama in Central America.

The Cordillera de la Costa montane forests is a montane ecoregion of the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, in the Venezuelan Coastal Range on the Caribbean Sea in northern Venezuela.

Podocarpus angustifolius is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It is endemic to Cuba.

The Cuban dry forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion that occupies 65,800 km2 (25,400 sq mi) on Cuba and Isla de la Juventud. The ecoregion receives 1,000–2,000 mm (39–79 in) of rainfall annually. Cuban dry forests can be differentiated into evergreen forests, semi-deciduous forests, mogotes, and sclerophyllous low forests.

The Puerto Rican moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in Puerto Rico. They cover an area of 7,544 km2 (2,913 sq mi).

The Hispaniolan moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the island of Hispaniola. They cover 46,000 km2 (18,000 sq mi), around 60% of the island's area.

The Cuban pine forests are a tropical coniferous forest ecoregion on the Caribbean islands of Cuba and Isla de la Juventud. They cover an area of 6,400 km2 (2,500 sq mi), occurring in separate sections in eastern Cuba and western Cuba and Isla de la Juventud.

The East African montane forests is a montane tropical moist forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. The ecoregion comprises several separate areas above 2000 meters in the mountains of South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania.

The Oaxacan montane forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in eastern Mexico. It includes a belt of montane tropical forest on the eastern slope of the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca and eastern Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt ranges. These forests lie between the lowland Petén–Veracruz moist forests and Veracruz moist forests, and the pine–oak forests of the higher mountains.

The Sierra Madre de Chiapas moist forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico and southern Guatemala, extending into the northwestern corner of El Salvador.

The Fiji tropical moist forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Fiji and Wallis and Futuna. It covers the windward sides of Viti Levu and Vanua Levu, Fiji's largest islands, as well as the smaller Fijian islands and the three islands that make up Wallis and Futuna, an overseas territory of France.

The Marquesas tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in the Marquesas Islands of French Polynesia.





















