Related Research Articles

CSX Transportation, known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad company operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. Operating about 21,000 route miles (34,000 km) of track, it is the leading subsidiary of CSX Corporation, a Fortune 500 company headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida.

The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad in the Northeastern United States built predominantly to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Northeastern Pennsylvania to major consumer markets in Philadelphia, New York City, and elsewhere.

The Norfolk and Western Railway, commonly called the N&W, was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America". In 1986, N&W merged with Southern Railway to form today's Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company was an American subsidiary of the Grand Trunk Railway, later of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants.

The Monongahela Railway was a coal-hauling Class II railroad in Pennsylvania and West Virginia in the United States. It was jointly controlled originally by the Pennsylvania Railroad, New York Central subsidiary Pittsburgh and Lake Erie Railroad, and the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, with NYC and PRR later succeeded by Penn Central Transportation. The company operated its own line until it was merged into Conrail on May 1, 1993.
The Tennessee Central Railway was founded in 1884 as the Nashville and Knoxville Railroad by Alexander S. Crawford. It was an attempt to open up a rail route from the coal and minerals of East Tennessee to the markets of the midstate, a service which many businessmen felt was not being adequately provided by the existing railroad companies. They also wanted to ship coal and iron ore to the Northeastern US over the Cincinnati Southern Railway, which was leased to the Southern and operated as the Cincinnati, New Orleans and Texas Pacific Railway (CNOTP), through their Cincinnati gateway. The N&K was only completed between Lebanon, where it connected to a Nashville, Chattanooga and St. Louis Railway branch from Nashville, and Standing Stone.

The Middletown and New Jersey Railroad is one of two railroads in the city of Middletown, New York; the other being its interchange partner, Norfolk Southern Railway. The MNJ consists of 43 miles (69 km) of track in southeastern New York serving Orange County and the Hudson Valley. The railroad also operates and has trackage rights on three additional branch lines totalling 40 miles (64 km) leased from Norfolk Southern in Orange County. It was known as the Middletown and New Jersey Railway until 2009, when East Penn Railroad parent Regional Rail, LLC bought the line through a new subsidiary. In 2015, Regional Rail was in turn acquired by Levine Leichtman Capital Partners ("LLCP").

New York New Jersey Rail, LLC is a switching and terminal railroad that operates the only car float operation across Upper New York Bay between Jersey City, New Jersey and Brooklyn, New York. Since mid-November 2008, it has been owned by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, which acquired it for about $16 million as a step in a process that might see a Cross-Harbor Rail Tunnel completed.

The Illinois and Midland Railroad is a railroad in the U.S. state of Illinois, serving Peoria, Springfield and Taylorville. Until 1996, when Genesee & Wyoming Inc. bought it, the company was named the Chicago and Illinois Midland Railway. It was once a Class I railroad, specializing in the hauling of coal. At the end of 1970 it operated 121 route-miles on 214 miles of track; it reported 255 million ton-miles of revenue freight that year.
Railroad electrification in the United States began at the turn of the 20th century and comprised many different systems in many different geographical areas, few of which were connected. Despite this situation, these systems shared a small number of common reasons for electrification.
The Sandersville Railroad was originally operated from Tennille, Georgia, to Sandersville, Georgia and chartered in 1893 as a subsidiary of the Central of Georgia Railroad.

Union Railroad is a Class III switching railroad located in Allegheny County in Western Pennsylvania. The company is owned by Transtar, Inc., which is a subsidiary of Fortress Transportation and Infrastructure Investors, after being acquired from U.S. Steel in 2021. The railroad's primary customers are the three plants of the USS Mon Valley Works, the USS Edgar Thomson Steel Works, the USS Irvin Works and the USS Clairton Coke Works.

The Knox and Kane Railroad (K&K) was a short-line railroad in Pennsylvania that operated between Knox, in Clarion County, to Kane and then on to Mount Jewett, in McKean County.

The Buffalo Creek and Gauley Railroad (BC&G) was a railroad chartered on April 1, 1904 and ran along Buffalo Creek in Clay County, West Virginia. The original Buffalo Creek and Gauley ended service in 1965.
The Brooklyn Eastern District Terminal was a shortline railroad and marine terminal with its main facilities and administrative offices located on 86–88 Kent Avenue in the Williamsburg section of Brooklyn, New York City.

The Squaw Creek Southern Railroad is a Class III railroad subsidiary of Respondek Railroad operating in the southern portion of the State of Indiana. Originally, the Squaw Creek Southern started operating 21 miles of former Yankeetown Dock Corporation/Peabody Coal trackage owned by Norfolk Southern, but has since started servicing Foresight Energy's Sitran Coal Terminal near Evansville, Indiana and SABIC's Innovative Plastics plant in Mount Vernon, Indiana.
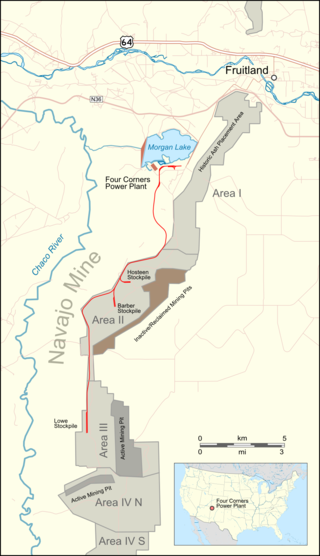
The Navajo Mine is a surface coal mine owned and operated by Navajo Transitional Energy Company (NTEC) in New Mexico, United States, within the Navajo Nation. The mine is about 20.5 miles (33 km) southwest of Farmington, New Mexico. The Navajo Mine Railroad has 13.8 miles (22.2 km) of track between the Four Corners Generating Station and Navajo Mine.

The Travis Branch is a branch of the Staten Island Railway in New York City, that operates from Arlington Yard to Fresh Kills, which is used for freight transportation along the West Shore, Staten Island.

The Farmville and Powhatan Railroad went bankrupt in 1905 and became the Tidewater and Western Railroad. The line survived until 1917 when it was pulled up and sent to France for the World War I effort. The Tidewater and Western Railroad carried freight and passengers along a route from Farmville, Virginia to Bermuda Hundred. The Tidewater and Western Railroad continued to have Western Union Telegraphs run along the rails. These connected to telegraphs on the Atlantic Coast Line along the East Coast of the US and to Europe.
References
- ↑ "Trains Newswire: Cumberland Mine, with rail operation, has new owner" . Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ↑ "Cumberland Mine Labelle Dock Site" (PDF). WallacePancher Group. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ↑ "FRS Facility Detail Report". EPA. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ↑ "Cumberland Coal Resources, LP in Kirby, PA". Trainorders.com. 9 February 2012. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- ↑ "ccrx 6700". Youtube ccrx. Retrieved 2 March 2021.